Comprehensive Guide to Breast Cancer: Risks, Prevention, and Early Detection
This comprehensive article delves into the critical aspects of breast cancer, including its risks, early signs, prevention strategies, and treatment options. Emphasizing the importance of regular screenings, healthy lifestyle choices, and genetic awareness, it aims to educate women on how to reduce their risk and detect the disease early. The content also explores recent advancements in treatment and encourages proactive health management to improve survival rates.

Comprehensive Guide to Breast Cancer: Risks, Prevention, and Early Detection
Breast cancer remains one of the most prevalent and life-threatening health issues affecting women worldwide. It is a complex disease influenced by multiple genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Globally, breast cancer accounts for a significant proportion of cancer-related morbidity and mortality among women. In the United States alone, it is estimated that about 1 in 8 women will be diagnosed with invasive breast cancer at some point in their lives. Each year, approximately 232,340 women and 2,240 men receive a new diagnosis of breast cancer, and sadly, around 39,620 women succumb to the disease annually. The impact of breast cancer extends beyond the physical health challenges, affecting emotional well-being, families, and communities.
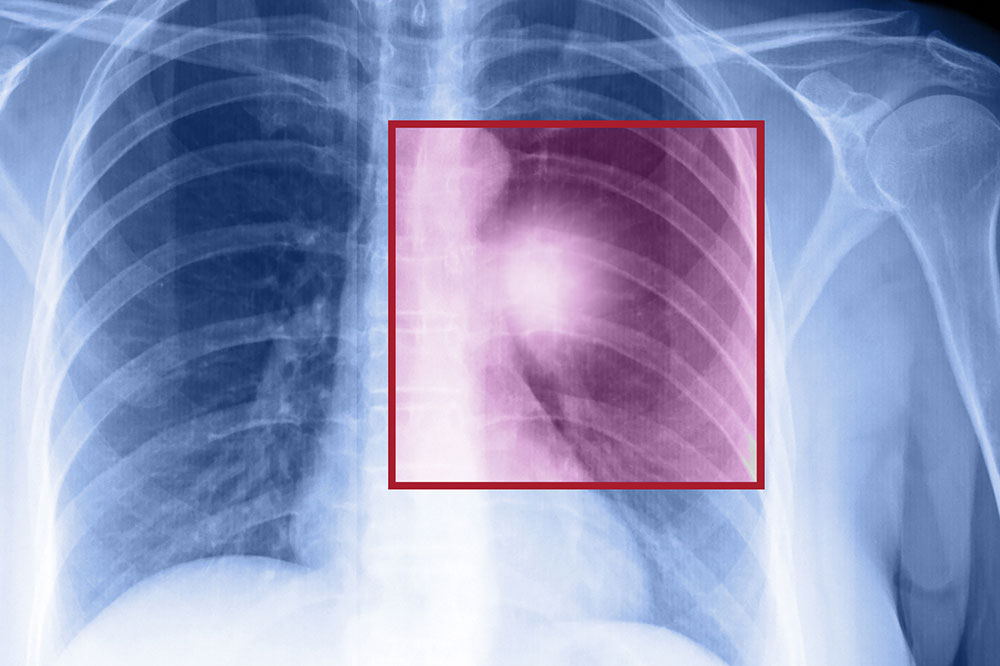
One of the notable challenges in managing breast cancer is its subtle onset. Early-stage breast cancer often presents no obvious symptoms, making it essential for women to be vigilant about regular screening. Typically, early signs include painless lumps or thickening in the breast tissue or armpit, which may sometimes be accompanied by skin changes such as retraction, redness, or dimpling. Changes in the nipple, including inversion or unusual discharge, can also signal underlying issues. Because these symptoms are not always apparent at the early stages, proactive screening becomes vital for early detection and improved treatment outcomes.
Understanding the risk factors associated with breast cancer can empower women and healthcare providers to take preventive measures. Genetic predispositions play a powerful role; women with a family history of breast cancer, especially those related to BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutations, are at higher risk. Dense breast tissue, which is more common among younger women, can make detection more difficult and may be associated with increased risk. Lifestyle choices also significantly influence risk: excessive alcohol consumption, sedentary habits, obesity, and exposure to radiation are notable contributors.
Other factors include age, with risk increasing as women grow older, and hormonal influences such as early menarche, late menopause, and hormone replacement therapy. Exposure to radiation, particularly during adolescence or young adulthood, also elevates risk. Environmental toxins and certain dietary patterns are also being studied for potential links to breast cancer development.
Prevention strategies are critical and involve a combination of lifestyle modifications, medical interventions, and natural remedies. Regular screening methods like mammography are fundamental in detecting abnormalities at an early, more treatable stage. Women at higher risk may benefit from additional screening techniques such as MRI scans.
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce risk. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains supports overall health. Keeping a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, limiting alcohol intake, and avoiding smoking are proven measures that lower breast cancer risk. Some studies suggest that natural supplements like vitamin D and green tea possess protective properties, but these should complement, not replace, conventional medical advice.
Advancements in treatment options have improved survival rates for breast cancer patients. Surgical removal of tumors, radiation therapy to destroy residual cancer cells, chemotherapy to target rapidly dividing cells, and hormone therapy to block cancer growth driven by hormones are the mainstay treatments. Personalized medicine, based on genetic profiling of tumors, is paving the way for more targeted and effective therapies.
Educational outreach and awareness campaigns play a crucial role in promoting early detection and destigmatizing the disease. Women should be encouraged to perform regular self-examinations and seek medical advice if they notice any abnormal changes. Healthcare providers must emphasize the importance of routine screenings, especially for women over 40 or those with high risk factors.
In conclusion, understanding the risks and implementing effective prevention strategies are essential components in the fight against breast cancer. Early detection saves lives, and a proactive approach involving lifestyle choices, regular screenings, and medical consultations can greatly improve the prognosis for women worldwide.