Comprehensive Safety Guidelines for Operating Power and Hand Tools
Discover essential safety tips for using power and hand tools. Learn how to protect yourself from injuries, maintain proper techniques, and create a safer work environment. Whether for DIY projects or professional work, these safety guidelines are crucial for injury prevention and effective tool handling.

Comprehensive Safety Guidelines for Operating Power and Hand Tools
Every year, countless accidents occur in workplaces and homes due to improper handling and safety neglect when using power and hand tools. These incidents can result in severe injuries, ranging from minor cuts to serious lacerations, burns, eye injuries, and even more critical harm. Many of these accidents are preventable, provided that users adhere strictly to established safety protocols. Whether you're an experienced tradesperson, a DIY enthusiast, or a maintenance worker, understanding and implementing strict safety measures when operating such tools is essential to ensure personal safety and prevent potential accidents.
Power tools and hand tools are ubiquitous in construction sites, factories, workshops, and even in household repairs. While they significantly enhance efficiency and productivity, their inherent power and moving parts pose risks if not handled correctly. This comprehensive guide aims to outline essential safety tips, best practices, and precautions to minimize risks associated with using these tools effectively. By following these safety guidelines, users can greatly reduce the likelihood of injuries and create a safer working environment for themselves and others around them.
Why Safety Is Crucial When Using Power and Hand Tools
The proper use of power and hand tools is essential not only for efficiency but also for safety. Power tools generate high torque, rapid movement, and sometimes sparks or debris, making injuries more likely if safety precautions are ignored. Hand tools, though seemingly safer, can cause injuries like cuts, punctures, or strains if used improperly or carelessly. Ensuring safety helps in avoiding costly medical treatments, downtime, and potential legal liabilities, especially in occupational settings. Proper safety practices promote a culture of responsibility, reduce accidents, and help maintain a productive, injury-free environment.
Key Safety Practices for Power Tools
Using power tools safely requires awareness, protective gear, and correct handling techniques. Here are fundamental safety practices to follow during operation:
Always wear safety goggles— Power tools such as drills, grinders, and chainsaws generate flying debris, wood splinters, metal shavings, and dust particles. Protecting your eyes is paramount to prevent serious injuries. Invest in high-quality, impact-resistant goggles or face shields to ensure maximum protection.
Use ear protection— Continuous exposure to loud noises from power tools can lead to hearing loss over time. Earplugs or earmuffs are effective in reducing noise levels and protecting your auditory health. Remember to wear them during prolonged use or in noisy environments.
Wear appropriate gloves— When operating hot or vibrating tools, gloves act as a barrier against burns, cuts, and abrasions. Select gloves suited for the specific task—thick rubber or leather gloves are advisable for handling rough or hot surfaces.
Maintain control— Always use both hands when operating powerful tools to manage vibrations and prevent slips. Keep a firm grip, stand in a balanced stance, and avoid overreaching. Regularly take breaks to reduce muscle fatigue, which can lead to slips or mishandling.
Use respiratory protection— Tasks such as grinding, sanding, or demolition generate dust and fumes that can be harmful when inhaled. Employ masks or respirators rated for the specific dust types to safeguard your respiratory health.
Avoid water contact— Power tools are generally not designed for use in wet conditions. Water exposure can cause electrical shorts, malfunctions, and increase the risk of electric shocks. Always operate in dry environments and keep tools away from rain or spills.
Inspect tools before use— Conduct a thorough inspection of your tools before each use. Check for damaged parts, loose attachments, frayed cords, or worn-out components. Proper maintenance and timely repairs prevent accidents caused by equipment failure.
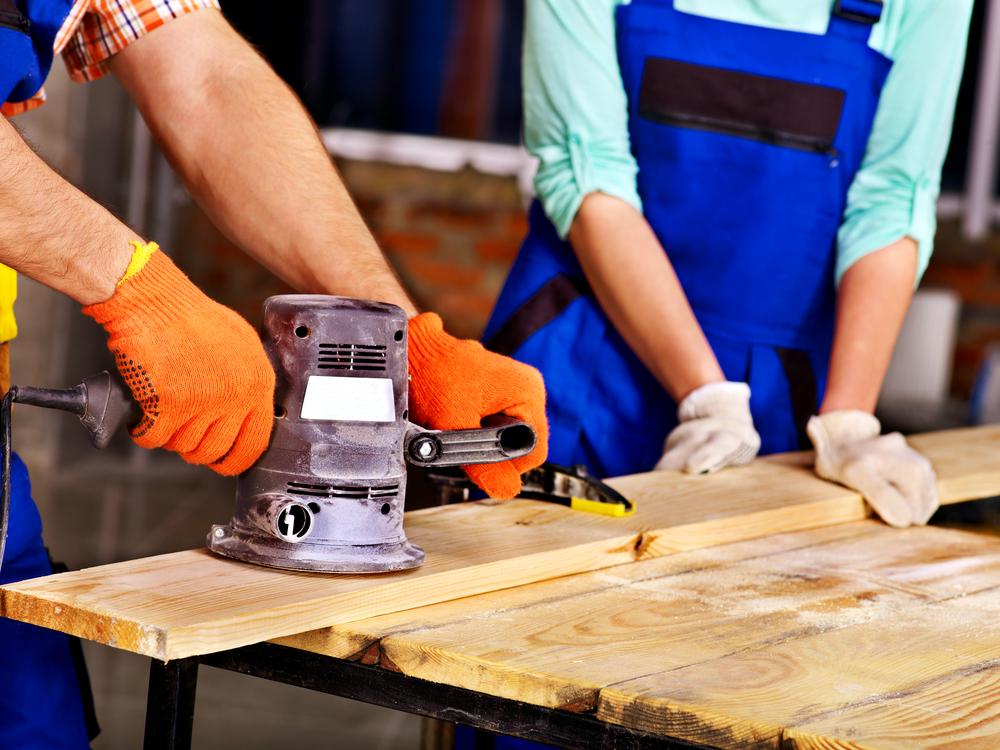
Safety Guidelines for Hand Tools
While hand tools are simpler and often perceived as safer, they still pose risks if not used properly. Proper technique and safety awareness are key to preventing injuries. Consider the following tips:
Use safety gear— Always wear protective equipment such as gloves, safety goggles, and helmets when working with hand tools to prevent cuts, punctures, eye injuries, and head trauma.
Employ correct techniques and posture— Maintain a firm grip, ensure proper stance, and use the correct technique for each tool. For example, when hammering, strike accurately and in a controlled manner to avoid glancing blows that could cause injuries.
Proper storage and handling— Store sharp or small tools in designated containers, tool belts, or drawers to prevent accidental punctures or cuts during handling. When transferring tools to higher places, use lifts, hoists, or place them securely on stable surfaces to avoid dropping.
Stay alert and avoid distractions— Focus entirely on the task when using hand tools. Distractions and fatigue can lead to mishandling and injuries.
Keep tools in good condition— Regularly sharpen blades, replace worn parts, and ensure handles are secure. Well-maintained tools operate smoothly and reduce the risk of accidents.
In conclusion, safety should always be a priority when working with power and hand tools. Proper training, protective gear, routine inspections, and adherence to safety protocols are vital to preventing injuries and ensuring a safe working environment. Whether in a professional workshop or a household setting, following these safety guidelines will help you work efficiently while minimizing risks.