Effective Strategies to Minimize Malodorous Flatulence and Promote Digestive Health
Discover comprehensive strategies to prevent foul-smelling gas. Learn how dietary choices, lifestyle habits, and health factors influence flatulence. Explore practical tips like moderating fiber intake, managing food sensitivities, and incorporating probiotic-rich foods to promote digestive health and reduce odors. Perfect for those seeking natural solutions to improve comfort and confidence in social situations.

Effective Strategies to Minimize Malodorous Flatulence and Promote Digestive Health
Flatulence, commonly known as passing gas, is a natural and inevitable aspect of human digestion. It occurs when gases produced during the breakdown of food in the gastrointestinal tract are expelled through the rectum. While passing gas is a normal bodily function, it can sometimes be accompanied by foul odors, which may cause embarrassment or discomfort. Understanding the causes behind smelly gas and adopting effective prevention strategies can significantly improve digestive well-being and social confidence.
Flatulence varies in smell, sound, and frequency among individuals. Some gases are odorless and barely noticeable, while others are pungent and disruptive. The unpleasant smell often results from the breakdown of specific foods and the presence of certain bacteria in the gut. Factors such as diet, health conditions, medication use, and lifestyle choices influence the odor and volume of flatulence. By addressing these factors, you can reduce the occurrence of foul-smelling gas and promote healthier digestion.
Understanding the Causes of Foul-Smelling Gas
Before exploring prevention tips, it’s essential to understand the primary reasons why flatulence can develop a strong, unpleasant odor.
High-Fiber Diets and Fermentation
Dietary fiber is crucial for healthy digestion, promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. Fibrous foods such as beans, lentils, and whole grains are excellent for overall health, but they can also lead to increased gas production. When fiber-rich foods enter the colon, bacteria ferment them, releasing gases such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. Some of these gases, especially sulfur-containing compounds, are responsible for the foul smell of flatulence.
To minimize the foul odor associated with high-fiber foods, consider moderating your intake of certain vegetables known for causing strong smells. These include:
Bok choy
Asparagus
Cabbage
Broccoli
Adjusting portion sizes and cooking methods, such as steaming rather than boiling, can also help reduce gas production and odor.
Food Sensitivities and Intolerances
Many individuals experience increased flatulence and foul smell due to sensitivities or allergies to specific foods. For example, lactose intolerance hampers the body’s ability to digest lactose, a sugar found in dairy products. Undigested lactose ferments in the gut, producing sulfurous and malodorous gases.
Similarly, sensitivities to certain artificial additives, preservatives, or high-fat foods can disrupt gut flora balance, leading to problematic digestion and stronger odors.
Impact of Medications on Gut Flora
Medications like antibiotics are known to alter the composition of gut bacteria. While antibiotics target harmful bacteria, they can also wipe out beneficial bacteria necessary for healthy digestion. This imbalance can lead to overgrowth of odor-producing bacteria, resulting in more potent and foul-smelling flatulence.
Practical Tips to Reduce Smelly Gas
Given that flatulence is a natural process, the goal isn’t to eliminate it but to control its odor and frequency. Here are comprehensive strategies to help you manage and reduce malodorous gas effectively:
Increase Fluid Intake: Drinking plenty of water supports smooth digestion and helps dilute and flush out waste products that contribute to gas formation.
Avoid Carbonated Beverages: Soft drinks, soda, and beer introduce additional carbon dioxide into the digestive system, increasing gas volume and potential odor.
Eat Smaller, More Frequent Meals: Smaller meals are easier for your digestive system to process, reducing fermentation and gas production.
Chew Food Slowly: Proper chewing initiates digestion in the mouth, eases the workload on your stomach and intestines, and decreases the likelihood of excessive gas.
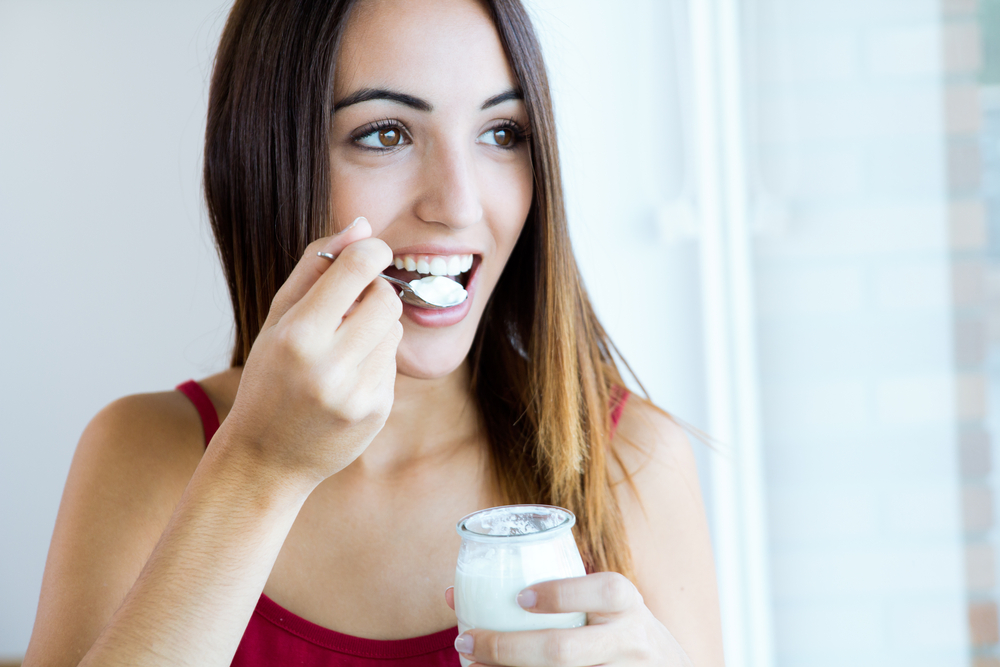
Incorporate Probiotic-Rich Foods: Yogurt, kefir, kimchi, and sauerkraut contain beneficial bacteria that restore gut flora balance, leading to less smelly gas over time.
Limit Gas-Enhancing Foods: Reduce consumption of foods known to produce strong odors during digestion, including certain vegetables and processed foods with additives.
Use Digestive Aids: Over-the-counter products containing enzymes like alpha-galactosidase can assist in breaking down complex carbohydrates in gas-producing foods, decreasing odor and volume.
Incorporating these habits into your daily routine can significantly improve your digestive comfort and social interactions. Remember, if persistent foul-smelling gas accompanies other symptoms like abdominal pain, diarrhea, or weight loss, consult a healthcare professional to rule out underlying conditions.
By understanding the role of diet, lifestyle, and health factors, you can take proactive steps to manage flatulence effectively. Maintaining a balanced diet, practicing mindful eating, and supporting gut health are essential components of reducing smelly gas and promoting overall digestive wellness.