Comprehensive Strategies for Managing Psoriatic Arthritis: Effective Treatments and Lifestyle Tips
This detailed article explores effective treatment options for psoriatic arthritis, including lifestyle changes, medications, and physiotherapy. It emphasizes early diagnosis, comprehensive management strategies, and the latest advancements in therapy to help patients improve joint health and skin condition, ultimately enhancing their quality of life.
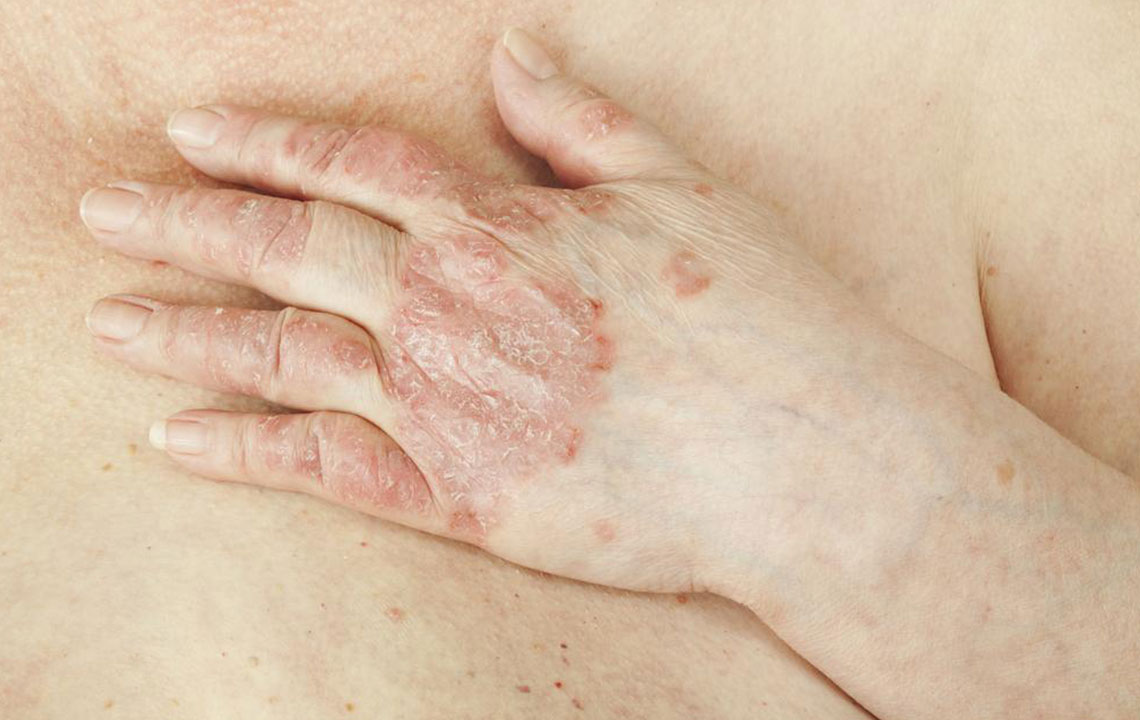
Understanding and Managing Psoriatic Arthritis: A Guide to Treatment and Lifestyle Adjustments
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a chronic, autoimmune condition that affects a significant number of individuals worldwide. Characterized by inflammation of the joints and the skin, particularly in individuals already suffering from psoriasis, this condition can substantially impact quality of life if not properly managed. The symptoms often include persistent joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and skin lesions that are typically dark, flaky, and itchy, resembling rash-like patches.
Understanding the complexities of psoriatic arthritis and implementing a comprehensive management plan is essential for reducing symptoms, preventing joint damage, and improving overall health. This article delves into the various treatment modalities available—ranging from lifestyle modifications and natural remedies to pharmacological interventions—aimed at providing effective relief and promoting long-term well-being.
What Is Psoriatic Arthritis?
Psoriatic arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that results from the immune system mistakenly attacking healthy joint tissues and skin. It most commonly affects individuals with a history of psoriasis, a skin condition characterized by red, scaly patches. The exact cause of PsA remains unknown, but genetic and environmental factors are believed to contribute to the disease process.
This condition can appear at any age but is most prevalent among adults between 30 and 50 years old. The progression of PsA varies; some experience mild symptoms with periods of remission, while others face more aggressive joint deterioration. Early diagnosis and intervention are critical to managing symptoms effectively and preventing irreversible joint damage.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Common symptoms of psoriatic arthritis include joint swelling, tenderness, stiffness especially in the mornings, and reduced range of motion. Skin manifestations are also prominent, with patches that are darker, flaky, and itchy. Nail changes, such as pitting or separation from the nail bed, are frequently observed.
Diagnosing PsA involves a thorough clinical evaluation, medical history review, blood tests to rule out other forms of arthritis, and imaging studies like X-rays or MRI scans to assess joint damage. Early diagnosis is crucial as it allows for timely intervention, which can significantly improve quality of life.
Effective Treatment Strategies for Psoriatic Arthritis
Managing psoriatic arthritis requires a multifaceted approach tailored to the severity of the disease, symptom control, and overall health status. Treatment options generally include lifestyle modifications, medication, and physical therapy, often used in combination for optimal results.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Regular Exercise : Engaging in low-impact activities such as swimming, walking, or yoga helps improve joint flexibility, reduce stiffness, and strengthen muscles supporting the affected joints. Regular exercise also benefits mental health and overall well-being.
Cold and Warm Therapy : Applying cold packs can alleviate swelling and numb area pain, while warm compresses help relax stiff muscles and joints. Alternating between cold and heat can be particularly soothing.
Stress Management and Rest : Stress can trigger or worsen flare-ups. Practices like meditation, deep breathing, and ensuring adequate sleep are essential components of managing PsA. Prioritizing rest allows the body to recover and reduces inflammation.
Skin Care : Using moisturizers and topical therapies can alleviate skin symptoms, reduce itching, and prevent skin cracks. Avoiding skin irritants and protecting skin from harsh environments also helps.
Medical Treatments and Pharmacotherapy
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) : Drugs such as ibuprofen or naproxen are often the first line of defense to reduce pain and inflammation.
Corticosteroids : For severe flare-ups, corticosteroid injections or oral steroids can provide rapid relief but are used cautiously due to potential side effects.
Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) : Medications like methotrexate, sulfasalazine, and leflunomide can slow disease progression and prevent joint destruction.
Biologic Treatments : These advanced therapies, including TNF-alpha inhibitors (like etanercept and adalimumab), IL-17 inhibitors, and IL-12/23 inhibitors, target specific immune pathways to control inflammation and skin symptoms effectively. Biologics are often prescribed for moderate to severe cases.
Targeted Systemic Agents : Drugs such as Cyclosporine can be used selectively to suppress the immune response, particularly in cases where other treatments are ineffective.
Role of Physiotherapy and Occupational Therapy
Physiotherapy plays a vital role in maintaining joint function, flexibility, and muscle strength. Tailored exercises designed by physiotherapists can help reduce stiffness and improve mobility. Occupational therapy can also assist individuals in adapting daily activities and workplace ergonomics to minimize joint stress.
When to Seek Medical Advice
If you notice persistent joint pain, swelling, skin changes, or difficulty moving, consult healthcare professionals promptly. Early intervention prevents complications and enhances treatment outcomes. Regular follow-ups and monitoring are essential for adjusting therapies as needed.
Emerging Therapies and Future Outlook
Research into psoriatic arthritis continues to evolve, with promising developments in biologic and targeted therapies. New drugs aiming to inhibit specific immune pathways are under clinical trials, offering hope for more effective and personalized treatment options in the near future.
This comprehensive overview highlights various strategies to manage psoriatic arthritis effectively. Combining lifestyle modifications, timely medication, and professional guidance can significantly improve symptom control and quality of life. Early diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan remain the cornerstone of successful disease management.