Comprehensive Methods to Prevent and Manage Groin Strain Injuries Effectively
Discover effective strategies to prevent and manage groin strain injuries. This comprehensive guide covers immediate first aid steps, rehabilitation exercises, injury prevention techniques, and when to seek surgical treatment. Learn how to protect yourself from further damage and promote speedy recovery through targeted exercises and proper warm-up routines, ensuring optimal health and injury-free activity.

Comprehensive Methods to Prevent and Manage Groin Strain Injuries Effectively
Groin strains and tears are common injuries, particularly among athletes and individuals engaged in vigorous physical activities. These injuries can result in significant pain, movement restrictions, and prolonged recovery periods if not addressed promptly and properly. Understanding how to prevent these injuries and what immediate actions to take can make a substantial difference in recovery outcomes. In this article, we will delve into detailed strategies that help minimize the risk of further complications from groin injuries and facilitate effective healing.
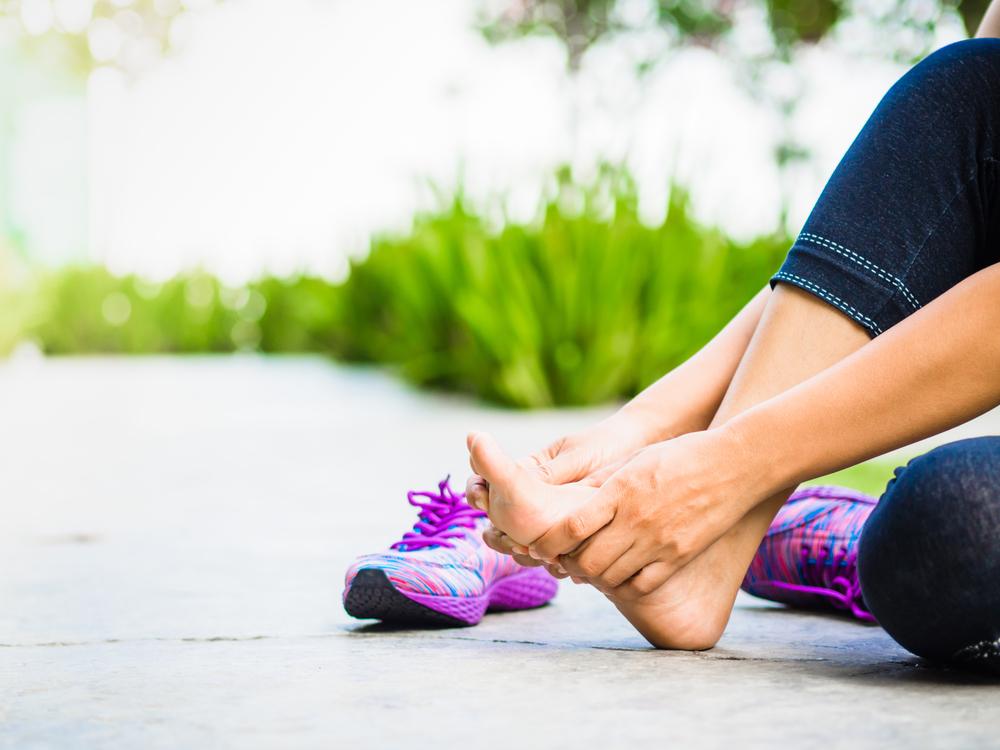
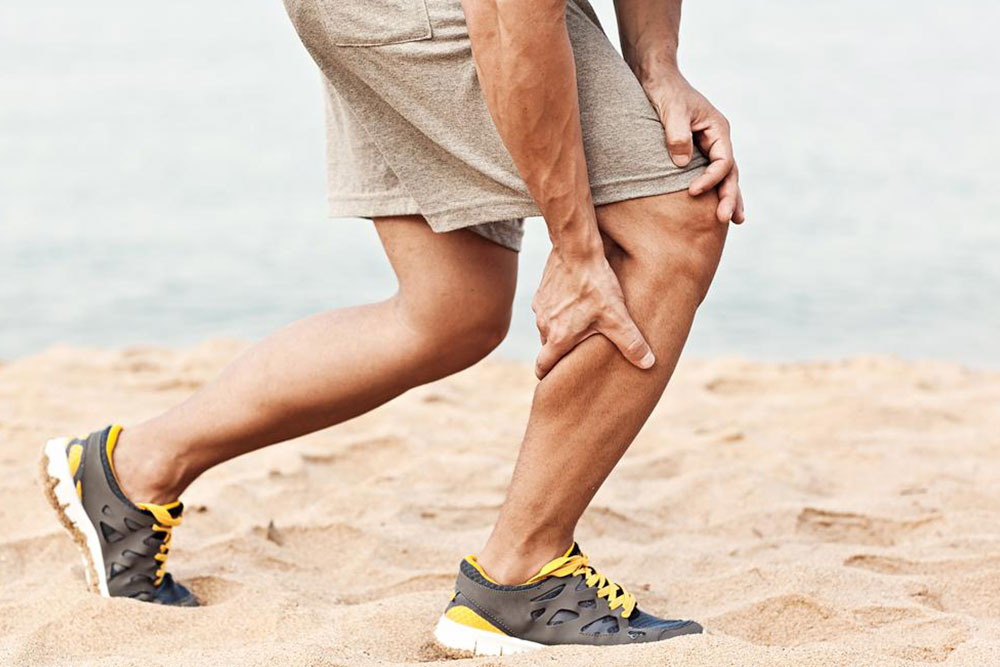
Recognizing the signs of a groin injury right away is crucial. The moment you suspect a strain, it’s vital to cease all physical activity immediately. Continuing to move or walk excessively can exacerbate the injury, leading to a more severe tear and a lengthier recovery process. Symptoms typically include sudden pain in the inner thigh or groin area, swelling, bruising, and difficulty with movement. Acting swiftly is essential to prevent the injury from worsening.
The initial management of a suspected groin injury involves implementing the well-known RICE protocol—Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. These steps provide immediate relief and help control inflammation and swelling. Rest involves avoiding weight-bearing activities to prevent further tissue damage. Applying ice packs to the affected region for 15-20 minutes every few hours helps reduce pain and swelling. Compression using elastic bandages can support the injured tissue and minimize movement that might worsen the tear. Elevating the leg or affected limb above heart level further assists in decreasing swelling. Together, these actions establish a solid foundation for recovery.
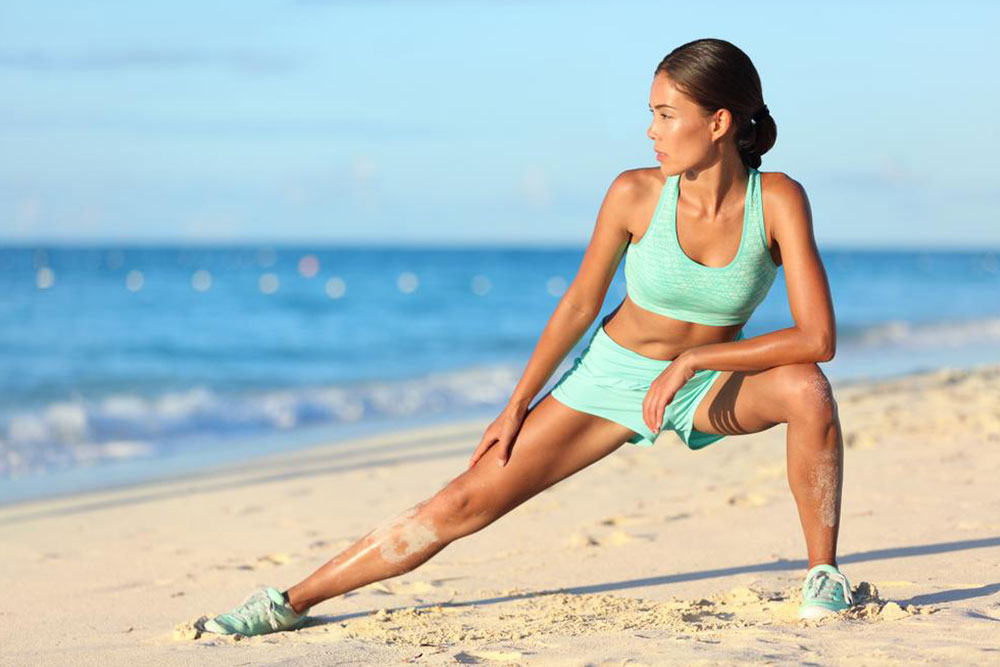
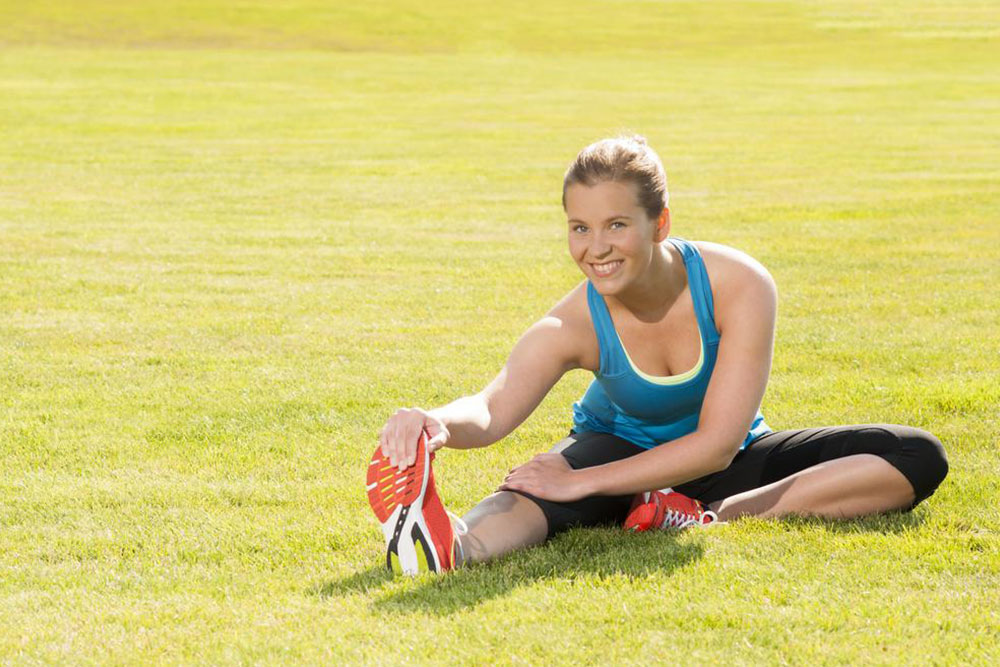
Once the initial acute phase subsides—usually after a few days—gentle stretching exercises can be safely introduced. These stretches aim to restore flexibility and prevent stiffness. Typical stretches include seated or standing groin stretches and hip flexor stretches. It’s important to perform these cautiously and never force a stretch that causes pain. Always consult with a healthcare professional before beginning any stretching or strengthening regimen.
Targeted strengthening exercises play a vital role in recovery, especially those that focus on the adductor muscles, hip flexors, and surrounding muscle groups. Exercises such as adductor squeezes with resistance bands, side-lying leg lifts, and controlled squats can help rebuild strength and stability in the groin area. Performing these exercises under supervision ensures proper technique and reduces the risk of re-injury.
Prevention remains the most effective strategy for avoiding groin injuries altogether. Proper warm-up routines before physical activity are crucial. A comprehensive warm-up should include dynamic stretches, light jogging, and specific mobility drills that activate the groin and hip muscles. Additionally, engaging in regular conditioning exercises to strengthen core stability and flexibility can significantly decrease injury risk.
It’s important to note that while over-the-counter pain medications, such as NSAIDs, can temporarily alleviate discomfort, they do not address the underlying injury. In more severe cases—such as complete tears—surgical intervention may be necessary. Post-operative rehabilitation often involves a structured physical therapy program tailored to restore strength, flexibility, and function.
In summary, preventing groin injuries involves proper preparation, including warm-up and conditioning exercises, while immediate response to injury with RICE and appropriate medical consultation can optimize recovery. Incorporating targeted stretching and strength training, along with attentive self-care, promotes healing and reduces the risk of long-term complications. Maintaining a vigilant approach towards these injuries ensures athletes and active individuals can return to their routines with minimal disruption and optimal health.