Understanding Nighttime Leg Cramps: Causes, Prevention, and Remedies
Nighttime leg cramps are involuntary muscle spasms that disrupt sleep and can be caused by dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, aging, pregnancy, or overexertion. Preventive measures such as hydration, proper nutrition, stretching exercises, and medical consultation are effective in managing the condition. Natural remedies like vitamin supplements may help alleviate severe cramps. Understanding the triggers and adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the frequency and intensity of these painful spasms, improving sleep quality and overall wellbeing.
Nighttime leg cramps are a common condition that can significantly disrupt sleep and overall quality of life. These involuntary muscle contractions typically occur in the calves, but can also affect the thighs and feet. Many people experience sudden, intense pain that can last from a few seconds to several minutes, often waking them from restful sleep. While the exact cause of these cramps is not always clear, several factors contribute to their occurrence. Understanding these causes, recognizing the symptoms, and adopting effective preventive measures can help reduce the frequency and severity of nighttime leg cramps.
Leg cramps at night are especially prevalent among middle-aged adults, pregnant women, individuals who consume excessive alcohol, and those suffering from musculoskeletal disorders such as peripheral neuropathy or lumbar spinal issues. Overexertion during physical activity, inadequate stretching, dehydration, and prolonged sitting or immobility are some of the common triggers. These spasms are often characterized by a sudden, sharp pain, accompanied by the feeling of muscle tightness or knotting. They can last from a few seconds to several minutes, sometimes leaving the muscles tender and sore afterward.
Several physiological and lifestyle factors contribute to nocturnal leg cramps. Dehydration is a significant factor, as it results in an imbalance of electrolytes — essential minerals like potassium, magnesium, and calcium — which are critical for proper muscle function. An electrolyte imbalance can cause muscles to become hyperexcitable, leading to spasms. Additionally, certain medications such as diuretics and statins have been linked to increased risk. Nutritional deficiencies, especially low levels of magnesium and potassium, are also common contributors.
Age-related changes can affect muscle and nerve function, making older adults more susceptible to cramps. During pregnancy, hormonal fluctuations and increased blood volume can impact electrolyte balance, heightening the risk for cramps, especially in the second and third trimesters. Athletes or individuals engaged in strenuous physical activity might experience cramps due to muscle fatigue or overuse. Similarly, sitting for long periods or standing in one position can lead to poor circulation and muscle fatigue, triggering spasms during periods of rest.
Recognizable symptoms of night leg cramps include sudden, intense pain in the calf muscles or feet, often felt in the late evening or after waking up. These cramps can cause the muscle to become visibly contracted or hardened. Sometimes, the muscle may remain tight for several minutes, and attempting to stretch or massage the muscle often provides relief. After a spasm, the muscles may feel tender or sore, and in some cases, recurrent cramps may develop if underlying issues are not addressed.
Preventive strategies are crucial for managing and reducing the occurrence of nighttime leg cramps. Staying well-hydrated throughout the day is essential, especially in hot weather or during physical activity. Incorporating a healthy diet rich in magnesium, potassium, and calcium can help maintain electrolyte balance. Foods high in magnesium include nuts, seeds, whole grains, and leafy green vegetables. Potassium-rich foods include bananas, oranges, potatoes, and tomatoes. Calcium can be found in dairy products, fortified foods, and leafy greens.
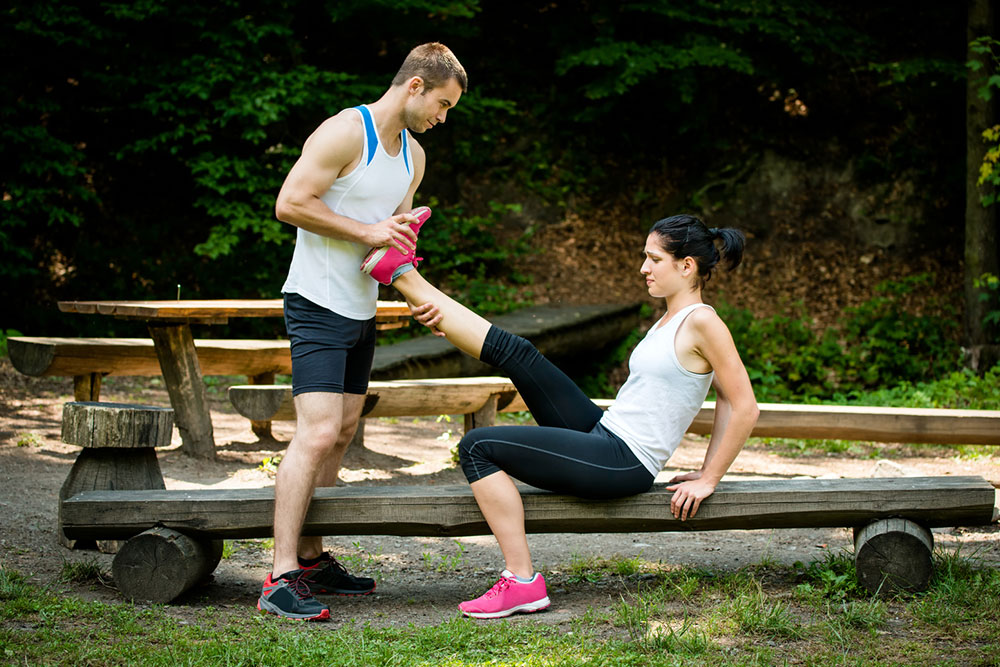
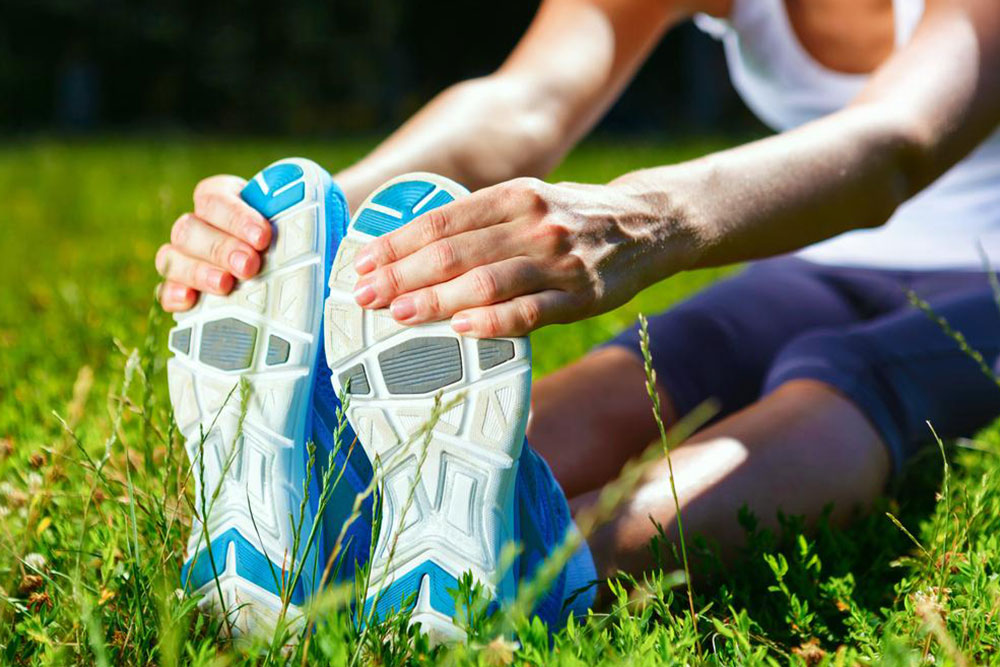
Engaging in regular stretching exercises before bedtime can effectively prevent cramps. Gentle stretches targeting the calf muscles, such as heel drops or toe stretches, help relax the muscles and improve flexibility. Massaging the affected muscles and applying warm compresses can also alleviate cramping episodes. Ensuring proper footwear that supports the feet and avoids tight or restrictive shoes can prevent muscle strain.
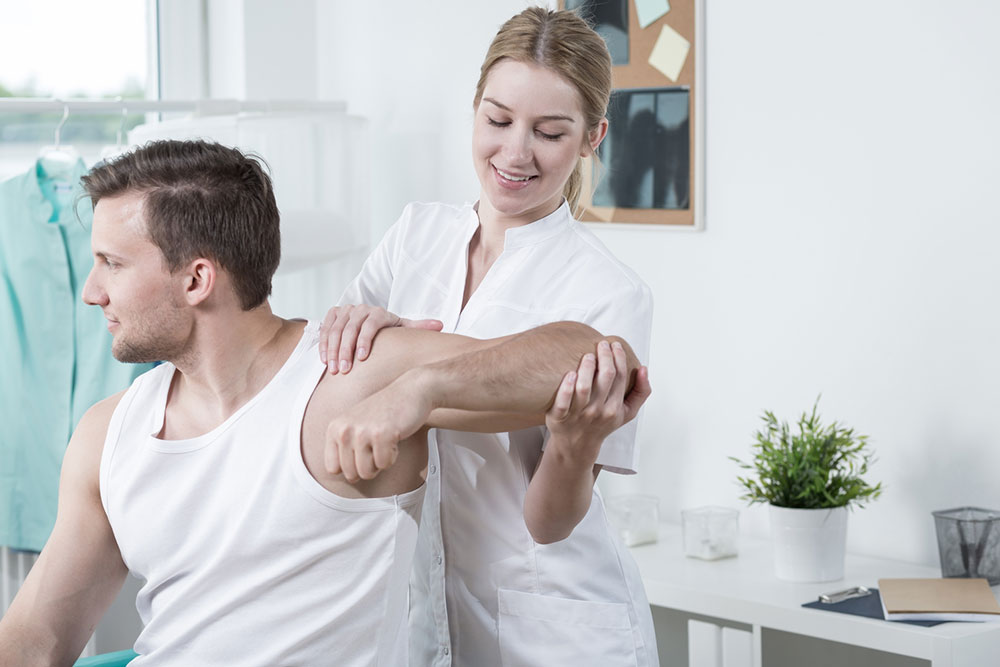
For those experiencing persistent cramps, medical consultation is advisable. A healthcare professional might recommend blood tests to check electrolyte levels or suggest supplements like magnesium or potassium if deficiencies are identified. In some cases, medication might be prescribed to reduce muscle spasms, especially if cramps are severe and interfere significantly with sleep. However, lifestyle modifications remain the first line of defense.
Additional natural remedies include supplementing with Vitamin E, which has been suggested to improve muscle function and reduce cramps, and Vitamin B complex to support nerve health. Maintaining a balanced intake of these vitamins can contribute to muscle health and overall wellbeing. For recurrent or particularly painful cramps, physical therapy or specific neuromuscular treatments may be beneficial. Habitual adherence to good hydration, diet, stretching routines, and medical guidance can significantly improve sleep quality and reduce episodes of leg cramps at night.