Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing Symptoms of Stage 3 Kidney Disease and How to Manage It
Stage 3 kidney disease is a critical health condition with subtle early symptoms that require careful attention. Recognizing signs such as fatigue, swelling, and blood in urine, along with understanding causes and preventive measures, can improve management and prognosis. This comprehensive guide discusses the progression, symptoms, causes, and lifestyle tips to help individuals at risk maintain better health and delay disease progression through early intervention and regular checkups.
Understanding the Signs and Management of Stage 3 Kidney Disease
Human health depends on the proper functioning of vital organs, each performing critical roles to sustain life. Among these, the kidneys are essential for filtering waste products, regulating electrolyte balances, controlling blood pressure, and maintaining overall fluid balance. Situated near the lower back, each kidney works tirelessly to cleanse the blood by removing toxins through urine, which then passes into the bladder for excretion. Unfortunately, kidney health can decline due to various factors, leading to a condition known as kidney disease or renal failure. When this occurs, the body's ability to eliminate harmful substances diminishes, potentially leading to life-threatening complications if not identified and managed early.
Kidney disease often develops gradually, progressing through several stages that can span many years. Recognizing and understanding these stages are crucial for timely intervention. Of particular concern is Stage 3 kidney disease, where notable symptoms begin to surface but are often overlooked or mistaken for less serious health issues. Early detection at this stage can significantly improve treatment outcomes and enhance quality of life. Therefore, knowing the causes, typical symptoms, and preventive measures is vital for those at risk.
Stage 3 kidney disease results from diminishing kidney function, where the kidneys' ability to filter toxins effectively becomes compromised. This can lead to a buildup of waste in the body, resulting in various health issues. Common causes include chronic conditions such as diabetes mellitus, high blood pressure (hypertension), reduced blood flow to the kidneys, dehydration, and adverse effects from certain medications, notably diuretics and other pharmacological agents. If left untreated, the condition can escalate to more severe impairment, but early management can often slow progress and improve life quality.
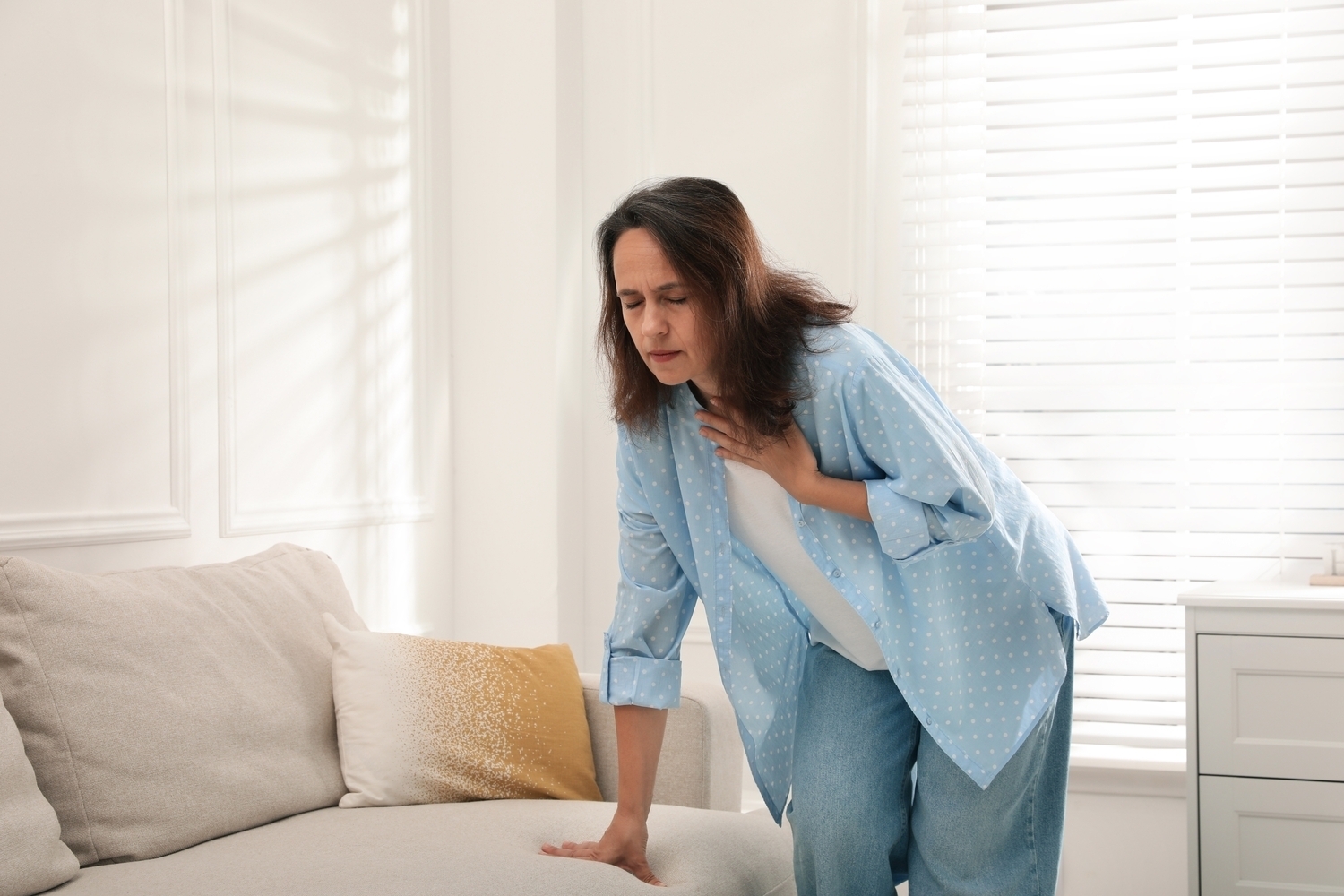
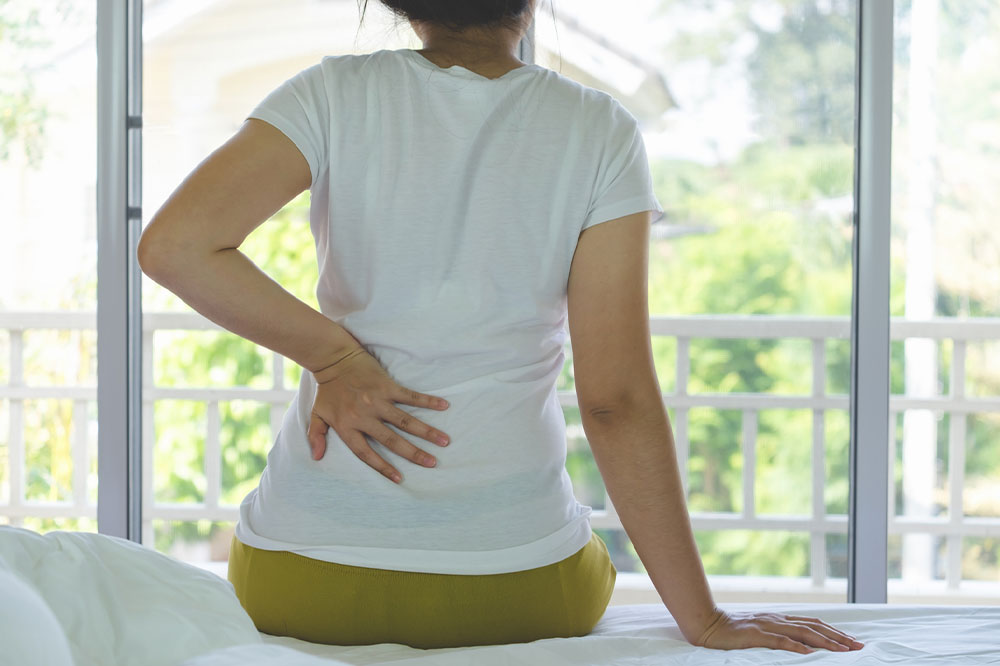
Symptoms in the early phase of Stage 3 are often subtle and may include persistent fatigue, weakness, and general malaise. However, as the disease advances, more prominent signs manifest. Patients may experience significant fluid retention leading to swelling in the abdomen, legs, ankles, and joints. Breathing difficulties can occur due to fluid accumulation in the lungs. Pain in the lower back or sides, cramping, and visible blood in urine also signal worsening kidney function. Recognizing these symptoms can prompt timely medical evaluation and intervention. While reversing kidney damage entirely remains challenging, lifestyle modifications, adherence to prescribed treatments, and routine health monitoring play vital roles in managing the condition effectively.
Preventive strategies include managing underlying health issues such as controlling blood glucose and blood pressure levels, maintaining proper hydration, avoiding nephrotoxic medications unless prescribed by a healthcare professional, and regular kidney function tests especially for high-risk individuals. Early diagnosis and proactive management are key to preventing progression to more severe stages of kidney disease. If you or your loved ones are experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned, consulting a healthcare provider promptly can make a significant difference in treatment success and overall prognosis.