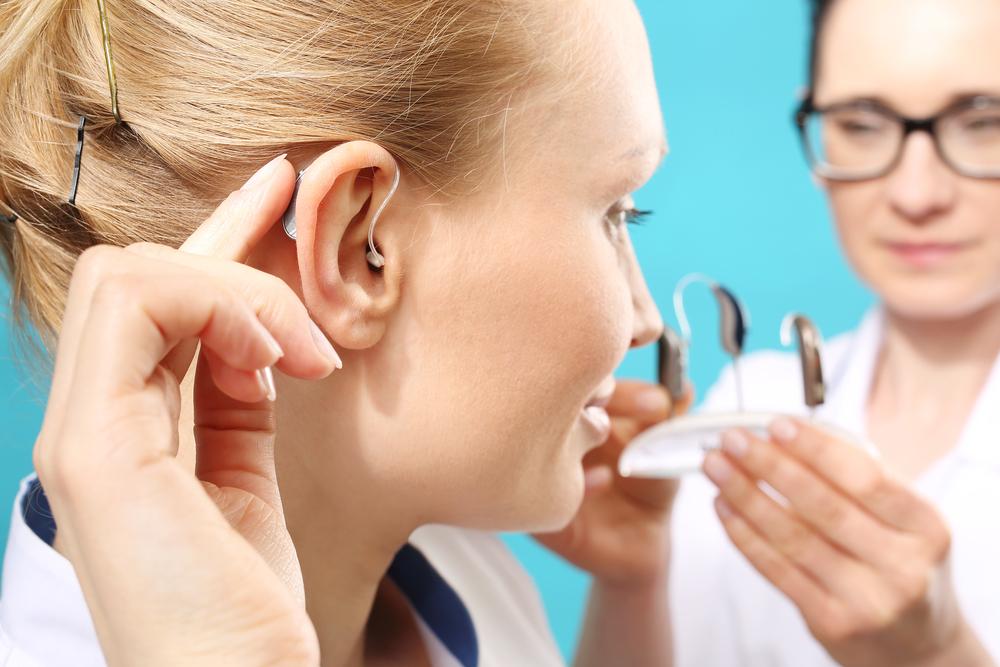
Comprehensive Guide to the Top 3 Hearing Aid Technologies for Enhanced Hearing Experience
This comprehensive guide explores the top three hearing aid options—Traditional Behind-the-Ear, Mini Behind-the-Ear, and In-the-Canal devices—detailing their features, benefits, and suitability for different needs. Discover how advances in technology have improved hearing aid performance, comfort, and discretion, helping individuals choose the best solution for their hearing enhancement journey.
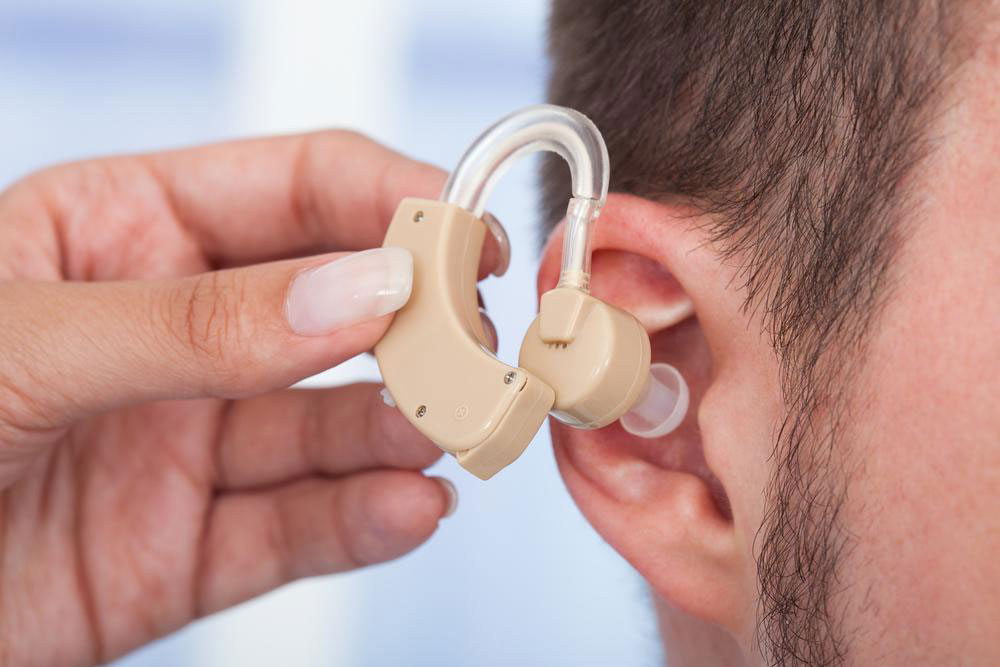
Comprehensive Guide to the Top 3 Hearing Aid Technologies for Enhanced Hearing Experience
Hearing aids are intricate devices designed to improve auditory perception for individuals with hearing impairments. At their core, these devices consist of three fundamental components: a microphone that captures ambient sound, an amplifier that increases the volume, and a receiver that transmits the processed sound directly into the ear canal. With the advent of digital technology, modern hearing aids incorporate sophisticated chips that enable precise sound processing, significantly enhancing clarity and allowing customization based on individual hearing profiles. The array of styles available today caters to various preferences and degrees of hearing loss, making it essential to understand the differences to choose the most suitable device. This comprehensive guide explores the top three hearing aid types that are currently favored for their effectiveness, comfort, and technological advancements.
1. Traditional Behind-the-Ear (BTE) Hearing Aids
Traditional BTE hearing aids are among the most recognizable and widely used models in the industry. These devices house all electronic components within a durable plastic case that is worn comfortably behind the ear. They are connected to a custom-fitted earmold through a slender tube, which directs amplified sound into the ear canal. The design of BTE aids offers a high degree of versatility, making them suitable for a broad spectrum of hearing loss severities—from mild to profound. Their robust construction makes them particularly durable, and they tend to require less maintenance compared to smaller models. Controls on these devices are typically straightforward, allowing users to adjust volume and settings easily. Additionally, many BTE aids are equipped with telecoils, which provide a seamless connection to hearing loop systems in public venues, improving speech understanding in noisy environments. The earmolds used with BTE aids are simple to clean and maintain, contributing to the device’s overall longevity. These hearing aids are ideal for users seeking a reliable, powerful, and easy-to-handle solution.
2. Mini Behind-the-Ear (mBTE) Hearing Devices
The second most popular category, the mini Behind-the-Ear devices, are also known by various nomenclatures such as Receiver-in-Canal (RIC), Receiver-in-the-Ear (RITE), or Receiver-in-the-Aid (RITA). These devices feature a compact receiver positioned directly inside the ear canal. The main body, housing the electronics, rests behind the ear, connected to the receiver by a thin, discreet wire or flexible tubing. This design offers an excellent balance between size and functionality, making the device nearly invisible when worn, which appeals to users who prefer discretion. The earmold fitting is custom-made from soft materials, ensuring a comfortable and secure fit during daily activities. The lightweight construction contributes to ease of use and reduces fatigue for the wearer. These devices are easy to insert and remove, making them a convenient choice. However, because the receiver is exposed within the ear canal, it can be susceptible to moisture and earwax accumulation, which might impact the device’s lifespan and performance. Regular maintenance and proper cleaning are essential for optimal functioning.
3. In-the-Canal (ITC) Hearing Aids
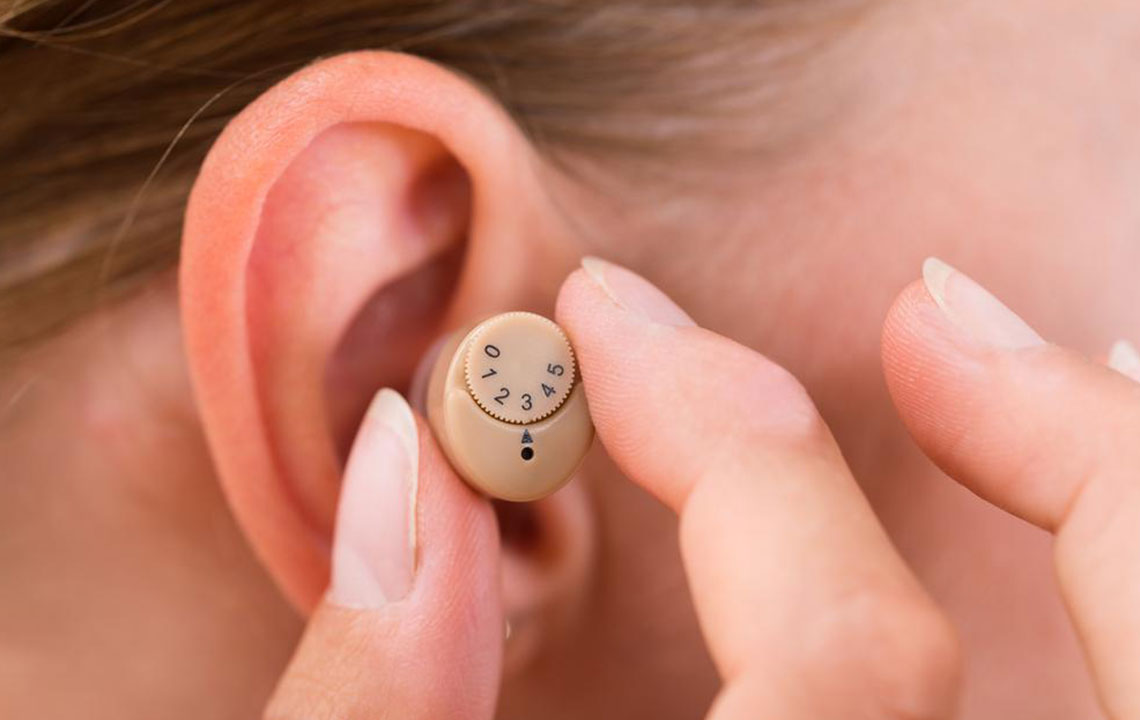
The most discreet options available, In-the-Canal hearing aids are designed to sit deeply within the ear canal, making them nearly invisible to outside observers. Their placement ensures minimal protrusion from the ear, offering users a natural and unobtrusive appearance. These aids are generally larger than completely in-the-ear models, accommodating additional features like directional microphones, which enhance speech focus in challenging listening environments. Despite their advantages, ITC hearing aids can sometimes cause a feeling of fullness or plugged sensation and might be less comfortable for users with small or sensitive ears. Their small size also means smaller batteries, leading to shorter operational periods between charges or replacements. Moreover, because the receiver is positioned deep within the ear canal, it can be more vulnerable to moisture, wax buildup, and debris, necessitating diligent maintenance and regular professional cleanings to sustain audio quality. These devices are best suited for individuals with mild to moderate hearing loss who prioritize discretion without compromising essential features.
In conclusion, selecting the appropriate hearing aid device depends on several factors, including the severity of hearing loss, lifestyle preferences, and physical comfort. Advances in digital sound processing and miniaturization have significantly expanded options, enabling users to find devices that seamlessly blend functionality with comfort. Whether opting for the traditional BTE models, the discreet mini Behind-the-Ear aids, or the virtually invisible in-the-canal options, modern hearing aids are designed to provide clear sound, ease of use, and enhanced quality of life. Consulting with an audiologist can help identify the most suitable device tailored to individual needs, ensuring an improved hearing experience with technological support and personalized care.