Comprehensive Insight into Kidney Problems and Their Role in Lower Back Pain
This detailed article explores how kidney issues such as infections and stones can cause lower back pain, emphasizing symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. Recognizing the signs of kidney-related discomfort is essential for timely intervention, preventing complications, and ensuring proper medical care. Understand the key differences between common back pain and renal pain, and learn how medical professionals diagnose and manage these conditions effectively to improve your health and quality of life.
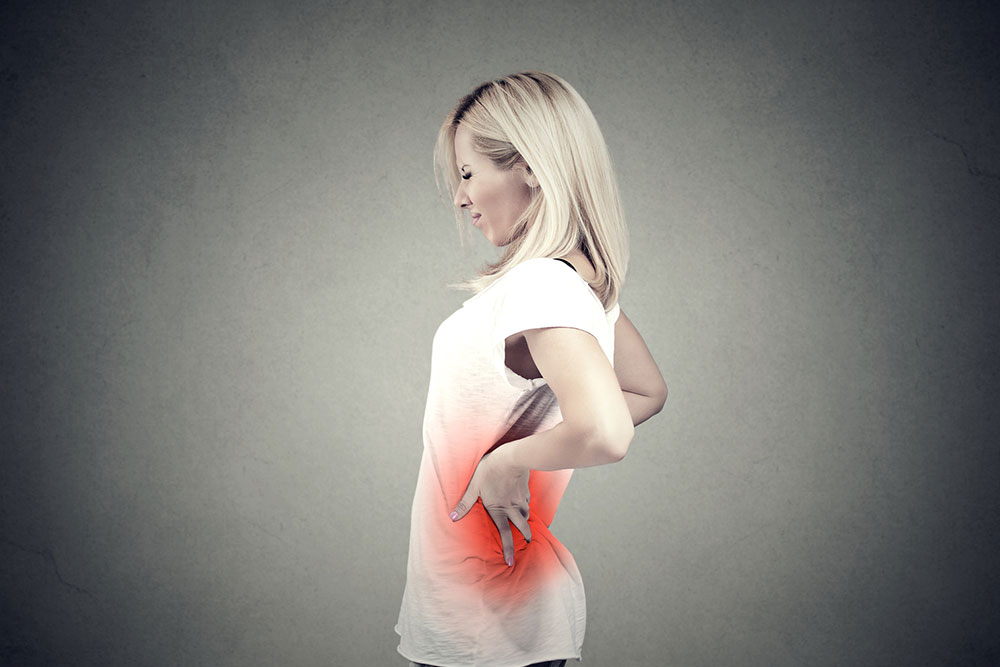

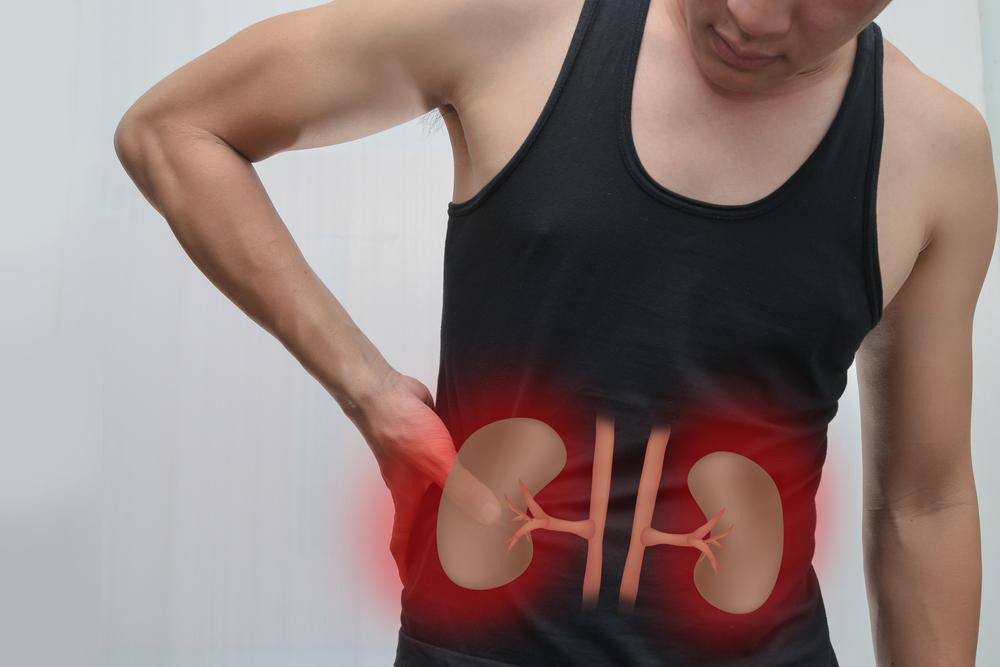
Understanding How Kidney Issues Can Lead to Lower Back Discomfort and Pain
Lower back pain is a common health complaint experienced by many people at some point in their lives. Usually, it’s associated with muscle strains, poor posture, or injuries related to everyday activities. However, in some cases, lower back discomfort may originate from internal organs, particularly the kidneys. Recognizing the difference between typical muscular back pain and pain caused by kidney problems is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective treatment. This comprehensive guide delves into how kidney issues such as infections, stones, and other renal conditions can manifest as lower back pain, helping you understand the key signs, causes, diagnosis methods, and treatment options.
Differentiating Normal Back Pain from Kidney-Related Discomfort
Usually, back pain that stems from muscular strain or ligament issues tends to be dull, aching, and spread across a larger area, often influenced by movement or posture. Conversely, pain linked to kidney problems tends to have a distinct profile. Kidney pain is often localized, sharp, and persistent, typically focused around the sides of the lower back, just below the ribs. If the pain radiates to the abdomen or inner thighs, it may indicate a renal issue. Recognizing these distinctions is vital to seeking appropriate medical intervention.
Common Causes of Kidney-Related Lower Back Discomfort
Kidney problems that frequently lead to lower back pain include kidney stones, infections, tumors, renal infarction, and glomerulonephritis. Each condition has unique features and underlying causes:
Kidney Stones: Formed from mineral deposits crystallizing in the urine, kidney stones are a prevalent cause of severe lower back pain. Stones can move within the kidney or along the urinary tract, causing intense, stabbing sensations, especially when lodged in the ureters. Risk factors include dehydration, a family history of kidney stones, certain dietary habits, and metabolic disorders.
Kidney Infections: Often originating from urinary tract infections, kidney infections cause localized inflammation and pain. Symptoms are usually accompanied by fever, chills, nausea, and sometimes blood in the urine. Those with compromised immune systems are more susceptible to developing such infections.
Other Renal Conditions: Conditions such as renal tumors or infarcts can also cause persistent pain, although these are less common. Rapid diagnosis is essential to treat these serious issues effectively.
How Healthcare Professionals Diagnose Kidney-Linked Back Pain
Accurate diagnosis is crucial to determine the exact cause of lower back pain related to the kidneys. Physicians generally employ a combination of laboratory tests and imaging studies:
Blood Tests: These measure kidney function, check for infection markers, and identify any metabolic abnormalities.
Urine Analysis: A crucial step, urine tests detect the presence of bacteria, blood, pus, crystals, or protein, indicating infection or stone formation.
Imaging Techniques: CT scans provide detailed images of the kidneys and urinary tract, helping locate stones, tumors, or structural abnormalities. Ultrasound and X-rays are also commonly used as supportive tools.
Additional Symptoms Associated with Kidney-Related Back Pain
Beyond localized pain, other symptoms can help identify renal issues:
Nausea and vomiting
Fever and chills
Blood in the urine (hematuria)
Persistent aching or sharp pain in the sides or lower back
Difficulty urinating or painful urination
Fatigue and malaise
These signs often accompany specific kidney problems, emphasizing the need for prompt medical evaluation.
Effective Management and Relief Strategies
Once diagnosed, treatment depends on the underlying condition:
For Kidney Infections: Antibiotics are essential to eliminate bacterial infection, along with supportive care like hydration and rest.
For Kidney Stones: Pain management involves analgesics, while larger stones may require procedures such as extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL), laser lithotripsy, or minimally invasive surgery.
For Other Conditions: Surgery, medication, or observation may be necessary depending on the specific diagnosis. Hydration remains a key component of treatment for most renal issues to prevent stone formation and aid recovery.
In addition to medical interventions, lifestyle modifications such as staying well-hydrated, maintaining a healthy diet, and avoiding excessive salt or mineral intake can help prevent future kidney problems. Applying heat pads and using over-the-counter pain relievers can provide temporary relief from discomfort. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers are crucial to monitor progress and prevent recurrence.
This comprehensive understanding highlights the importance of differentiating between muscular back pain and kidney-related pain. Recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate medical care can drastically improve outcomes, reduce complications, and ensure better management of underlying kidney conditions. Whether it’s a kidney infection, stones, or other renal issues, prompt attention is essential for effective treatment and alleviation of lower back discomfort.