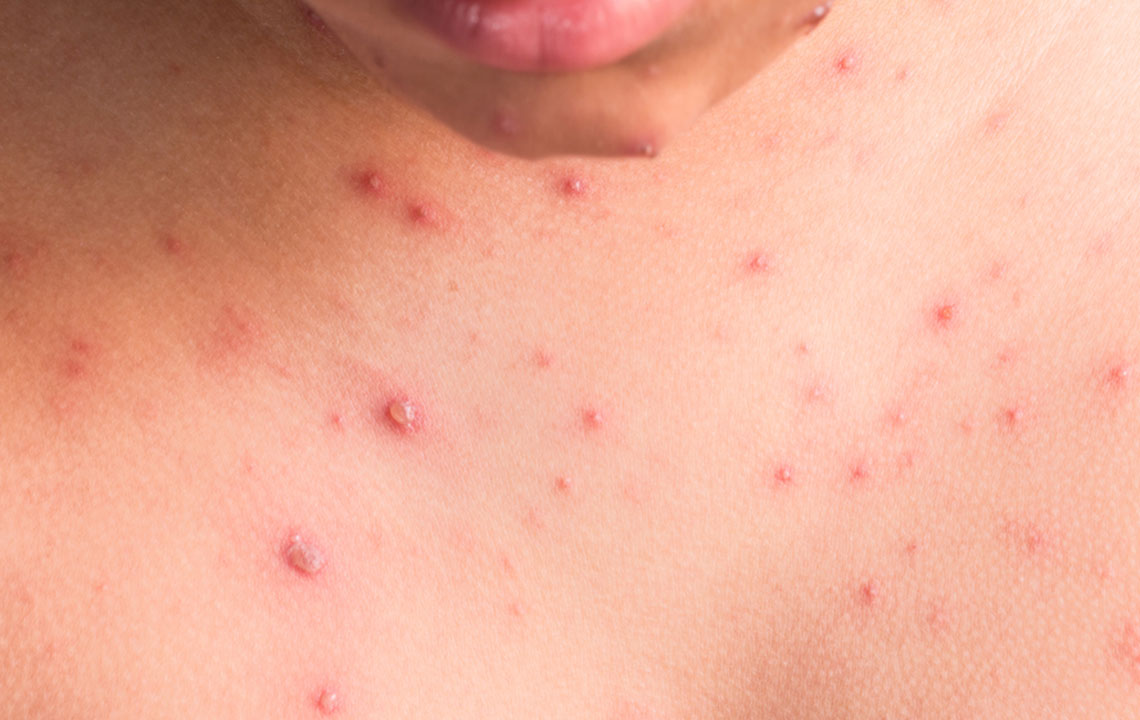
Comprehensive Guide to Preventing Early Lyme Disease Symptoms and Protecting Your Health
This comprehensive guide offers detailed strategies to prevent early Lyme disease symptoms. From proper outdoor attire and insect repellent use to environmental management and thorough tick checks, it emphasizes proactive measures to safeguard your health against tick-borne infections. Implementing these tips can greatly reduce your risk of Lyme disease and ensure prompt action if bitten, promoting overall well-being and disease prevention.
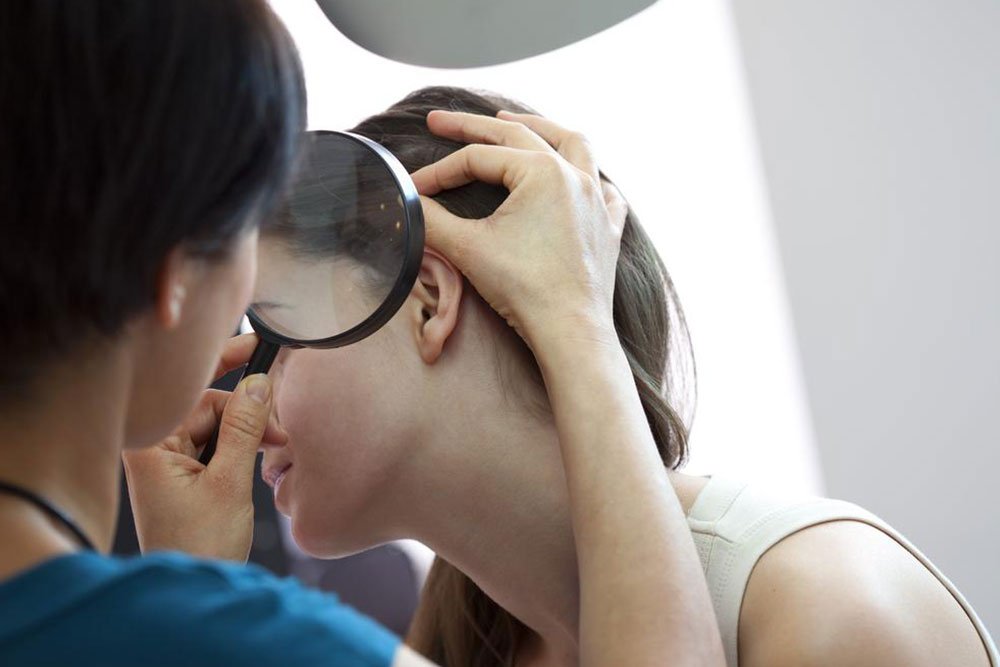
Comprehensive Strategies to Prevent Early Lyme Disease Symptoms and Safeguard Your Well-being
Lyme disease, caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi transmitted through tick bites, can lead to serious health complications if not identified and treated early. Prevention is the most effective approach to avoid the onset of symptoms and long-term health issues associated with this disease. This detailed guide provides extensive tips, practical advice, and proactive measures to protect yourself, your family, and your pets from early signs of Lyme disease.
Understanding how to prevent tick bites and eliminate their habitats is crucial. The majority of tick encounters happen in wooded, grassy, or brushy areas where ticks thrive. By adjusting your outdoor activities and implementing preventive measures, you can significantly reduce your risk of contracting Lyme disease.
Dress strategically when outdoors: When venturing into wooded or grassy environments, it's vital to wear protective clothing. Long-sleeved shirts, full-length pants tucked into socks, sturdy closed-toe shoes, and wide-brimmed hats can serve as effective barriers against tick bites. Use gloves if necessary, especially when handling outdoor objects or pets. Additionally, keep pets on leashes and prevent them from wandering into high-risk zones, as they can carry ticks into your home.
Walking through dense bushes and tall grass should be avoided whenever possible. Stick to well-maintained trails or open areas with sparse vegetation to minimize exposure to ticks. Wearing protective clothing is vital, but it's also recommended to use insect repellents as a supplementary defense.
Effective use of insect repellents: Apply repellents containing at least 20% DEET on exposed skin and clothing for maximum protection. Consider using permethrin-treated clothing or gear, which repels ticks effectively. When applying repellents, follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully—avoid contact with the face, eyes, and mouth, especially on children, due to potential toxicity. Be cautious and use repellents sparingly around sensitive areas.
Maintaining your outdoor environment also plays a vital role in preventing tick proliferation. Ensure your yard is regularly cleaned and free of debris, leaves, and tall grass. Create a barrier of wood chips or gravel between your lawn and wooded areas to limit tick migration. Store firewood in sunny, dry areas, as ticks thrive in humid environments. Remove leaf litter, overgrown shrubs, and brush where ticks tend to hide and wait for hosts.
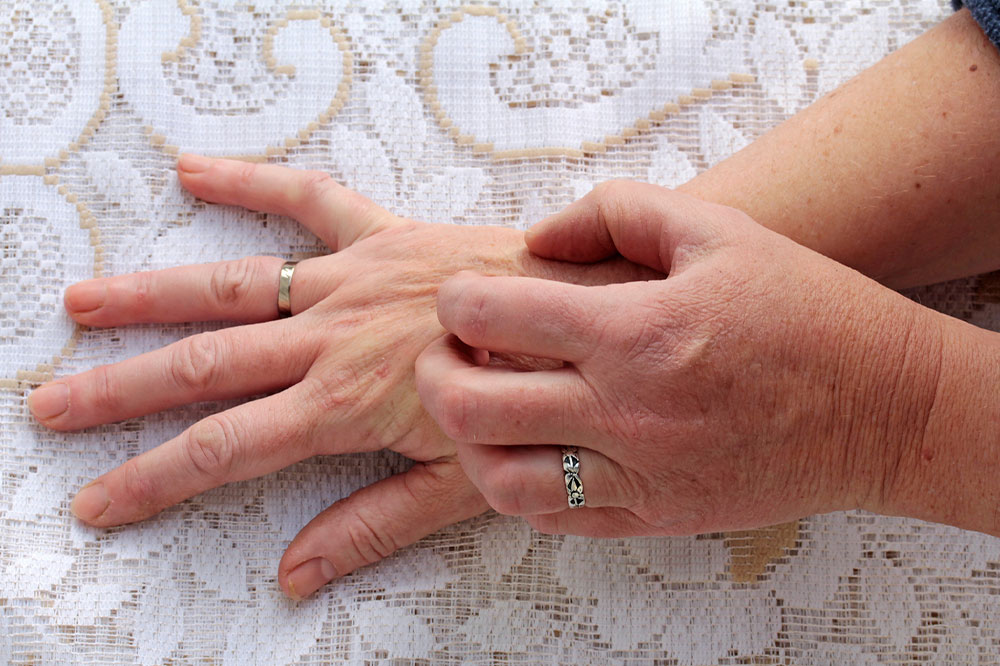
Post-outdoor activity checks are critical. Carefully inspect yourself, children, and pets for ticks after visiting tick-prone areas. Ticks are tiny—about the size of a sesame seed—and can be difficult to detect, but early removal is key to preventing disease transmission. Take a shower promptly after outdoor adventures, ideally within 36 hours, to wash away unattached ticks and conduct a thorough body scan. Pay special attention to hidden areas like armpits, scalp, behind the ears, around the waist, and knees.
If you find a tick attached to your skin or your pet’s fur, remove it immediately using fine-tipped tweezers. Grasp the tick as close to the skin’s surface as possible and pull upward with steady, even pressure. Avoid twisting or squeezing the tick, as this may cause mouthparts to break off and increase infection risk. Once removed, clean the bite area and your hands with rubbing alcohol or soap and water. Monitoring the bite site is essential; if a rash, fever, or flu-like symptoms develop within days to weeks, seek medical attention promptly.
Early detection and removal of ticks can prevent the transmission of Lyme disease. The bacteria typically require 36 to 48 hours to be transmitted after attachment, so quick action drastically reduces your risk. Educate yourself and your family about the appearance of ticks and symptoms of Lyme disease to facilitate early diagnosis and treatment.
In conclusion, preventing Lyme disease is a multifaceted process that involves personal protection, environmental management, and vigilance. By dressing appropriately, using repellents, keeping your outdoor spaces tidy, and performing regular tick checks, you can enjoy outdoor activities while minimizing health risks associated with tick-borne diseases. Awareness and proactive measures are your best defense against early Lyme disease symptoms.