Comprehensive Guide to COPD: Recognizing Symptoms, Causes, and Effective Management Techniques
This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth overview of COPD, exploring its causes, symptoms, and management options. It emphasizes early detection, lifestyle changes, and medical treatments that can help improve quality of life for those affected by chronic lung diseases. Learn about effective strategies to manage COPD and prevent its progression, ensuring better respiratory health and overall well-being.
Comprehensive Guide to COPD: Recognizing Symptoms, Causes, and Effective Management Techniques
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, commonly known as COPD, is a widespread and progressive respiratory condition that significantly impacts millions worldwide. It encompasses a group of diseases characterized by long-term breathing problems and airflow limitation. These conditions include chronic bronchitis, emphysema, asthma, and cystic fibrosis, all of which contribute to airflow obstruction, making breathing laborious and less efficient. COPD develops as a result of numerous factors that cause chronic inflammation and structural changes within the lungs, leading to a decrease in lung function over time.
Understanding what causes COPD and how it manifests is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. The disease primarily results from long-standing exposure to lung irritants, such as tobacco smoke, air pollution, occupational dust, fumes, or genetic predispositions. Continuous exposure to these irritants induces persistent inflammation of the airways and lung tissue, leading to swelling, increased mucus production, and structural damage. These changes impair the lungs' elasticity, which is essential for normal breathing cycles, causing the airways to over-expand and fail to return to their normal state during exhalation.
This pathological process results in reduced oxygen transfer from the lungs into the bloodstream and increased retention of carbon dioxide within the alveoli—the tiny air sacs where gas exchange occurs. As a consequence, individuals with COPD often experience a decline in overall oxygen levels, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, difficulty breathing, and reduced exercise tolerance. Detecting COPD early can be challenging because the initial symptoms may be subtle and often mistaken for other respiratory illnesses like asthma or bronchitis.
Symptoms and Early Detection of COPD
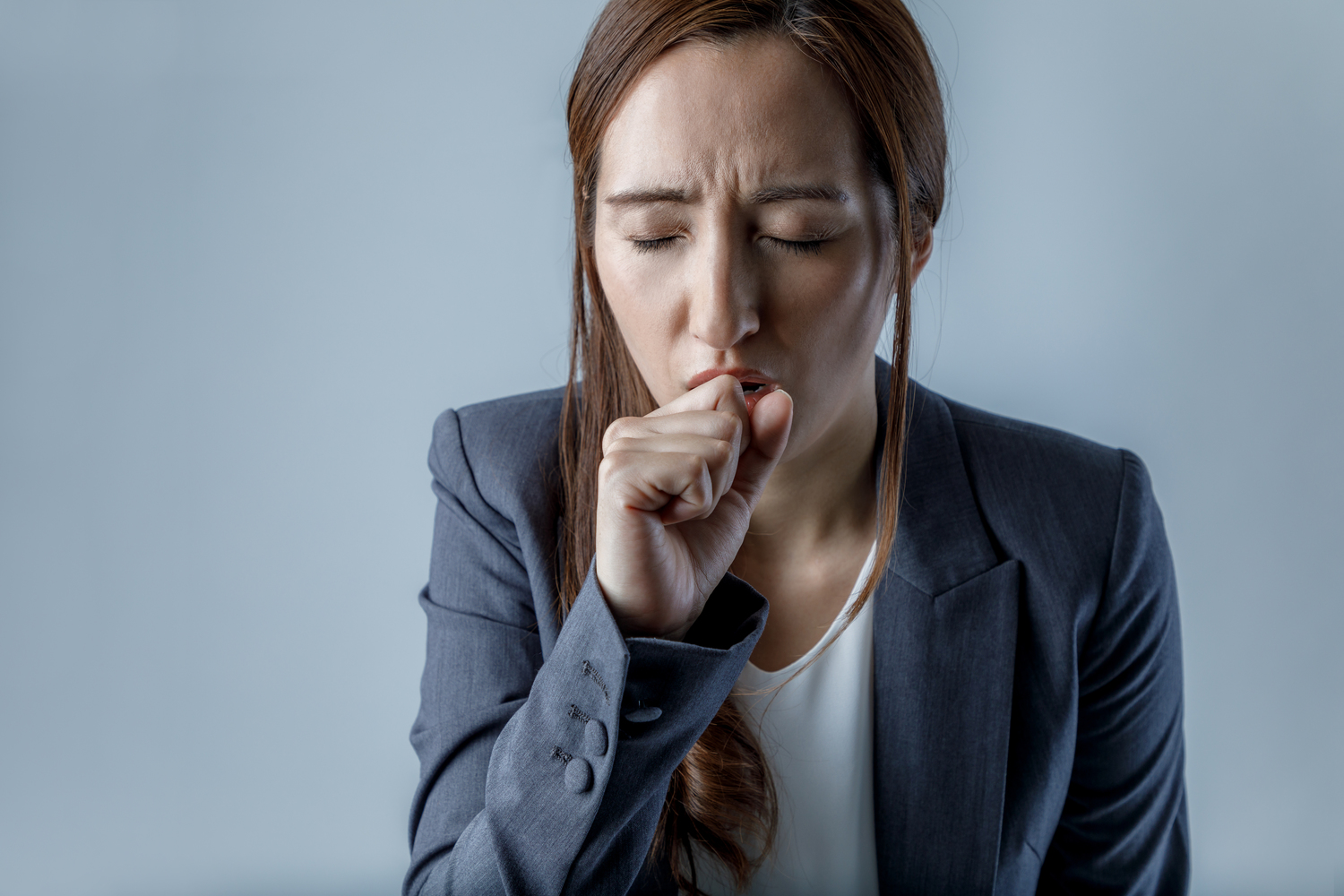
The symptoms of COPD often develop gradually, and many individuals do not notice them until lung damage becomes significant. Early symptoms can include a persistent cough producing mucus, shortness of breath during physical activity, wheezing, chest tightness, and frequent respiratory infections. Some patients report morning mucus clearing or a bluish tint to lips and fingernails—a condition known as cyanosis, indicating insufficient oxygenation. As the disease progresses, symptoms tend to worsen, with increased difficulty in breathing even at rest, persistent fatigue, and swelling in the ankles or legs due to right-sided heart strain. Unexplained weight loss and frequent lung infections are also common in advanced stages.
During exacerbations or flare-ups, symptoms can intensify suddenly, often lasting days and requiring immediate medical attention. These episodes are characterized by increased wheezing, cough, mucus production, and severe dyspnea. Over time, the lung's ability to transfer oxygen diminishes further, leading to hypoxemia—a dangerous condition marked by low blood oxygen levels. Hypoxemia can impair vital organ functions and cause symptoms at rest, including confusion, sleep disturbances, and even respiratory failure.
Managing COPD: Lifestyle Changes and Medical Interventions
Once diagnosed, managing COPD involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, medications, and sometimes oxygen therapy. The cornerstone of treatment is to eliminate or minimize exposure to lung irritants such as cigarette smoke and environmental pollutants. Smoking cessation is paramount and can slow disease progression significantly. Patients are encouraged to avoid respiratory irritants, invest in air purifiers, and adopt a healthy lifestyle that supports lung health.
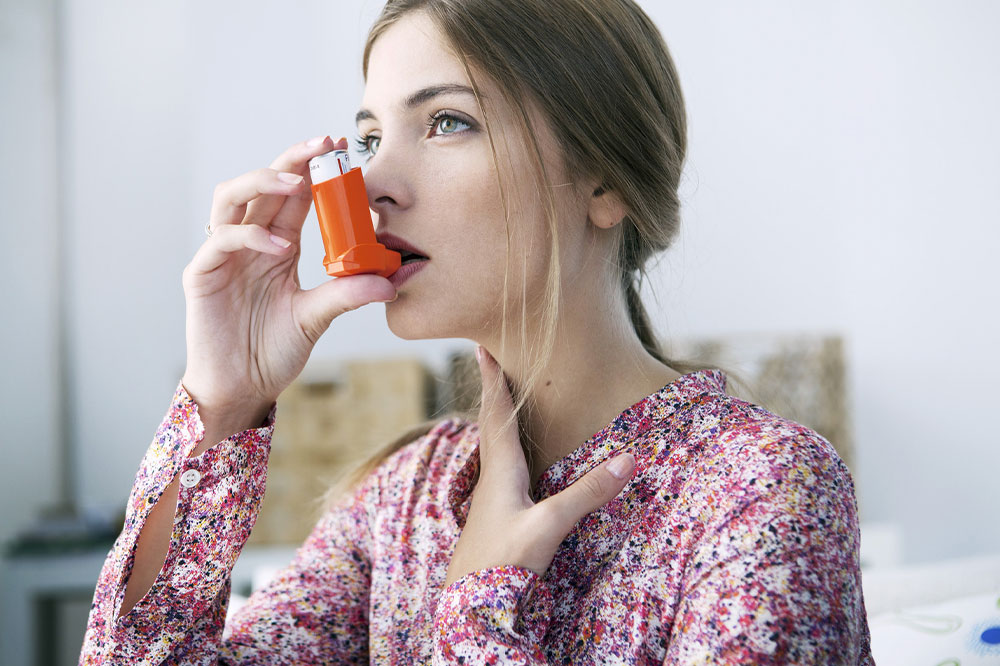
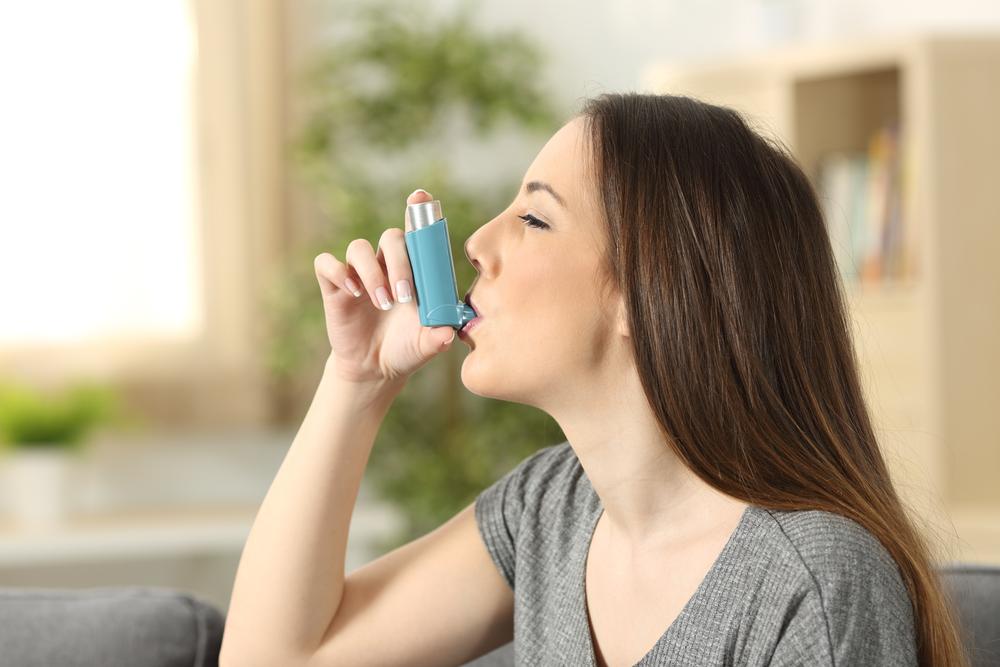
Medications play a vital role in controlling symptoms and preventing exacerbations. These include bronchodilators, which help relax airway muscles; corticosteroids, which reduce airway inflammation; and antibiotics, used during infections. Inhalers are commonly prescribed for quick relief and maintenance therapy. Pulmonary rehabilitation programs, which combine exercise, education, and support, help improve quality of life and enhance lung function.
Severe COPD Treatment and Advanced Care
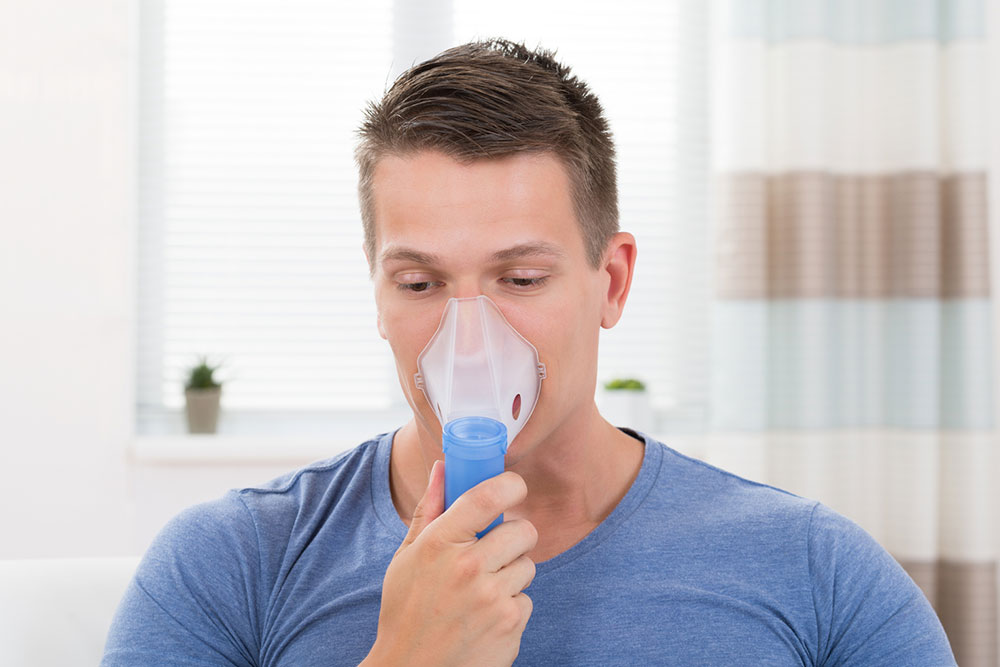
As COPD progresses and symptoms become more severe, supplementary oxygen therapy may be necessary to maintain adequate oxygen levels. Oxygen can be delivered via nasal cannulas or masks, helping reduce hypoxemia and improve overall stamina. Patients with advanced COPD might require hospitalization during exacerbations, where treatments include mechanical ventilation, intensive medications, and careful monitoring.
In some cases, surgical interventions such as lung volume reduction surgery or, rarely, lung transplantation may be considered for suitable candidates. Palliative care options are also available for those with end-stage disease to manage symptoms and improve comfort. The goal of treatment at this stage is to enhance quality of life, manage symptoms effectively, and prevent further complications like pulmonary hypertension or right heart failure.
Living with COPD involves ongoing management and close medical supervision. Regular check-ups, adherence to prescribed medications, vaccinations against influenza and pneumonia, and avoiding respiratory infections are crucial. Patients are also advised to maintain a balanced diet, stay active within their limits, and seek prompt medical attention for any worsening symptoms or exacerbations.
In conclusion, COPD is a complex yet manageable condition when diagnosed early and treated appropriately. Understanding its causes, recognizing early symptoms, and adopting comprehensive management strategies can significantly improve the quality of life for affected individuals. With advances in medicine and increased awareness, many COPD patients are able to lead active, fulfilling lives despite their condition.