Comprehensive Guide to Eye Health: Understanding Common Conditions and Prevention Strategies
This comprehensive article explores common eye conditions, their symptoms, causes, and available treatments. It emphasizes the importance of regular eye exams, preventive measures, and early intervention to preserve eyesight. Learn about refractive errors, cataracts, glaucoma, retinal diseases, and more, along with tips for maintaining healthy vision through diet, protection, and lifestyle choices. Essential reading for anyone interested in safeguarding their eye health and understanding how to prevent vision impairment or loss.

Comprehensive Guide to Eye Health: Understanding Common Conditions and Prevention Strategies
Overview of Common Eye Disorders and Effective Prevention Methods
Our eyes are remarkable organs that provide us with the gift of sight, allowing us to perceive the world around us in stunning detail. Given their vital role in daily life, maintaining eye health is crucial. However, numerous eye conditions can compromise vision, reduce quality of life, and, in some cases, cause irreversible damage. Recognizing the signs, understanding risk factors, and adopting preventive measures are essential steps to protect this precious sense.
If you experience persistent or unusual symptoms related to your eyes, seeking professional advice from a qualified ophthalmologist is highly recommended to ensure early diagnosis and effective treatment.
Types of Eye Conditions and Their Impact
Understanding these common eye problems enables timely intervention, which is vital for maintaining healthy vision. Some of the most prevalent eye conditions include:
Refractive Errors: These are the most common visual impairments, manifesting as nearsightedness (myopia), farsightedness (hyperopia), and astigmatism. People with refractive errors experience difficulty seeing clearly at certain distances. These issues are often inherited and tend to increase with age. Corrective methods include eyeglasses, contact lenses, and laser surgeries such as LASIK, which have high success rates in restoring clear vision.
Cataracts: Cataracts involve clouding of the eye's natural lens, leading to blurred or faded vision. They predominantly affect individuals over the age of 50 but can occur earlier due to injury, medication, or underlying health conditions. Fortunately, cataracts are treatable with surgical removal of the clouded lens, followed by implantation of an artificial intraocular lens, enabling restored vision for most patients.
Other significant eye issues include:
Optic Nerve Diseases: Conditions like glaucoma damage the optic nerve, often due to increased intraocular pressure, leading to progressive peripheral vision loss. Early diagnosis is crucial as damage is irreversible once vision starts declining.
Retinal Disorders: Damage or malfunctions of the retina, such as retinal detachment or degeneration, can cause partial or complete vision loss. Regular eye exams can help detect these problems early.
Macular Degeneration: This age-related condition affects the central part of the retina (macula), resulting in loss of detailed vision necessary for activities like reading and recognizing faces. There are dry and wet forms, with current treatments focused on slowing progression.
Diabetic Retinopathy: Diabetes can damage the blood vessels in the retina, leading to bleeding, swelling, and vision impairment. Managing blood sugar levels and regular eye screenings are key to preventing severe complications.
Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye): An infection or allergy causes inflammation of the conjunctiva, leading to redness, itching, and discharge. It typically resolves within two weeks but can be highly contagious, necessitating good hygiene and appropriate treatment.
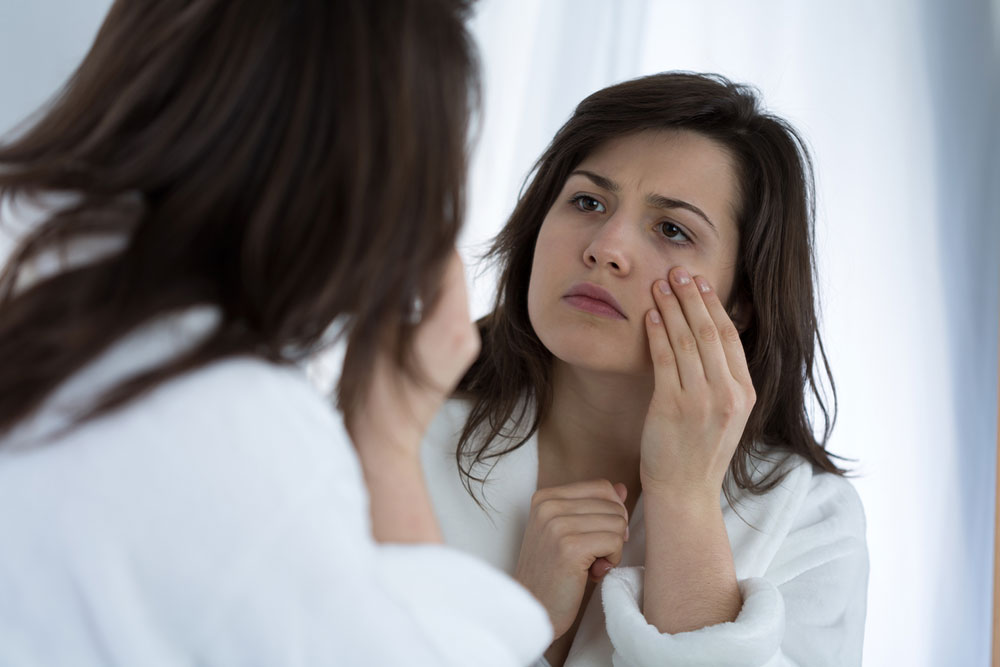
Recognizing Symptoms of Eye Health Issues
Understanding Causes of Eye Conditions
Common Treatment Options Available
Preventive Measures to Protect Eye Health
Maintain a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins A, C, E, and omega-3 fatty acids to support eye health.
Limit screen time and take regular breaks using the 20-20-20 rule: every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for at least 20 seconds.
Wear protective eyewear when engaging in activities with potential eye hazards, such as sports, construction, or using hazardous chemicals.
Avoid smoking, which increases the risk of cataracts, macular degeneration, and other eye diseases.
Manage systemic conditions like diabetes and hypertension effectively to prevent secondary eye complications.
Schedule routine eye examinations, especially if you are over 40 or have a family history of eye diseases.
Stay informed about eye health and promptly address any visual changes or discomfort.
Early detection and appropriate care are instrumental in preventing irreversible vision loss and ensuring long-term eye health.