Comprehensive Guide to Bunion Treatment and Management Strategies
This comprehensive guide explores various bunion correction and management strategies, including surgical and non-surgical treatments, post-operative care, and home remedies. Learn how to effectively address bunions, alleviate pain, and prevent progression with expert advice. Ideal for those seeking detailed information on bunion treatment options and preventive tips to maintain foot health.

An In-Depth Exploration of Bunion Remedies and Care Options
A bunion, medically termed hallux valgus, manifests as a prominent bony bump situated at the base of the big toe. This condition results in the outward angulation of the toe, leading to inflammation of the toe joint, noticeable deformity, and discomfort. Causes of bunions include genetic predisposition, the wearing of narrow or ill-fitting footwear, and certain inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis. Patients often experience pain, swelling, and difficulty walking, especially after prolonged activity or standing. While conservative treatments can help manage symptoms, complete reversal of bunions without surgery remains rare. Most treatment plans focus on alleviating pain, improving foot function, and preventing progression of the deformity.
Available Bunion Treatment Methods
Choosing the appropriate treatment depends largely on the severity of the bunion, patient symptoms, and overall foot health. Surgical procedures are often considered when conservative measures fail to relieve pain or prevent worsening deformity. These surgeries aim to correct the misalignment of bones and address soft tissue issues that contribute to bunion formation.
Soft Tissue and Ligament Corrections
Surgery may involve adjusting or releasing tight or lax tendons and ligaments that influence toe positioning. Restoring proper tension helps realign the toe and reduce deformity.
Osteotomy (Bone Surgery)
This commonly performed procedure involves cutting and realigning the affected bone of the big toe. Surgeons may remove a wedge-shaped section of the bone to straighten the toe and secure it with screws, pins, or plates. Sometimes, this is combined with soft tissue repairs to optimize results.
Arthrodesis (Joint Fusion)
Especially suitable for patients with concurrent arthritis, this technique involves removing damaged joint surfaces and fusing the bones together using metal hardware. This permanently stabilizes the joint, alleviating pain but may limit toe movement.
Bump (Exostectomy) Removal
In this less invasive procedure, only the prominent bony bump is shaved off. Often performed alongside other corrective surgeries, it aims to reduce prominence and improve toe appearance.
Resection Arthroplasty (Joint Removal)
This method involves removing parts of the joint to create more space and realign the toe bones. Typically used in elderly patients or cases where previous surgeries failed, this technique can weaken toe push-off power but effectively reduces deformity and pain.
Post-Surgery Recovery and Care
Recovery involves wound care, pain management, and avoiding weight-bearing activities initially. Healthcare providers may use casts, splints, or braces to protect the surgical site. Postoperative physical therapy is crucial for regaining mobility and strength. Transitioning to proper footwear that accommodates the foot's new shape is essential to prevent recurrence, with supportive shoes recommended for long-term health.
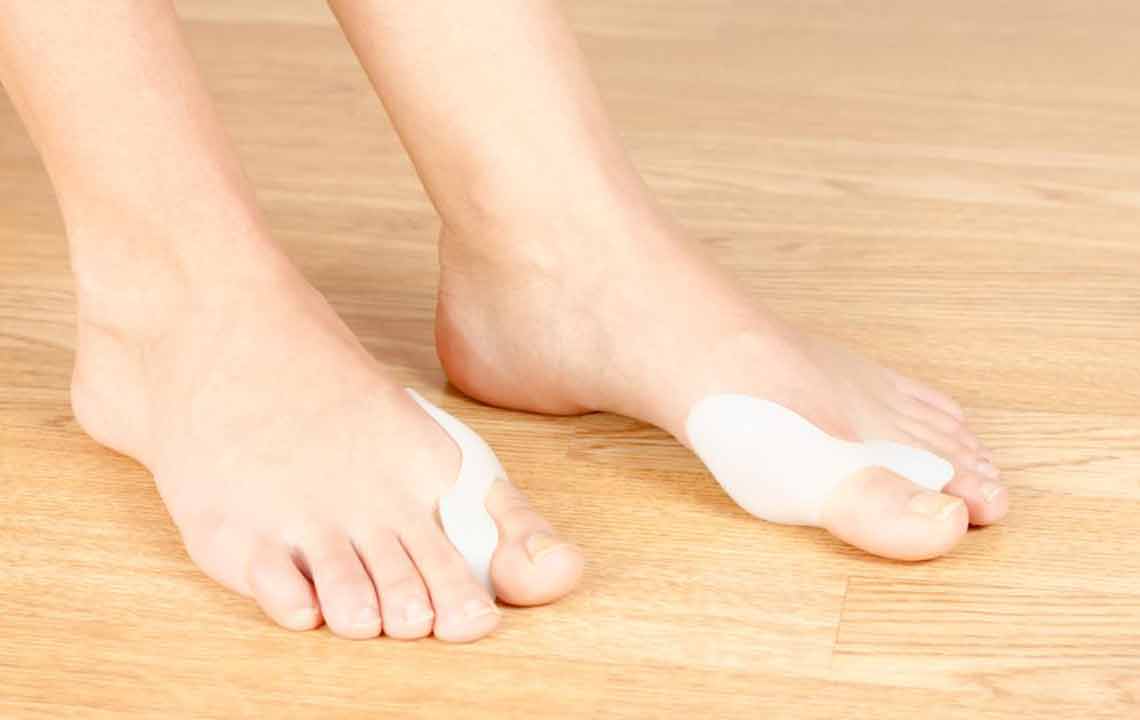
Non-Surgical Treatments for Bunion Management
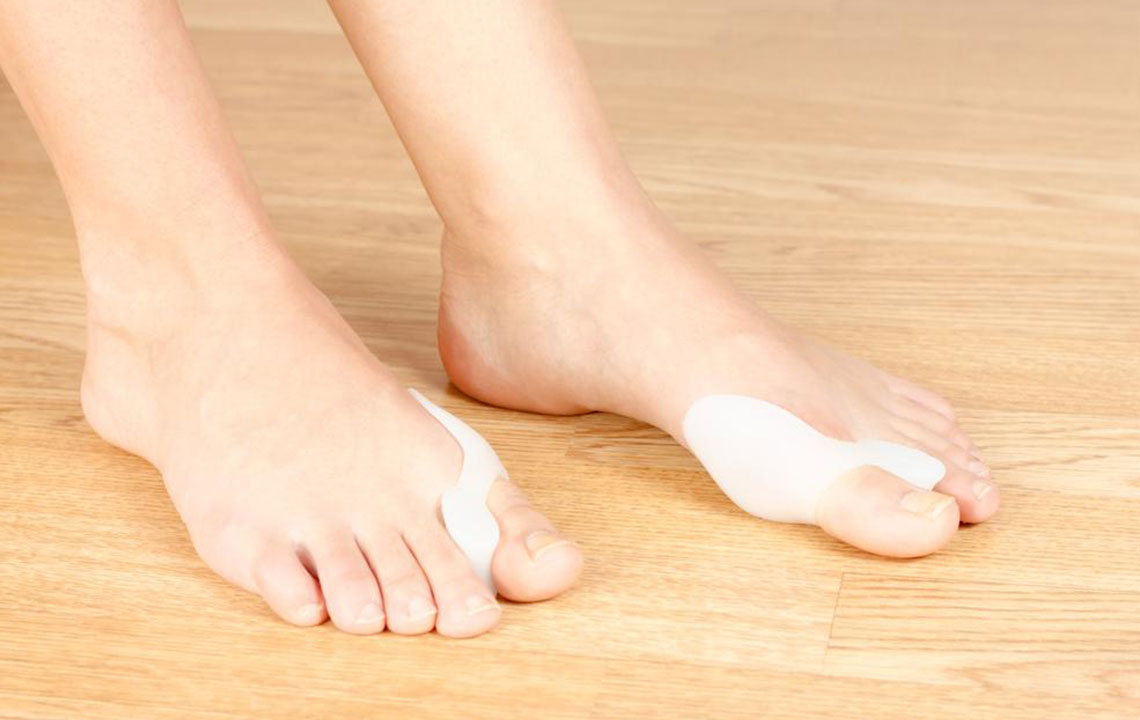
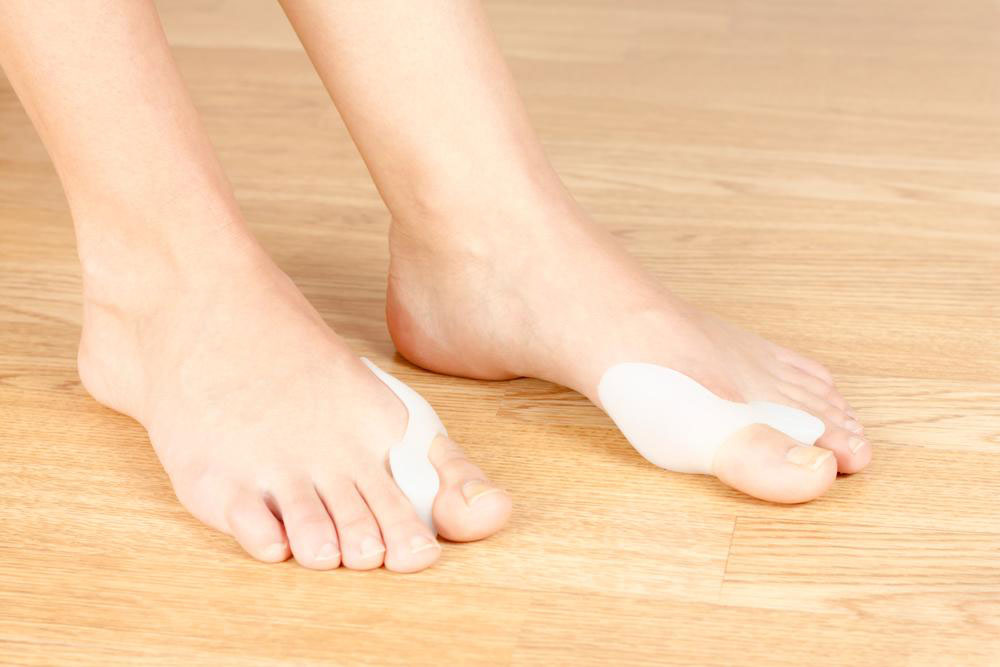
Orthotic devices such as bunion pads, toe separators, splints, and custom insoles can provide relief by supporting the toe and redistributing pressure during activities. While these devices do not cure bunions, they can slow deformity progression and reduce discomfort, especially in early stages.
Natural Home Remedies and Lifestyle Adjustments
Although scientific evidence is limited, some individuals find relief through home remedies like applying ice packs to reduce swelling, soaking feet in Epsom salt baths, using topical turmeric pastes for anti-inflammatory effects, or massaging the toes to improve circulation. Toe stretching exercises and foot massages may provide comfort but are not substitutes for medical treatment. Preventive measures include wearing properly fitting, supportive shoes that do not exert excessive pressure on the toe joint. Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce stress on the feet. Women are statistically more prone to bunion development, often due to footwear choices such as high heels and narrow shoes, as well as genetic factors.
Monitoring symptoms and consulting podiatrists or orthopedic specialists are critical for tailored management. Early intervention can prevent worsening deformity and improve quality of life.