Comprehensive Guide to Managing Pulmonary Fibrosis: Essential Dietary Strategies and Treatment Options
This detailed guide offers comprehensive strategies for managing pulmonary fibrosis, emphasizing the importance of diet, key medications, and lifestyle modifications. Learn about beneficial foods that support lung health, medications like Esbriet® and OFEV®, and practical tips to improve quality of life. A holistic approach combining nutrition, drugs, and lifestyle changes is crucial for slowing disease progression and alleviating symptoms in pulmonary fibrosis patients.

Comprehensive Guide to Managing Pulmonary Fibrosis: Essential Dietary Strategies and Treatment Options
Pulmonary fibrosis is a serious and often progressive lung disease characterized by the abnormal formation of scar tissue within the lung parenchyma. This condition can significantly impair respiratory function, leading to decreased oxygen exchange, difficulty breathing, and a reduced quality of life. While there is currently no definitive cure for pulmonary fibrosis, early diagnosis, proper management, including pharmacological treatments and lifestyle modifications, can slow disease progression and alleviate symptoms. A vital component of managing this condition involves adopting specific dietary practices that can support lung health and reduce inflammation.
Symptoms of pulmonary fibrosis commonly include persistent dry cough, progressive shortness of breath, fatigue, chest discomfort, and unintended weight loss. Patients often find their daily activities becoming more challenging as their lung capacity diminishes. Because of the complex nature of this disease, a multidisciplinary approach that combines medication, nutritional interventions, and lifestyle adjustments is crucial for better disease management.
This comprehensive guide explores vital dietary strategies, outlining foods that can support lung function and reduce inflammation, as well as those that should be avoided. Additionally, the article reviews key pharmacological options, such as Esbriet® (pirfenidone) and OFEV® (nintedanib), which are prescribed to manage pulmonary fibrosis effectively. Recognizing the importance of holistic care, this article aims to provide patients with practical information to improve their health outcomes and overall quality of life.
Key Dietary Guidelines for Pulmonary Fibrosis Management
Proper nutrition plays an integral role in managing pulmonary fibrosis. A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can help mitigate symptoms and potentially slow disease progression. Conversely, consuming certain foods may exacerbate symptoms or contribute to complications, underscoring the importance of dietary awareness in disease management.
Beneficial Foods to Support Lung Health
Consuming a balanced diet that emphasizes nutrient-dense foods can greatly benefit individuals with pulmonary fibrosis. Here are some of the most recommended food categories:
Whole Grains: Incorporating whole grains such as oats, quinoa, brown rice, and whole wheat bread provides high fiber content alongside essential vitamins and minerals. These foods are known to reduce systemic inflammation, lower cholesterol levels, and improve overall cardiovascular health, indirectly supporting lung function. Including these in daily meals can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce the burden on respiratory muscles.
Lean Proteins
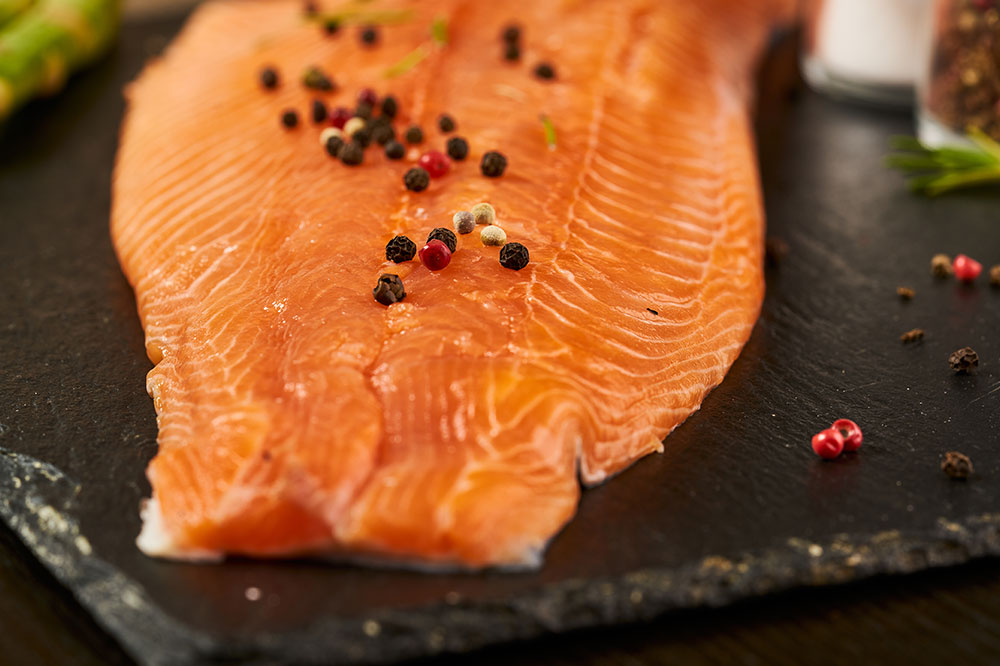
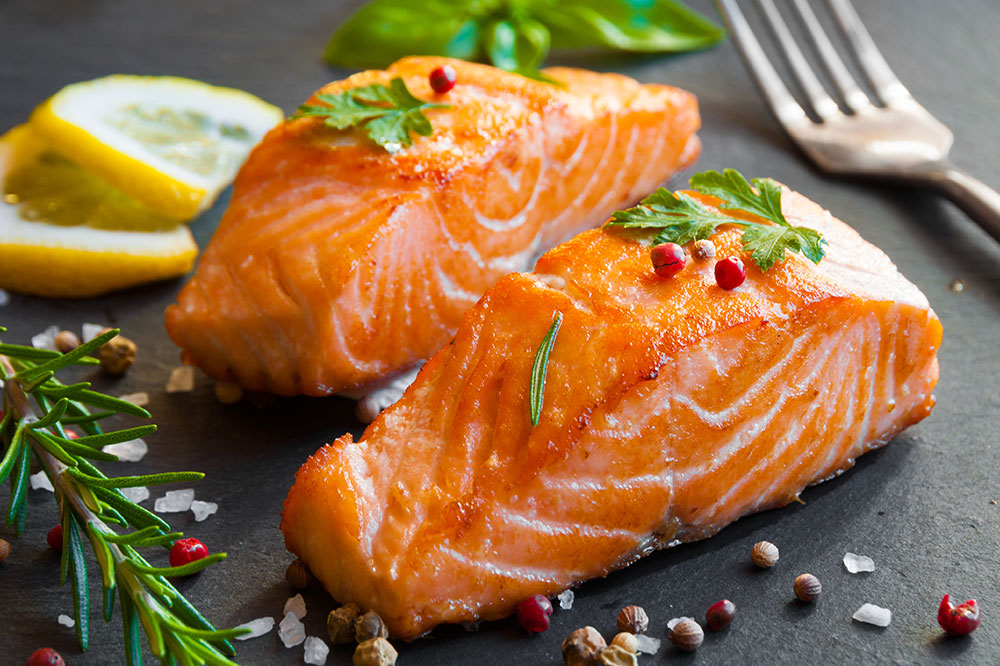
Proteins are crucial for repairing tissues, strengthening muscles—including those involved in respiration—and maintaining overall body strength. Favor lean protein sources like skinless poultry, eggs, and fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, or sardines, which are also rich in omega-3 fatty acids known for their anti-inflammatory properties. Plant-based proteins such as beans, peas, lentils, nuts, seeds, and tofu are excellent options for vegetarians and can add diversity to a lung-friendly diet. Proper protein intake supports respiratory muscle strength, making breathing easier and more efficient.
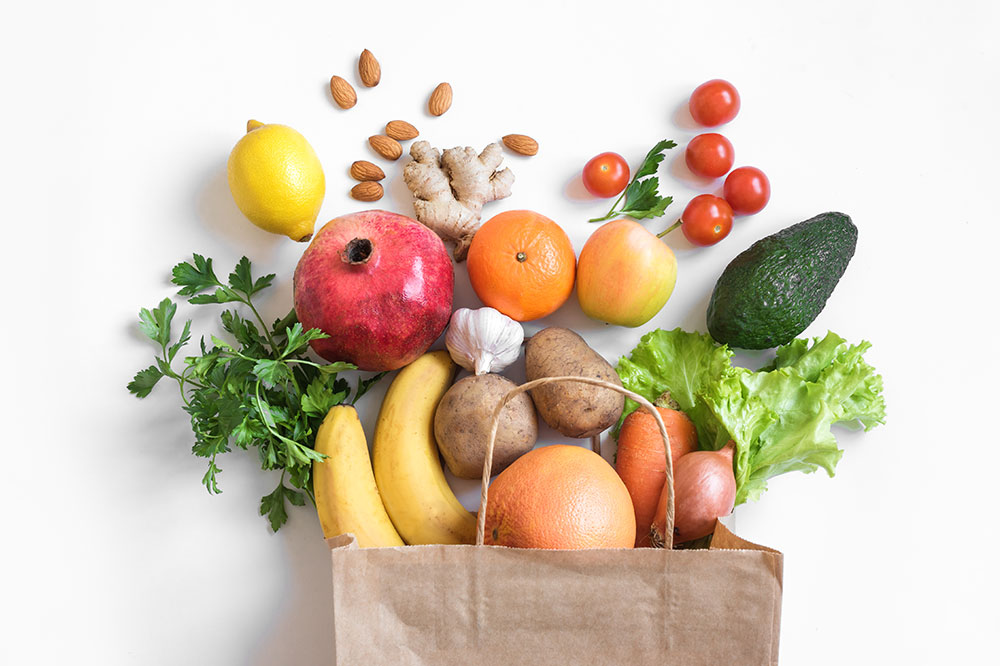
Fruits and Vegetables
Fruits and vegetables are vital for their high antioxidant, vitamin, and mineral content. For pulmonary fibrosis patients, including a variety of colorful produce can help combat oxidative stress and inflammation in lung tissues. Carrots, celery, spinach, kale, and other leafy greens provide essential nutrients like vitamin C, vitamin A, and magnesium—crucial for lung tissue repair and immune support. Berries, kiwifruit, pineapple, and citrus fruits supply antioxidants that neutralize harmful free radicals, potentially reducing lung tissue damage and inflammation. High fiber fruits and vegetables also aid digestion and overall well-being, contributing to improved energy levels.
Foods to Limit or Avoid
While focusing on beneficial foods, patients should also be aware of items that could worsen symptoms or contribute to disease progression:
Fried Foods: Foods such as French fries, fried chicken, onion rings, and chips are high in unhealthy fats. These fats can irritate the throat, provoke coughs, and lead to bloating, which hampers breathing efforts. Moreover, fried foods can contribute to weight gain and cardiovascular issues, placing added strain on compromised lungs.
Cured and Preserved Meats: Processed meats like bacon, hot dogs, hams, and salami contain nitrates and preservatives that may promote inflammation and damage lung tissue over time. These foods are often high in sodium, which can lead to fluid retention and exacerbate breathing difficulties.
Critical Medications for Pulmonary Fibrosis
Alongside nutritional adjustments, pharmacological treatments are essential in controlling pulmonary fibrosis. Two notable medications approved for treatment include Esbriet® (pirfenidone) and OFEV® (nintedanib), which have shown significant benefits in slowing disease progression and improving patients' quality of life.
Esbriet® (Pirfenidone): Esbriet® is an antifibrotic agent prescribed primarily for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). It works by reducing the accumulation of scars in the lung tissue, thereby helping to preserve lung function. Patients on Esbriet® often experience a slower decline in respiratory capacity. The medication is usually taken orally in capsule form, with dosage adjustments based on individual tolerability.
OFEV® (Nintedanib): Approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), OFEV® is another antifibrotic medication that targets the pathways involved in fibroblast activity and scar formation. It is typically administered twice daily, as a pill, and has been shown to slow the decline of lung function in patients with pulmonary fibrosis. Regular monitoring for side effects, such as gastrointestinal discomfort and liver enzyme elevations, is necessary during therapy.
The Importance of Holistic Management
Combining medication with proper nutrition, physical activity, smoking cessation, and regular medical follow-up forms the cornerstone of effective pulmonary fibrosis management. Patients are encouraged to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop an individualized plan tailored to their condition and lifestyle. Support groups and counseling can also be beneficial, helping patients cope with the emotional and physical challenges posed by the disease.
In conclusion, while pulmonary fibrosis remains a challenging disease with no definitive cure, a proactive approach involving the right nutrition and medications can significantly improve patient outcomes. Understanding which foods support lung health and which to avoid empowers patients to make better choices daily. Medical treatments like Esbriet® and OFEV® play a vital role in slowing disease progression when used appropriately. With comprehensive management, patients can achieve improved quality of life and potentially slow the advancement of this debilitating condition.