Complete Guide to Effective Treatments for Sciatica Relief
This comprehensive guide explores effective treatments for sciatica, including chiropractic care, yoga, acupuncture, massage therapy, medication options, and advanced procedures. It emphasizes personalized approaches to relieve nerve pressure, reduce inflammation, and restore mobility. Whether through conservative therapies or surgical interventions, understanding these options helps manage sciatic pain effectively for a better quality of life.

Comprehensive Strategies to Alleviate Sciatica Pain
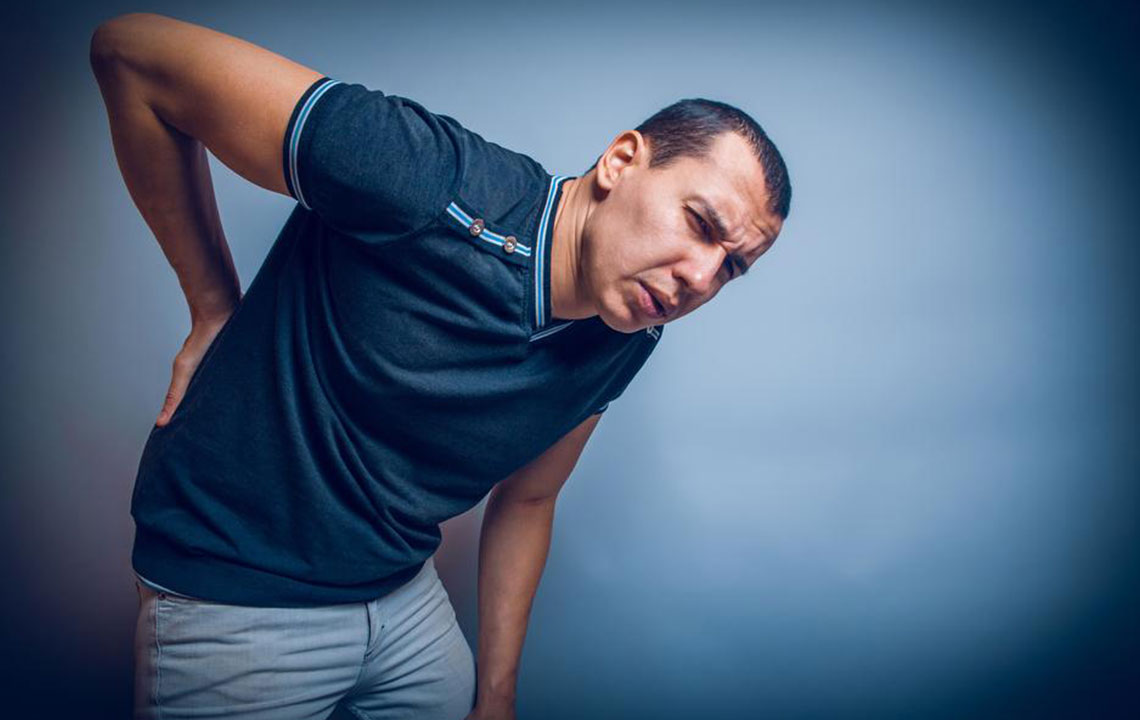
Are you suffering from sharp, shooting pain that radiates from your lower back down through your thighs and legs? Or perhaps you experience persistent discomfort in your lower back that extends all the way to your feet? These symptoms are common indicators of sciatic nerve issues. Sciatica is characterized by pain originating from compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve, the largest nerve in the human body, which runs from the lumbar spine through the hips and down each leg.
If untreated, sciatic nerve problems can significantly interfere with daily activities, causing discomfort, reduced mobility, and diminished quality of life. Fortunately, there is a broad spectrum of treatment options available aimed at alleviating symptoms, improving nerve function, and restoring movement. From conservative, non-invasive therapies to more advanced surgical procedures, understanding these options can help you make informed decisions about managing and treating sciatic pain effectively.
Most cases of sciatica respond well to conservative management, with surgical options considered only when other treatments fail or in severe cases. It is essential to assess the severity and underlying cause of your condition to choose the most appropriate treatment plan.
Selection of suitable treatment options depends on individual cases, cause severity, and patient health status. Here, we explore some of the most effective and widely recommended approaches:
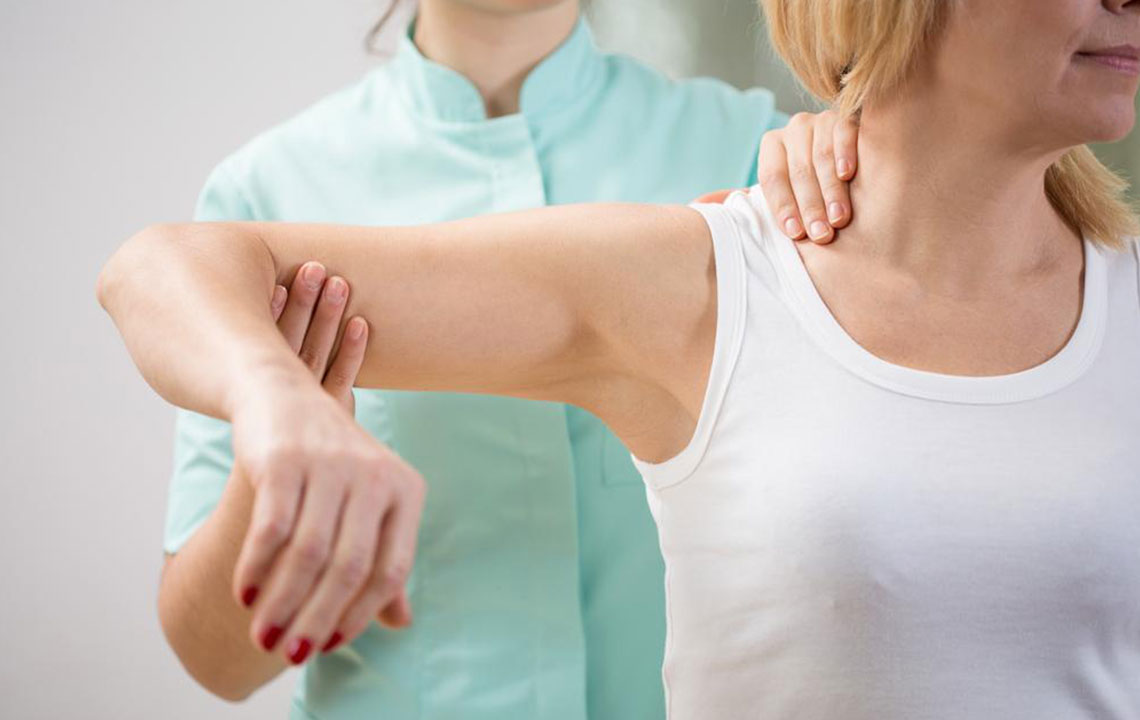
Chiropractic Care and Spinal Manipulation
Herniated discs, degenerative disc disease, and spinal misalignments often contribute to sciatic nerve compression. Chiropractic practitioners utilize spinal adjustments to correct misalignments, restore proper disc positioning, and relieve nerve pressure. They often employ diagnostic imaging such as X-rays and MRIs to accurately identify problematic discs or vertebral structures. Regular chiropractic care can significantly reduce sciatic pain, improve mobility, and prevent recurrence by promoting spinal health and disc integrity.
Yoga and Flexibility Exercises
Specific yoga practices, particularly Iyengar yoga, are beneficial in managing sciatic discomfort. These exercises focus on gentle stretching, muscle strengthening, and improving flexibility. Proper yoga techniques help relieve nerve tension, foster better posture, and reduce inflammation in the lower back and hips. Combining yoga with targeted lower back exercises creates a holistic approach that diminishes pain while enhancing overall spinal health. Practicing yoga regularly can contribute to long-term pain management and improve quality of life.
Traditional Chinese Medicine: Acupuncture
Acupuncture involves inserting fine needles at precise points on the body to stimulate energy flow and promote natural healing. Multiple studies have demonstrated that acupuncture can effectively reduce sciatica symptoms, with positive results seen in up to 70% of cases. This therapy provides a drug-free, natural remedy that can be integrated with other treatments to enhance overall efficacy without side effects associated with medications.
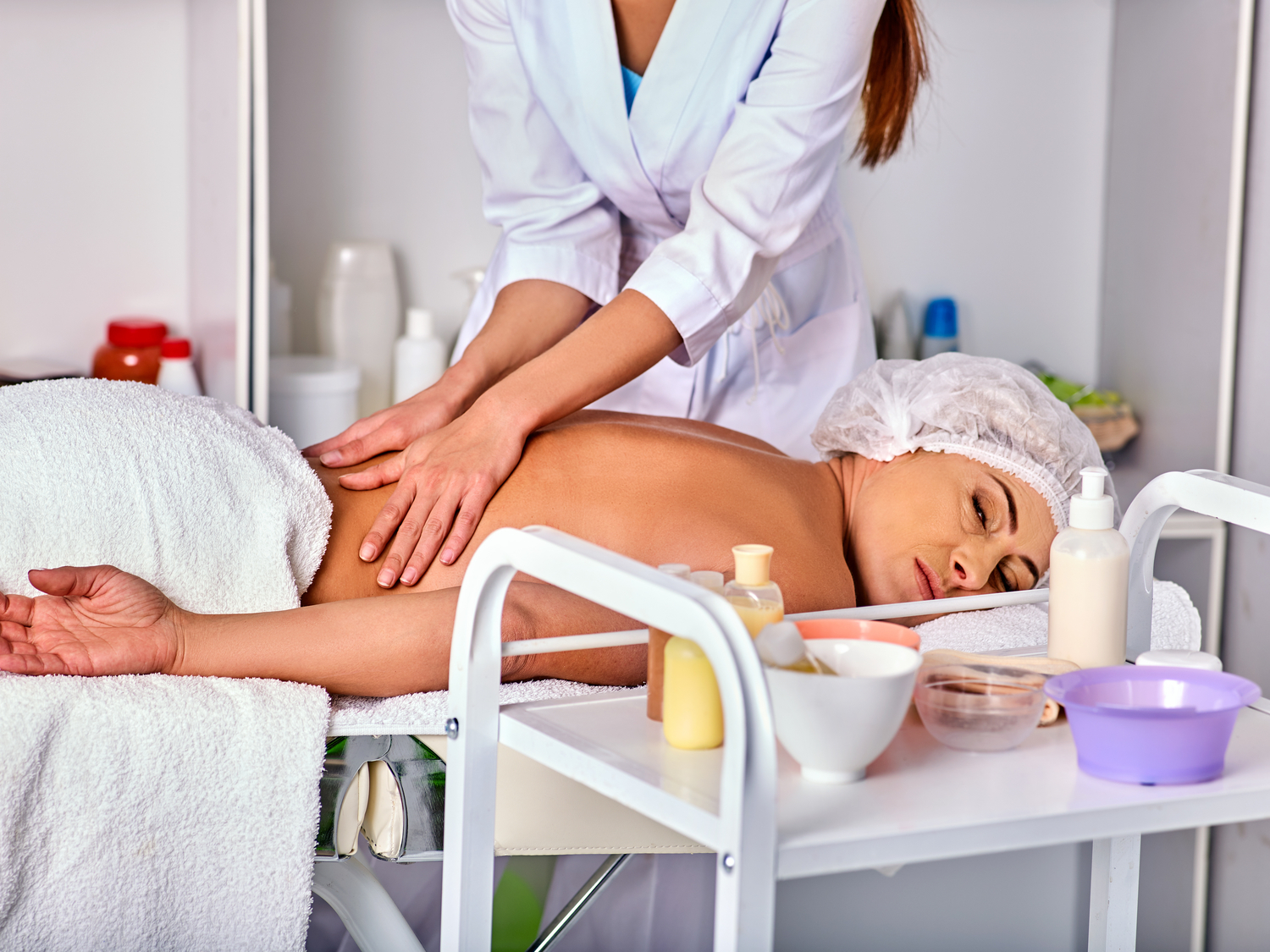
Massage Therapy and Myofascial Release
Targeted massage techniques, especially trigger-point therapy, can relax tight muscles contributing to nerve compression, such as the piriformis muscle. Massage increases blood flow, facilitates the release of endorphins, and reduces muscle tension, providing immediate relief from pain and stiffness. Regular massage therapy can help prevent muscle spasms and improve circulation, aiding in faster recovery and long-term symptom management.
Topical Pain Relievers
Creams, gels, and ointments containing capsaicin, menthol, or anti-inflammatory agents can offer localized relief from sciatic nerve pain. These topical remedies are easy to apply and can provide temporary relief, especially during flare-ups. Over time, consistent application helps to diminish nerve sensitivity and muscle inflammation, offering an adjunct to other treatment modalities.
Heat and Cold Therapy
Applying heat packs or cold compresses can significantly reduce nerve irritation and muscle tightness. Heat therapy increases blood flow, relaxes muscles, and alleviates stiffness. Conversely, cold therapy numbs the area, reduces inflammation, and diminishes swelling. Alternating between heat and cold treatments in 15-minute intervals can optimize pain relief and enhance recovery.
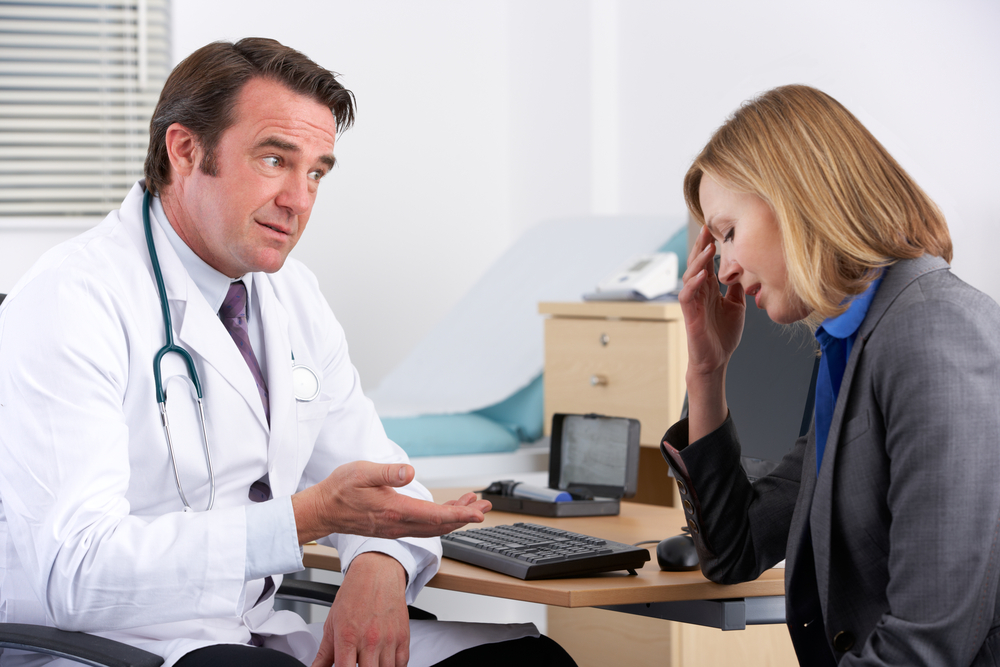
Over-the-Counter Medications: NSAIDs
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen and naproxen are commonly used to reduce inflammation and relieve sciatic pain. These medications are effective for short-term symptom management but should be used cautiously to prevent side effects like gastrointestinal issues or kidney problems.
Injections: Corticosteroids
For persistent or severe inflammation, corticosteroid injections administered into the epidural space can decrease swelling and nerve pressure. This minimally invasive procedure provides significant relief, often delaying or circumventing the need for surgery. However, repeated injections should be carefully considered due to potential side effects.
Prescription Painkillers and Opioids
In cases of intense pain that do not respond to other treatments, doctors may prescribe opioids. While effective for short-term pain relief, opioids carry risks of dependence and other side effects. Therefore, they should be used under strict medical supervision and as part of a comprehensive pain management strategy.
Antidepressants and Nerve Pain Medications
Some antidepressants, especially tricyclics and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), are prescribed to help relax tense nerves and modulate nerve signals, reducing chronic pain associated with sciatica. These medications can be particularly beneficial for nerve-related pain that persists beyond the acute phase.
Choosing the right combination of these treatments and making appropriate lifestyle adjustments, like maintaining proper posture, engaging in regular gentle exercises, and managing weight, can significantly improve your condition. Early intervention and consistent management are key to achieving lasting relief from sciatic nerve pain and restoring full mobility.