Comprehensive Guide to Preventing Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease: Essential Strategies for Safety
This comprehensive guide provides essential preventive measures against hand, foot, and mouth disease. Covering hygiene practices, environmental sanitation, and behavioral precautions, it offers detailed strategies to minimize infection risk, especially for caregivers and educational institutions. Staying informed and vigilant during high-risk seasons can effectively control contagion and protect vulnerable populations from this highly contagious viral illness.

Comprehensive Guide to Preventing Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease: Essential Strategies for Safety
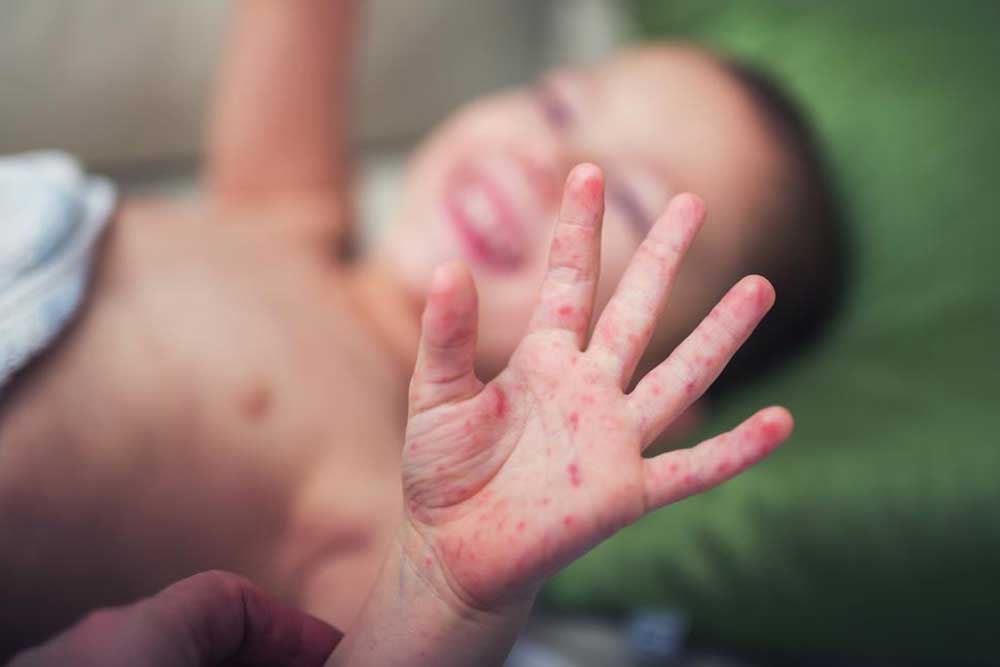
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a highly contagious viral infection that predominantly affects infants and young children, although individuals of all ages can contract it. This illness is characterized by fever, painful mouth sores, and distinctive rashes that appear on the hands, feet, buttocks, and legs. Caused primarily by the coxsackievirus, HFMD spreads easily through close contact with infected persons, contaminated surfaces, or shared items. Understanding the precise transmission methods and adopting effective preventive measures are crucial to limit outbreaks and protect vulnerable populations.
HFMD tends to be more prevalent during the warm months of summer and early autumn, correlating with increased outdoor activities and close interactions among children. The initial symptoms often include mild fever, fatigue, and sore throat, which can progress within a day or two to include painful mouth ulcers and rash formations. These skin eruptions may develop into blisters, causing discomfort and distress, especially in young children. Notably, while the disease usually resolves within a week to ten days without specific medical treatment, some cases can lead to complications that require medical attention.
Due to the contagious nature of HFMD and the absence of a targeted vaccine, prevention hinges on meticulous hygiene practices, environmental sanitation, and behavioral precautions. These measures are essential for caregivers, parents, teachers, and healthcare providers striving to minimize the risk of infection and curb widespread outbreaks.
Effective prevention of HFMD involves a combination of hygiene habits and environmental measures. Key practices include:
Isolation of infected individuals: Keep children affected by HFMD at home until they are fully recovered. This prevents the spread of the virus through coughs, open blisters, or saliva contact with others.
Regular hand and foot hygiene: Encourage frequent handwashing with soap and water, especially after using the bathroom, changing diapers, or before eating. Proper foot hygiene should also be maintained, particularly after outdoor play, to remove potential contaminants.
Environmental sanitation: Disinfect common surfaces and objects such as toys, doorknobs, tabletops, and bathroom fixtures regularly. Pay special attention to environments like homes, schools, and childcare centers where children gather.
Physical distancing: Avoid close physical contact, including hugging or sharing utensils, during outbreaks or when someone exhibits symptoms of HFMD.
Travel precautions: Individuals traveling to regions with known HFMD activity should adopt rigorous hygiene practices, carry disinfectants, and limit exposure to crowded places.
Clothing hygiene: Disinfect clothing of infected persons by washing with hot water and detergents to eliminate viral particles effectively.
Avoid outdoor activities: During an active infection, limit outdoor play and communal activities to reduce transmission risk.
Maintaining good hydration and nutritious meals is vital for children experiencing symptoms, supporting immune function and recovery. Monitoring health closely and seeking medical advice if symptoms worsen or complications develop are crucial steps in managing HFMD effectively.
By adhering to these preventive strategies, caregivers and communities can significantly reduce the incidence of HFMD outbreaks, safeguarding children's health and well-being during peak seasons.