Comprehensive Guide to Causes and Effective Treatments for Swollen and Painful Fingers
This comprehensive guide explores the causes of finger swelling and pain, including injuries, infections, and medical conditions like arthritis. It provides detailed home remedies, preventive tips, and guidance on when to seek medical help. Understanding these aspects can help individuals manage symptoms effectively and prevent long-term issues, ensuring healthier hand function. Recognizing early signs and applying appropriate care can significantly improve recovery outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.
Comprehensive Guide to Causes and Effective Treatments for Swollen and Painful Fingers
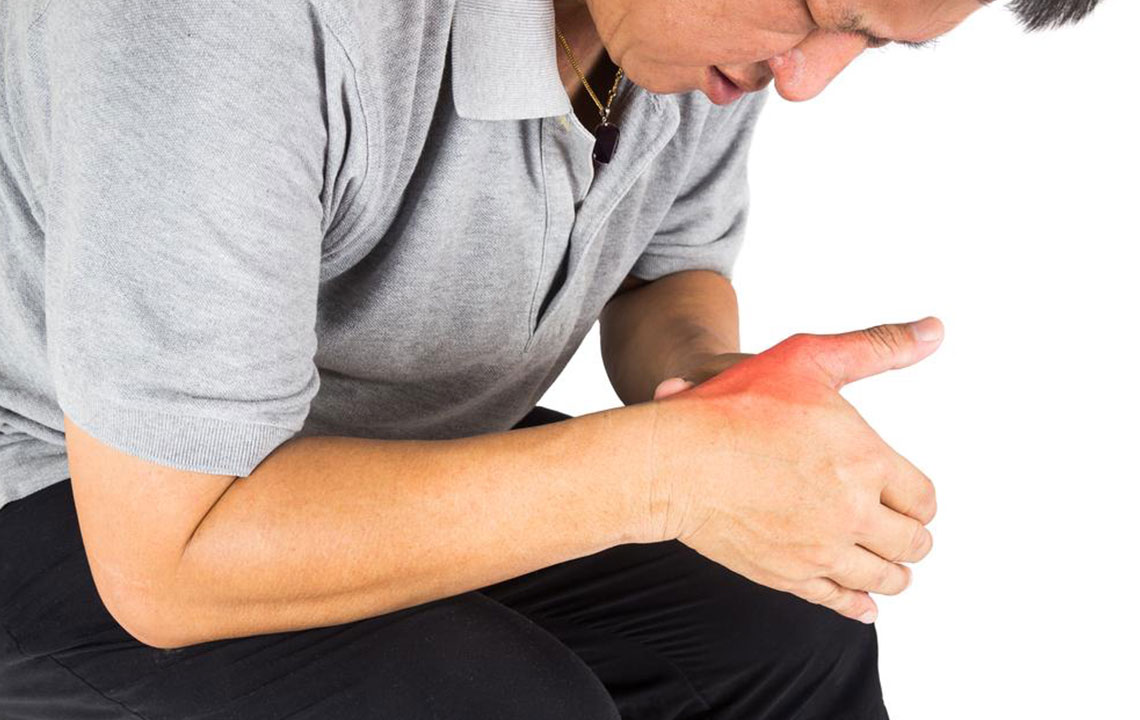
Finger swelling and discomfort are common concerns that many individuals experience at some point in their lives. These symptoms can result from a wide array of causes, ranging from minor injuries to more serious health conditions. Recognizing the underlying reason behind finger swelling is crucial for effective management and relief. Symptoms typically include redness, warmth, tenderness, stiffness, numbness, tingling sensations, and visible changes in skin color. While arthritis is among the primary culprits, other factors such as infections, inflammatory conditions, and traumatic injuries can also lead to painful swelling in the fingers.
Understanding the common causes of finger swelling and pain can help you identify when to seek medical attention and how to manage symptoms at home. This comprehensive guide explores the typical reasons behind finger discomfort, discusses effective home remedies, and emphasizes when it is essential to consult healthcare professionals for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Common Causes of Swollen and Painful Fingers
Trauma and Physical Injury: Sudden impacts, such as jamming a finger during sports or accidents, can cause swelling and pain. Contact sports like football, basketball, or volleyball are frequent contributors to finger injuries.
Overuse and Repetitive Movements: Activities involving repetitive hand motions, such as typing, sewing, or playing musical instruments, can lead to strain and inflammation of tendons and joints, resulting in swelling.
Heavy Lifting and Strenuous Activities: Handling heavy objects or engaging in physically demanding tasks at work or home can cause micro-injuries, leading to inflammation and swelling in the fingers.
Infections: Bacterial or viral infections can invade finger tissues, causing redness, warmth, swelling, and sometimes pus formation. Paronychia, an infection of the nail folds, is a common example.
Inflammatory Conditions and Autoimmune Diseases: Arthritis, including osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, is a leading cause of chronic finger swelling, stiffness, and deformity. Conditions like gout and psoriatic arthritis can also contribute.
Other Medical Conditions: Several health issues can manifest as finger swelling, such as carpal tunnel syndrome, where nerve compression causes swelling and pain; trigger finger, where tendons become inflamed, hindering smooth movement; Dupuytren’s contracture, which causes hand thickening and finger deformities; and Raynaud’s phenomenon, which results in blood flow problems and swelling episodes.
Tumors and Cysts: Rarely, benign or malignant growths in the hand can cause swelling and discomfort, requiring medical assessment.
Recognizing Symptoms and When to Seek Help
While occasional minor swelling may resolve with rest and home care, persistent or worsening symptoms warrant prompt medical attention. Key signs that indicate the need for professional evaluation include:
Severe or ongoing pain lasting more than a week despite home remedies
Visible deformity of the fingers or joints
Inability to straighten or bend the finger
Unexplained redness, warmth, and swelling accompanied by fever
Development of numbness or tingling sensations that interfere with daily activities
Fingers becoming purple or bluish, indicating circulation problems
Home Remedies and Self-Care Tips
Many cases of finger swelling can be managed effectively at home through simple remedies and lifestyle adjustments. These include:
Rest and Immobilization: Avoid activities that exacerbate symptoms and keep the affected finger immobile to prevent further injury.
Elevation: Keep your hand elevated above heart level to reduce swelling by promoting fluid drainage.
Ice Application: Apply an ice pack wrapped in a cloth to the swollen area for 15-20 minutes every few hours. This helps reduce inflammation and numbs the area, alleviating pain.
Compression: Lightly wrapping the finger with an elastic bandage can provide support and minimize swelling, but it should not be too tight to impair circulation.
Warm Compresses and Gentle Massage: After initial swelling subsides, warm compresses and gentle massaging can improve blood flow and promote healing.
Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce pain and inflammation.
Protection and Taping: Taping the finger to adjacent digits can offer additional support, but care must be taken not to restrict blood flow or cause further discomfort.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Tips
Preventing finger swelling involves mindful habits and protective measures. These include:
Wearing protective gear during sports or hazardous activities
Practicing ergonomic techniques when using computers or tools
Stretching and strengthening hand muscles regularly
Avoiding repetitive strain by taking breaks during prolonged activities
Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce joint stress
When to See a Doctor
If symptoms persist or worsen despite home management, or if you experience signs of infection, joint deformity, or neurological impairment, seeking medical care is essential. Healthcare professionals will perform physical exams, review your medical history, and often order imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs to determine the cause. Based on the diagnosis, treatments can include medications, physical therapy, splinting, or, in severe cases, surgical intervention.
Early diagnosis and appropriate management are key to preventing permanent damage or deformity caused by chronic conditions like arthritis or severe injuries. Do not ignore persistent or severe symptoms—consult your healthcare provider promptly for personalized advice and treatment options.