Comprehensive Guide to Managing Asthma: Treatment Options and Lifestyle Tips
This comprehensive guide offers in-depth insights into asthma management, covering treatment options, medication types, lifestyle tips, and future therapies. Effective control involves medication adherence, trigger avoidance, and monitoring symptoms, empowering patients to manage this chronic condition successfully and improve their quality of life.
Comprehensive Guide to Managing Asthma: Treatment Options and Lifestyle Tips
Asthma remains one of the most common chronic respiratory conditions affecting millions of individuals worldwide, spanning all age groups from young children to seniors. This condition involves persistent inflammation and narrowing of the airways, which significantly impairs breathing and can lead to life-altering symptoms if not properly managed. Understanding asthma's underlying mechanisms, recognizing its symptoms early, and exploring various treatment options are crucial for individuals living with this condition. While there is currently no permanent cure for asthma, advancements in medications and management strategies have vastly improved the quality of life for many sufferers.
Asthma manifests through a range of symptoms, including shortness of breath, wheezing, persistent coughing, tightness in the chest, and sleep disturbances. These symptoms can vary in frequency and severity, often triggered by specific environmental or physiological factors. The two predominant types of asthma are allergic (atopic) asthma, which is triggered by airborne allergens like pollen, dust mites, and pet dander, and non-allergic asthma, which may be initiated by factors such as cold air, exercise, stress, respiratory infections, or exposure to irritants.
Although a definitive cure remains elusive, effective management revolves around controlling symptoms, preventing attacks, and minimizing exposure to triggers. This involves a combination of medication regimen adherence, lifestyle adjustments, and awareness of personal triggers. Adequate knowledge and proactive management are essential for maintaining normal activities and preventing severe asthma exacerbations.
Recognizing Asthma Symptoms and When to Seek Medical Help
Early recognition of asthma symptoms can make a significant difference in managing the condition. Symptoms such as episodes of wheezing, difficulty breathing, especially during physical activity or at night, persistent cough, and chest tightness should prompt immediate consultation with a healthcare provider. Severe symptoms like inability to speak in full sentences, bluish lips or face, and extreme shortness of breath require urgent medical attention as they indicate a potential life-threatening asthma attack.
Key Medications and Treatment Strategies for Asthma
Managing asthma effectively involves a tailored approach, combining various medications to control ongoing symptoms and provide quick relief during exacerbations. Here's an overview of the most common treatment options:
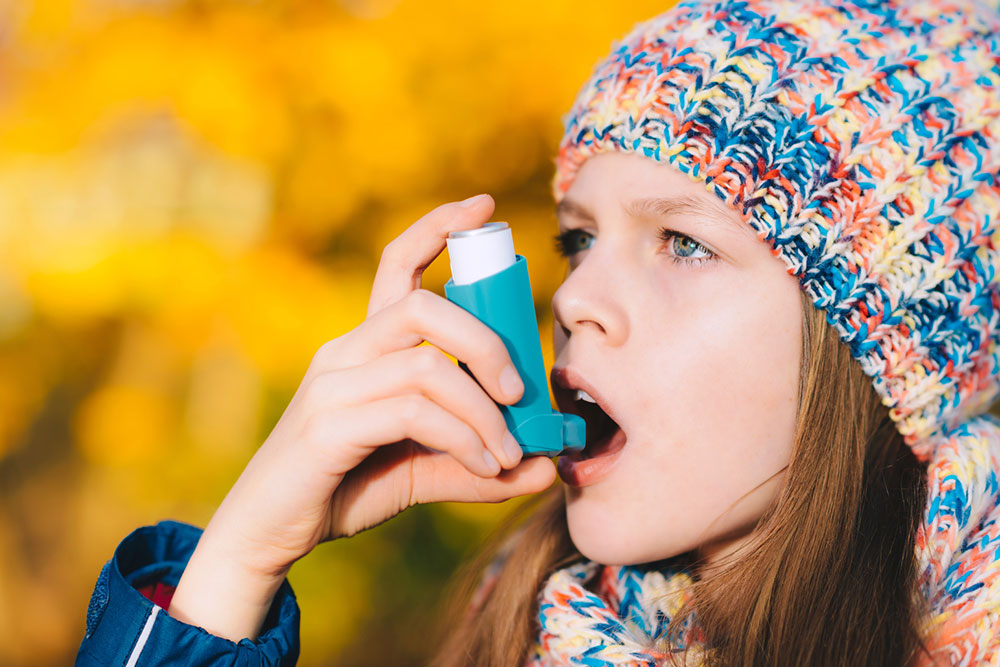
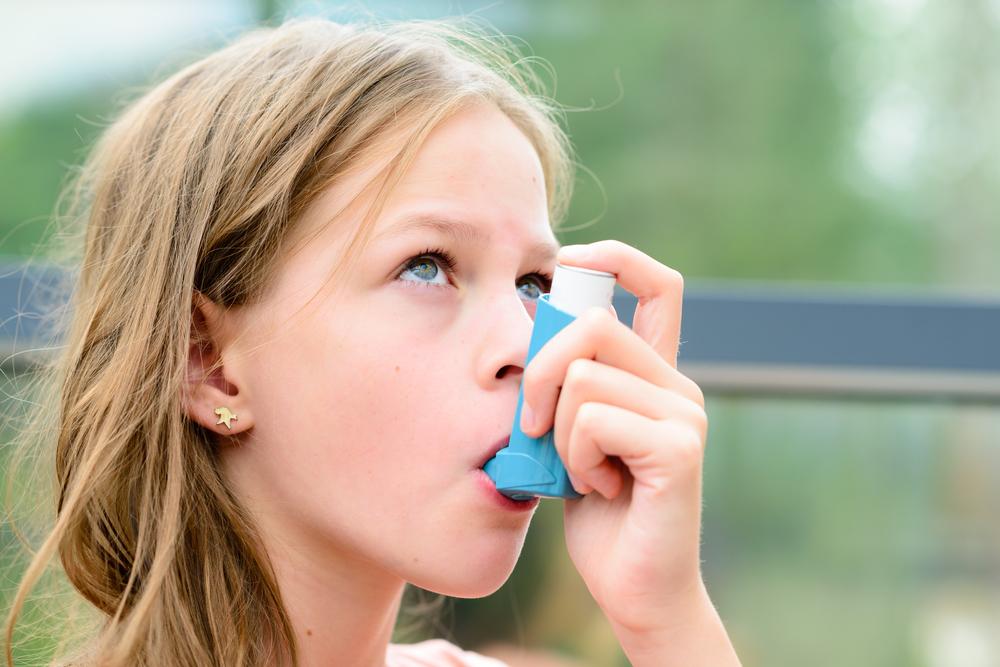
Inhalers
Inhalers are a cornerstone in asthma management. They deliver medication directly to the lungs, providing rapid symptom relief or control. There are two main types: metered-dose inhalers (MDIs) and dry powder inhalers (DPIs). MDIs release a specific dose of medication via aerosol, while DPIs deliver medication in powder form, activated by inhalation. Depending on individual needs, inhalers can contain single medications or combination therapies, such as corticosteroids and bronchodilators.
Anti-inflammatory Drugs and Corticosteroids
These medications are fundamental in reducing airway inflammation, swelling, and mucus secretion, thereby preventing the frequency and severity of attacks. They are available as inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) for daily use and systemic steroids for more severe exacerbations. Consistent use of inhaled corticosteroids has been shown to significantly improve lung function and decrease hospitalizations.
Oral Corticosteroids
When inhaled medications are insufficient, doctors may prescribe oral corticosteroids, such as prednisone, for short-term flare-up management or long-term control in severe cases. While effective, these medications require careful monitoring due to potential side effects like weight gain, osteoporosis, and blood sugar elevation.
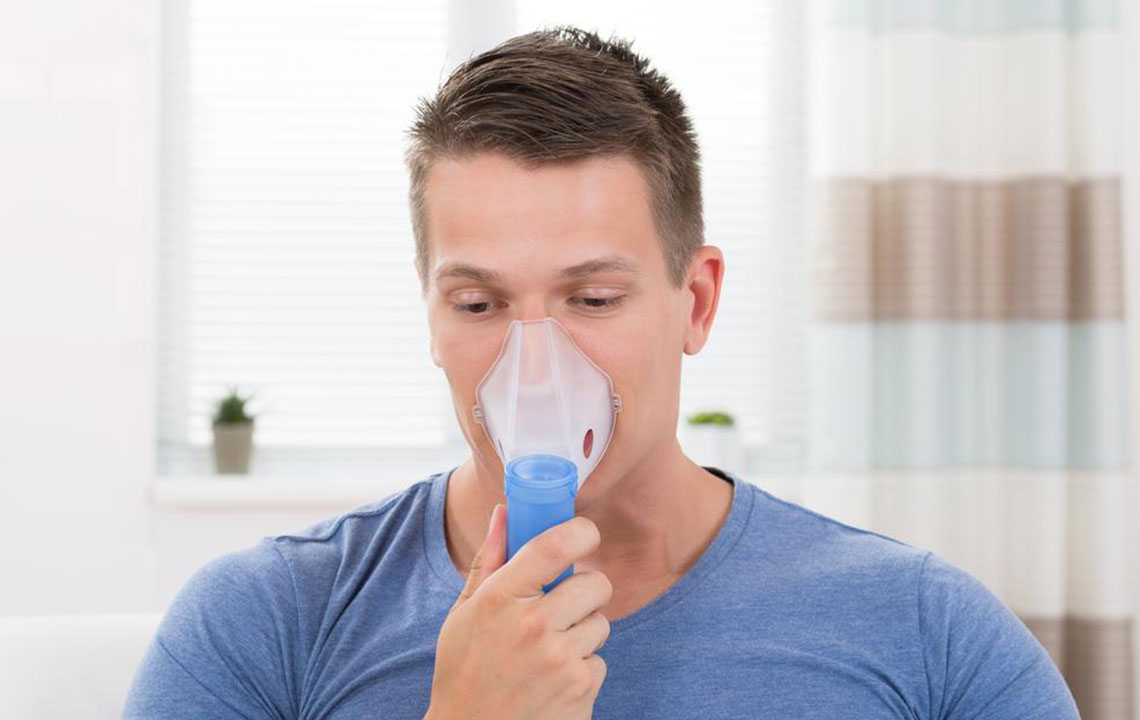
Nebulizers
Nebulizers convert liquid medication into fine aerosols that can be inhaled comfortably, making them especially useful for children, elderly patients, or those unable to use inhalers effectively. They are versatile and can deliver various medications, including bronchodilators and steroids, in a single session.
Beta-agonists
These medications are rapid-acting bronchodilators that relax airway muscles, providing quick relief from acute symptoms. Short-acting beta-agonists (SABAs) like albuterol are commonly prescribed for rescue therapy. Long-acting beta-agonists (LABAs) are used for ongoing control but should be combined with anti-inflammatory drugs for safety and effectiveness.
Immunotherapy
More commonly known as allergy shots, immunotherapy is aimed at desensitizing the immune response to specific allergens. Over time, this treatment can reduce allergy symptoms and decrease reliance on medication. It is particularly beneficial for patients with allergic asthma and can lead to long-term improvements in disease management.
Additional Lifestyle and Environmental Management Tips
Beyond medication, lifestyle modifications play a vital role in asthma management. Avoiding known triggers such as cigarette smoke, strong odors, pollution, and cold weather can substantially decrease the frequency of attacks. Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity tailored to one's capacity, and managing stress through relaxation techniques also contribute to better control.
Monitoring lung function through peak flow meters helps detect early signs of worsening asthma, allowing preemptive adjustments to medication. Patients should develop an individualized asthma action plan with their healthcare provider to navigate daily management and respond effectively during exacerbations.
Advances and Future Perspectives in Asthma Treatment
In recent years, biotechnological advances have led to the development of biologic therapies targeting specific pathways involved in asthma. Monoclonal antibodies such as omalizumab, mepolizumab, and benralizumab have shown promising results, especially for severe eosinophilic and allergic asthma. These therapies offer targeted relief and reduce the need for systemic steroids, minimizing side effects.
Research continues into personalized medicine approaches, aiming to tailor treatments based on genetic, phenotypic, and environmental factors. This evolving landscape promises more effective, safer, and more convenient options for asthma sufferers in the future.
Living with asthma requires commitment, awareness, and proactive management. With the right combination of medications, lifestyle modifications, and medical guidance, individuals can lead active, fulfilling lives despite the respiratory challenges posed by asthma.