Comprehensive Guide to Choosing Between Portable Oxygen Cylinders and Devices for Respiratory Support
This comprehensive guide explores the key differences between portable oxygen cylinders and concentrators, providing essential information to help patients choose the best device for their specific respiratory needs. Learn about their functions, advantages, limitations, and how to select the right option with professional guidance, ensuring effective oxygen therapy and improved quality of life.
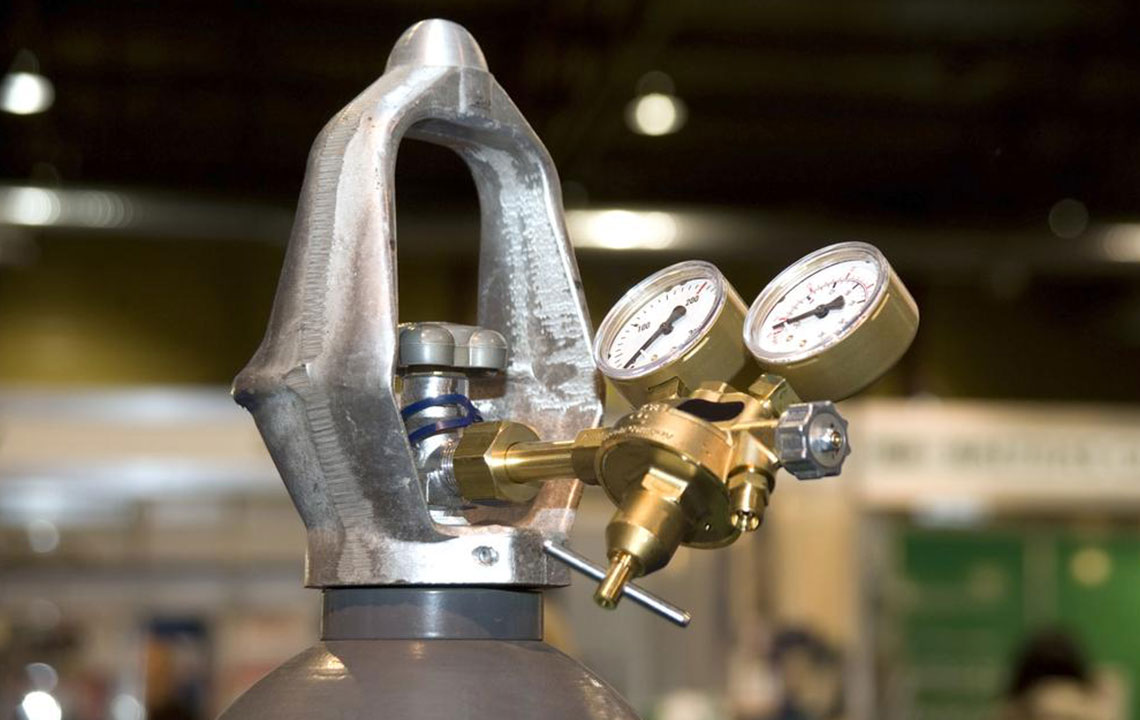

Portable Oxygen Cylinders vs. Portable Oxygen Concentrators: How to Select the Best Option for Your Needs
For individuals suffering from respiratory conditions such as COPD, cystic fibrosis, or certain heart diseases, maintaining adequate oxygen levels is vital for health and quality of life. Portable oxygen solutions like cylinders and concentrators have revolutionized accessibility to oxygen therapy, especially during travel or outdoor activities. Understanding the differences, advantages, and limitations of each device can help patients make informed decisions that optimize their health outcomes and daily comfort.
Understanding the Differences Between Portable Oxygen Cylinders and Concentrators
The primary purpose of both devices is to deliver supplemental oxygen, but they function differently and have distinct features that cater to varying medical needs. Oxygen cylinders typically store compressed or liquid oxygen, offering high purity oxygen (up to 100%) suitable for severe respiratory impairments. They are ideal for emergency use, long-distance travel, or situations where continuous power sources are unavailable. Conversely, portable oxygen concentrators (POCs) draw in ambient air and process it to produce oxygen that is approximately 95% pure. This makes them a suitable option for patients with mild to moderate oxygen requirements, providing a balance of portability and efficient oxygen delivery.
Oxygen cylinders store compressed or liquid oxygen and need to be refilled or replaced regularly. They are usually heavier and bulkier but can provide a steady supply of oxygen in remote areas or during power outages.
Liquid oxygen tanks, while offering a more compact form factor, can be costly, require careful handling, and may need multiple backups for long trips or extended use.
Portable concentrators are powered by electricity, offering a more convenient and environmentally friendly option. They are typically smaller, lighter, and designed for ease of carry, making them suitable for everyday use and travel.
Modern oxygen concentrator models have advanced significantly, with some weighing less than 10 pounds, featuring quiet operation, and enhanced battery life, thus providing greater independence for users.
Large oxygen tanks tend to be stationary, suitable for home use, while portable cylinders and concentrators are designed for mobility and outdoor activities.
Choosing the right device significantly depends on individual health status, lifestyle, and usage context. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before making a decision. A medical professional can evaluate your oxygen needs, device compatibility, and safety considerations to recommend the most effective solution for your respiratory therapy.
Proper assessment ensures optimal oxygen delivery, enhances quality of life, and minimizes potential risks associated with device misuse or incompatibility. Whether opting for a portable oxygen cylinder or a concentrator, expert guidance can help you enjoy greater freedom and comfort in your daily activities.