Nutritional Strategies for Managing Schizophrenia: Essential Dietary Tips for Mental Health Support
Discover comprehensive nutritional strategies to support mental health in schizophrenia management. Learn about essential dietary tips, including omega-3 intake, gluten reduction, and antioxidant-rich foods. These dietary adjustments can complement medical treatments, potentially alleviating symptoms and improving quality of life. Always consult healthcare providers before making significant dietary changes or starting supplements to ensure safety and effectiveness.

Nutritional Strategies for Managing Schizophrenia: Essential Dietary Tips for Mental Health Support
Maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet is a vital component of overall health, particularly when it comes to supporting mental health and improving symptoms associated with schizophrenia. While medication remains the cornerstone of treatment, emerging evidence suggests that diet and nutrition can play a supportive role in managing symptoms, enhancing treatment efficacy, and improving quality of life for individuals affected by this complex mental disorder. This comprehensive article delves into specific dietary strategies that can complement medical therapy, focusing on nutritional intake that fosters brain health and mitigates some of the challenges faced by schizophrenia patients.
Enhance Omega-3 Fatty Acids Consumption for Brain Function
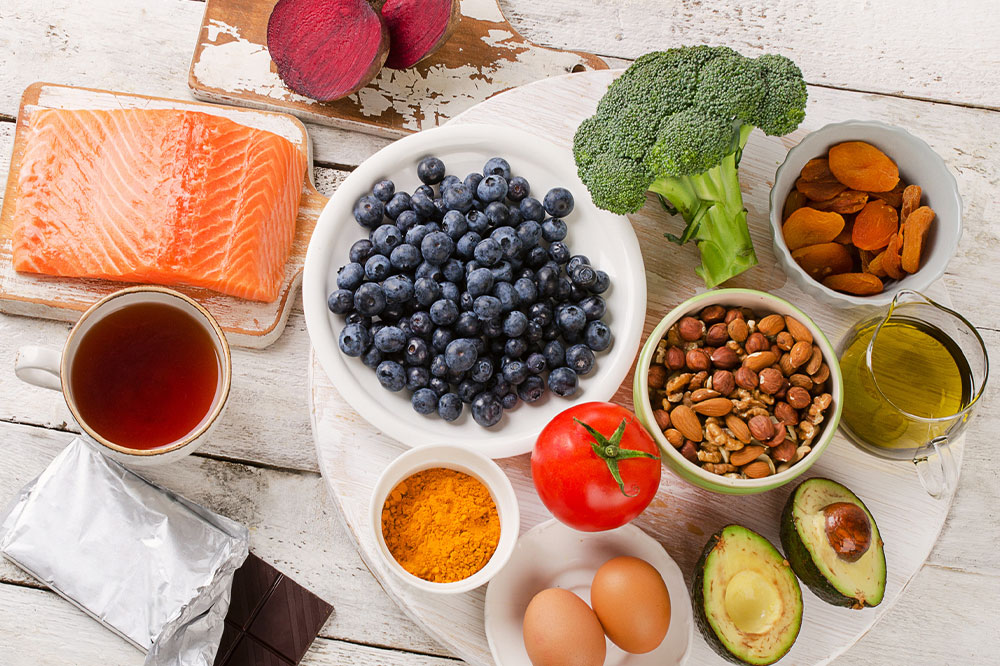
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for maintaining optimal brain health and function. They play a pivotal role in reducing inflammation and supporting neural communication, which is crucial for managing mental health conditions such as schizophrenia. Incorporating omega-3-rich foods into daily meals can potentially alleviate some symptoms related to mood, cognition, and perception. Foods such as fatty fish—salmon, sardines, mackerel—are excellent sources. Vegetarians and vegans can rely on plant-based options like flaxseeds, walnuts, and pumpkin seeds. Additionally, omega-3 supplements like cod liver oil are often recommended under medical guidance to ensure adequate intake.
Reduce Gluten Intake to Minimize Gut Inflammation
Gluten, a protein found in wheat, rye, and barley, may contribute to gut inflammation and immune responses in sensitive individuals, potentially worsening psychiatric symptoms. A gluten-free diet emphasizing grains like rice, oats, quinoa, and buckwheat can help reduce inflammation and improve gut health. Since gut health has a significant impact on mental well-being, especially in neuropsychiatric disorders, shifting to gluten-free options may offer symptom relief and enhance overall mental clarity.
Boost Fruit and Vegetable Consumption for Nutrient Density
Eating a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables supplies essential vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants that are critical for brain health and bodily functions. Rich in nutrients such as vitamin C, E, and beta-carotene, they help combat oxidative stress, improve immune function, and support cognition. Berries, apples, oranges, melons, spinach, kale, and bell peppers are especially beneficial. Regular intake of these foods can help strengthen the immune system and may contribute to reducing the severity of symptoms and medication side effects.
Antioxidant-Rich Foods for Reducing Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress caused by free radicals has been linked to neurodegenerative processes and psychiatric conditions. Consuming foods high in antioxidants—including berries (blueberries, strawberries), citrus fruits (oranges, grapefruits), nuts, beans, and green leafy vegetables—can neutralize free radicals, protect cells, and promote neural resilience. Incorporating these foods into the diet may complement psychiatric treatment by supporting cellular health and possibly reducing medication-related side effects.
Increase Intake of Niacin-Rich Foods for Brain Support
Niacin, also known as vitamin B3, is vital for proper nerve function and energy metabolism in the brain. It has been observed that deficiency in niacin can be associated with neuropsychiatric symptoms. Foods such as chicken, eggs, fish, mushrooms, and green vegetables are excellent sources. In some cases, healthcare providers may recommend niacin supplements to address deficiencies, but always under medical supervision to avoid adverse effects.
Adopting these nutritional strategies should be seen as a supportive measure rather than a replacement for conventional medical treatments like antipsychotic medications. For example, medications such as CAPLYTA® that contains lumateperone are effective in controlling hallucinations, agitation, and other symptoms of schizophrenia. It is essential to discuss any dietary changes with healthcare professionals to prevent potential interactions—such as avoiding grapefruit when on certain medications—and to ensure a holistic approach to managing the disorder.