Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing Meningitis: Symptoms, Causes, and Early Detection
Meningitis is a life-threatening condition characterized by inflammation of the protective membranes around the brain and spinal cord. Recognizing early signs such as neck stiffness, high fever, severe headaches, and skin rashes is crucial for prompt diagnosis and treatment. This comprehensive guide covers causes, symptoms, and preventive measures, emphasizing the importance of early intervention to prevent serious health outcomes. Particularly affecting children, young adults, and seniors, meningitis can spread rapidly, making awareness and vaccination essential for at-risk populations.

Understanding the Key Signs and Symptoms of Meningitis
Meningitis is a serious medical condition characterized by inflammation of the meninges, which are the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. These membranes—comprising the dura mater, arachnoid, and pia mater—serve as crucial shields for our central nervous system. When infections such as bacteria, fungi, or viruses invade these membranes, meningitis develops, potentially leading to severe health consequences if not diagnosed and treated promptly.
There are primarily three types of meningitis—bacterial, fungal, and viral—each with distinct causes, severity levels, and treatment approaches. Bacterial meningitis is considered the most dangerous, spreading easily through close contact, and requires immediate medical intervention. Viral meningitis, on the other hand, tends to be less severe, often resolving on its own without extensive treatment. Fungal meningitis is less common but can be life-threatening, especially for individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those undergoing cancer treatments or living with immunodeficiency disorders.
Potential Causes of Meningitis Include:
- Syphilis and Tuberculosis
- Fungal infections like Cryptococcus or Candida
- Autoimmune conditions that trigger inflammation
- Certain cancer treatments that compromise immunity
- Less common causes, such as autoimmune disorders and specific infections, can also lead to meningitis.
Meningitis can affect individuals across all age groups but is particularly prevalent among children under five years old, young adults between 16 and 25, and seniors over 55. Recognizing this pattern helps prioritize screening and awareness efforts for vulnerable populations.
Early detection of meningitis is vital because its symptoms often mimic those of common illnesses like colds or the flu, which can delay diagnosis. Being aware of specific signs such as back pain, loss of appetite, and pallor can enable timely medical intervention. The following are key symptoms that should prompt immediate medical attention:
Light Sensitivity
Sudden increased sensitivity to bright lights may be an early indicator of meningitis. Persistent or new-onset photophobia warrants prompt evaluation by healthcare professionals.
Cold or Flu-like Symptoms
Symptoms such as fever, vomiting, muscle aches, and fatigue resembling a common cold can be signs of meningitis, especially if they come on suddenly and are severe. Persistent symptoms should be checked by a doctor.
High Fever
An abrupt high temperature spike, particularly when accompanied by other symptoms like neck stiffness or nausea, indicates a possible serious infection such as meningitis. Immediate testing and treatment are crucial.
Unexplained Vomiting
Severe or persistent vomiting can be a sign of neurological infection, necessitating urgent medical evaluation.
Neck Stiffness and Swelling
Neck stiffness, often accompanied by pain or swelling, is a hallmark symptom of meningitis. This sign should never be ignored, especially when paired with other symptoms.
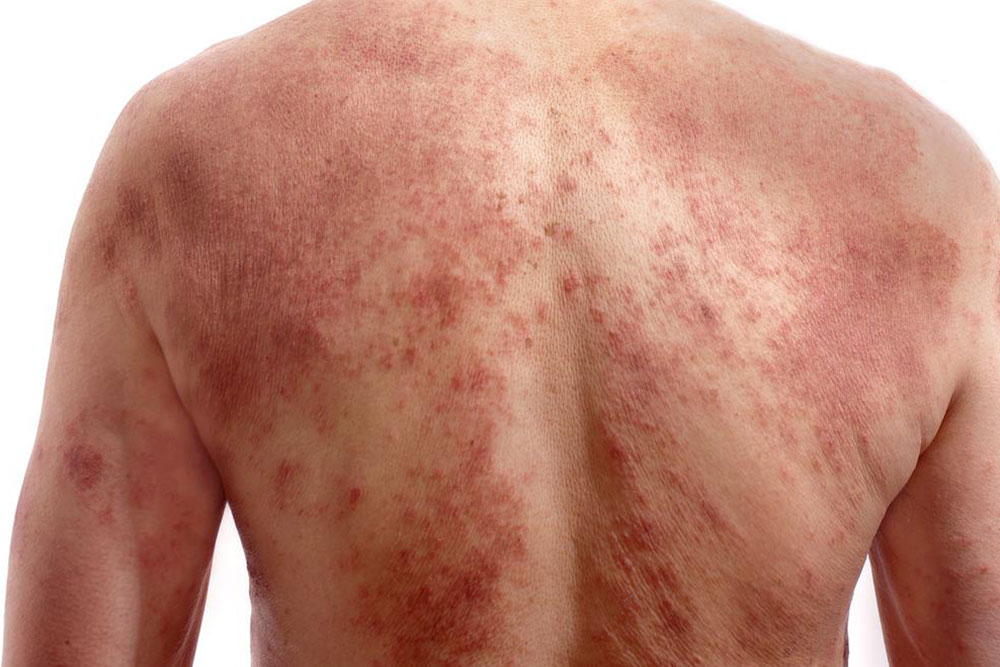
Skin Rashes or Red Spots
The appearance of reddish spots, rashes, or petechiae may signify bloodstream infection spread, which demands immediate medical attention.
Intense Headaches
Headaches that are different from usual migraines in intensity or pattern can be indicative of meningitis. Severity and persistence warrant prompt diagnosis.
Muscle Aches
Widespread muscle pains that impair movement or cause significant discomfort should be assessed by healthcare providers.
Seizures
The occurrence of seizures is a critical emergency symptom of meningitis, requiring immediate hospital care to prevent serious complications.
Children are also particularly susceptible to meningitis. Their symptoms may include high-pitched crying, irritability, refusal to be touched, or poor feeding. Due to rapid spread and potential severity in children, vaccination remains an essential preventive measure to protect against this dangerous disease.