Comprehensive Approaches to Natural and Medical Pain Management for Better Quality of Life
This comprehensive guide explores both natural and medical approaches to pain management. It covers the latest treatments, natural remedies, and alternative therapies to help individuals find effective relief tailored to their needs, enhancing overall quality of life. Combining these strategies with professional guidance ensures safe and long-lasting pain relief for various conditions.

Comprehensive Approaches to Natural and Medical Pain Management for Better Quality of Life
Pain is a complex and multifaceted sensation that can range from mild discomfort to severe, chronic conditions that significantly impair daily functioning. While occasional pain from injuries or overexertion often resolves quickly with minimal intervention, chronic pain persists over weeks, months, or even years, often resisting standard treatments. This persistent discomfort not only affects physical health but also impacts emotional well-being, relationships, and overall quality of life. Therefore, effective pain management requires a multifaceted approach that combines modern medical techniques with natural and holistic remedies.
Exploring various strategies can help individuals find relief tailored to their specific needs and circumstances. Here we cover a comprehensive spectrum of options, including medical interventions, innovative treatments, natural remedies, and alternative therapies, with an emphasis on safety, effectiveness, and improving daily living.
Medical Options for Pain Relief
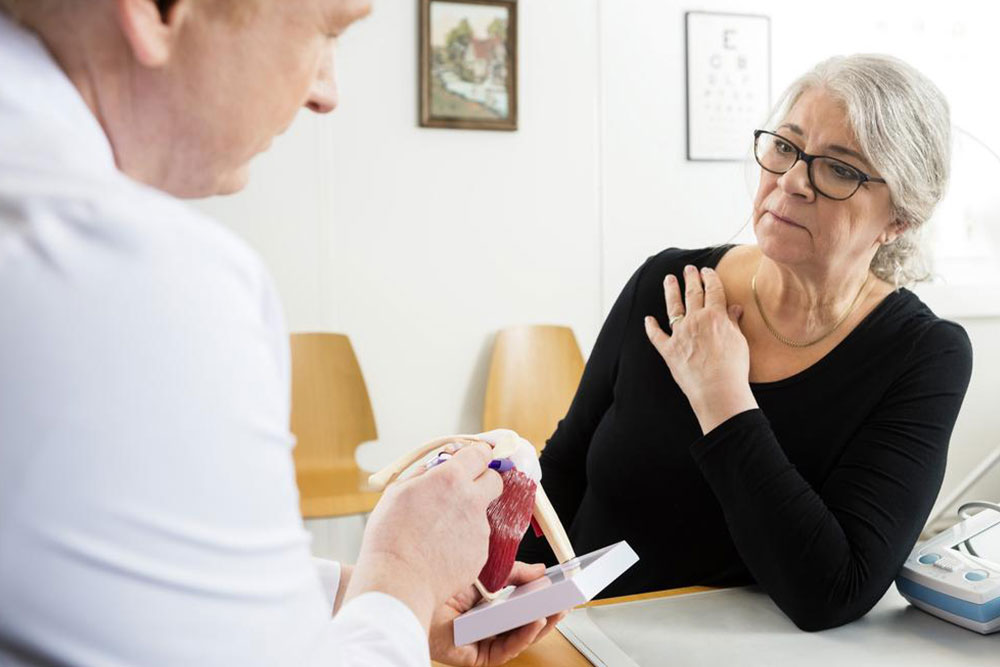
Medical intervention remains a cornerstone of pain management, especially for moderate to severe discomfort. However, these therapies often come with limitations and potential side effects, so they must be used judiciously under professional supervision. Many patients benefit from combining medication with other treatments for optimal results.
Anti-inflammatory Medications
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen, naproxen, and aspirin are widely used for their effectiveness in alleviating pain caused by inflammation, such as arthritis, muscle strains, or post-injury swelling. While they provide quick relief, prolonged use may lead to gastrointestinal issues, kidney damage, or cardiovascular risks. Therefore, it’s essential to consult healthcare providers to determine appropriate dosages and duration of use.
Antidepressants
Certain classes of antidepressants, notably tricyclic antidepressants and selective serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), have demonstrated efficacy in managing chronic neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia. These medications modulate pain signaling pathways in the nervous system but require careful dosing and monitoring to minimize side effects such as dry mouth, drowsiness, or cardiovascular changes.
Anti-seizure Drugs
Medications like gabapentin and pregabalin are primarily prescribed for nerve pain related to conditions like diabetic neuropathy or post-herpetic neuralgia. They work by calming overactive nerve signals, providing substantial relief. Usage should always be overseen by a healthcare professional to avoid adverse effects and interactions with other drugs.
Muscle Relaxants
Often prescribed during episodes of muscle spasms or acute strains, muscle relaxants such as cyclobenzaprine or methocarbamol can alleviate discomfort stemming from muscle injuries. They are typically used short-term due to their sedative effects and potential dependency risks.
Innovative and Advanced Medical Treatments
Progress in medical technology has led to new, minimally invasive options that target pain at its source, often offering longer-lasting relief and fewer side effects.
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)
RFA uses heat generated by radio waves to disrupt nerve activity, effectively blocking pain signals. It is particularly useful for chronic back, joint, and nerve pain, providing relief that can last for up to a year or longer. The procedure is minimally invasive, performed under local anesthesia, and suitable for patients who have not responded well to conventional therapies.
Pain Injections
Localized injections, such as nerve blocks, epidural steroid injections, or joint injections, deliver targeted medication directly to painful areas. These injections can provide rapid relief during flare-ups or persistent pain episodes, helping to improve mobility and reduce reliance on systemic medications.
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS)
TENS therapy involves delivering low-voltage electrical pulses through skin electrodes to interfere with pain signals. It’s a non-invasive, drug-free method often used in managing chronic low back pain, osteoarthritis, and sports injuries, with minimal side effects.
Natural and Holistic Remedies for Pain Management
Complementing medical treatments, natural remedies and lifestyle adjustments can significantly help in alleviating mild to moderate pain. These approaches emphasize gentle, non-invasive methods that promote healing and relaxation.
Turmeric and Ginger Tea
Both turmeric and ginger possess anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce joint inflammation and pain associated with arthritis. Incorporating these into your diet or drinking teas infused with these spices can provide natural pain relief. Turmeric contains curcumin, a potent compound, while ginger contains bioactive compounds that inhibit pain pathways.
Epsom Salt Baths
Soaking in warm water enriched with Epsom salts allows magnesium absorption through the skin, which can reduce muscle tension, ease stiffness, and decrease inflammation. This simple, soothing remedy is especially popular among athletes and those suffering from chronic pain conditions.
Fomentation Techniques
Applying hot or cold packs to painful areas offers immediate, non-invasive relief. Cold packs help reduce swelling and numb sharp pains, while heat packs promote blood flow, relax muscles, and soothe stiffness. Alternating between hot and cold can maximize benefits for complex or fluctuating pain.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
Many individuals find relief through holistic practices that focus on mind-body connections and stress reduction. These therapies help manage not only physical pain but also associated emotional distress.
Massage Therapy
Gentle massage techniques, including deep tissue and Swedish massage, improve circulation, relax tense muscles, and enhance mobility. Regular sessions can help reduce pain caused by muscular knots, tension, or inflammation.
Counseling and Mindfulness
Psychological approaches, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), help deal with the emotional aspects of chronic pain. Mindfulness meditation and breathing exercises can also reduce stress levels, which often exacerbate pain perceptions.
By integrating these diverse strategies—medical, natural, and alternative—individuals can develop a personalized and effective pain management plan. Early intervention, proper medical supervision, and lifestyle adjustments are key to maintaining a good quality of life despite chronic discomfort. Always consult healthcare professionals before starting new treatments or combining multiple approaches to ensure safety and effectiveness.