Comprehensive Dietary Approaches to Boost Kidney Health and Functionality
This comprehensive guide provides essential dietary strategies to improve kidney health. It emphasizes controlling sodium, moderating protein intake, selecting heart- and kidney-friendly foods, managing minerals like potassium and phosphorus, and eliminating sugary drinks. Implementing these nutritional tips can help prevent further kidney damage, support overall health, and enhance quality of life. Suitable for those with kidney conditions or at risk, this article offers detailed advice to foster better kidney function through mindful eating habits and smart food choices.

Comprehensive Dietary Approaches to Boost Kidney Health and Functionality
Maintaining optimal kidney health is essential for overall well-being, especially for individuals affected by chronic kidney conditions or at risk of developing kidney disease. Proper nutrition plays a pivotal role in supporting kidney function, reducing the workload on these vital organs, and preventing further deterioration. This extensive guide explores vital diet strategies that can help safeguard kidney health, highlighting the importance of selecting the right foods, managing nutrient intake, and avoiding harmful substances. Adopting these dietary practices not only enhances kidney function but also promotes overall health and vitality.
Prioritize Low-Sodium Food Choices
One of the cornerstone principles of kidney-friendly eating is managing sodium intake. The kidneys' ability to regulate sodium and water balance becomes compromised when they are impaired. Excessive sodium consumption can lead to fluid retention, swelling, high blood pressure, and increased stress on the kidneys and cardiovascular system. To protect your kidneys, aim to consume meals with less than 400 milligrams of sodium per serving. Reading nutrition labels diligently is crucial, as processed and packaged foods often contain high levels of hidden salts. When cooking at home, it's advisable to use herbs, spices, and other flavorings like garlic powder, lemon juice, and vinegar instead of salt. Fresh, whole foods are generally lower in sodium, making them an ideal choice over canned or preserved products. Controlling portion sizes also aids in sodium management, ensuring that intake remains within safe limits. By making these adjustments, individuals can effectively reduce their risk of hypertension and fluid overload, thus contributing to stronger kidney health.
Incorporating low-sodium foods into your daily diet is straightforward with careful meal planning and mindful eating habits. Remember to select fresh produce over canned options, check food labels diligently, and experiment with salt substitutes like herbs and spices. These practices help ensure that your meals remain flavorful while supporting your kidney health effectively.
Moderate Your Protein Consumption
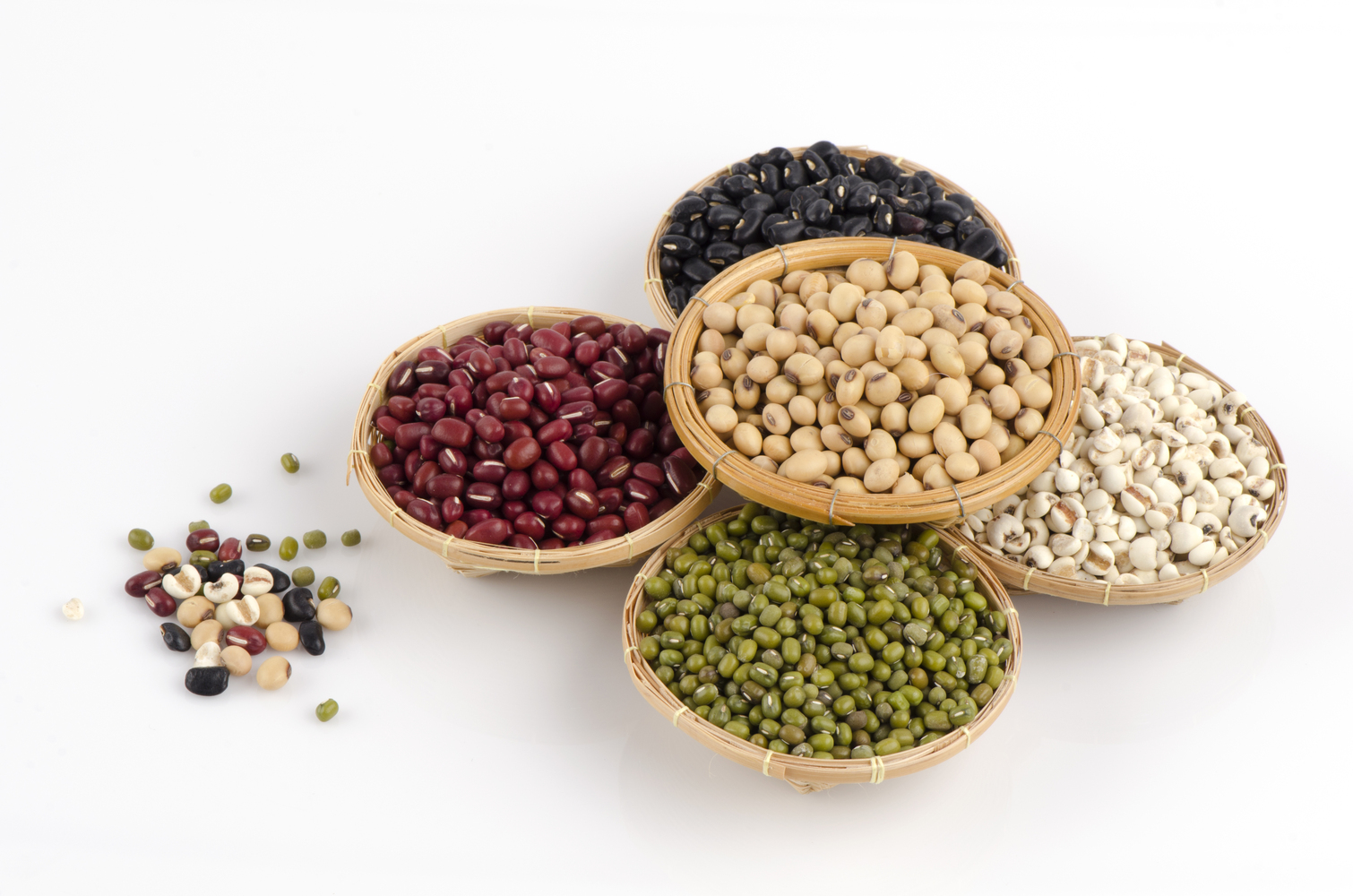
Protein is essential for growth, repair, and overall bodily functions; however, excessive protein intake may impose additional stress on the kidneys. For individuals with compromised kidney function, it is crucial to strike a balance by consuming moderate portions of high-quality protein sources. Consulting with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian ensures you determine the appropriate amount tailored to your specific health status. Recommended sources of protein include lean meats such as chicken and fish, eggs, and plant-based options like beans, nuts, grains, and legumes. Typical serving sizes involve 2-3 ounces of lean meats per meal, alongside small portions of dairy products like yogurt, cheese, or milk. Plant-derived proteins should be consumed in moderation, with attention to portion sizes and preparation methods. Proper protein management not only helps maintain muscle mass but also reduces the burden on the kidneys, thereby slowing disease progression and supporting overall health.
Focus on Heart- and Kidney-Friendly Foods
Maintaining a healthy metabolic rate and preventing fat accumulation are essential in reducing the risks associated with kidney and heart diseases. To achieve this, cut back on saturated and trans fats found in fried foods, baked goods, and processed snacks. Instead, opt for cooking techniques such as baking, grilling, roasting, and stir-frying that preserve food flavors while reducing fat content. Incorporate healthier fats, particularly monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats like olive oil, avocados, and fish oils, into your diet. Consuming foods that support both cardiovascular and kidney health can significantly improve overall well-being. Examples include fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, skinless poultry, beans, and low-fat dairy options. These choices help in reducing inflammation, controlling blood pressure, and promoting proper functioning of the kidneys and heart.
Maintain Balanced Potassium and Phosphorus Levels
Proper regulation of potassium and phosphorus is vital. Elevated potassium levels can cause dangerous cardiac rhythm disturbances, while excessive phosphorus can weaken bones and cause mineral imbalances. To manage these minerals, focus on foods that are naturally low in phosphorus and potassium. Suitable options include fresh fruits like apples, peaches, and berries; vegetables such as carrots, green beans, and lettuce; and grains like rice and corn. Be cautious with high-phosphorus foods, including animal proteins, dairy products, nuts, beans, lentils, dark-colored sodas, and canned drinks. These should be limited or avoided based on your healthcare provider's recommendations. Fruits like oranges, bananas, tomatoes, and potatoes contain high levels of potassium and should be included sparingly. Always check labels and, when necessary, use cooking methods like boiling to reduce mineral content. Achieving a balance of these nutrients supports heart and bone health while preventing complications related to kidney disease.
Exclude Sugary and Artificially Sweetened Drinks
Beverages such as sodas, energy drinks, and sweetened fruit juices contain excessive sugars and additives that put additional strain on the kidneys. These drinks contribute to obesity, insulin resistance, and increasing inflammation, all of which are detrimental to kidney health. Replacing sugary drinks with plain water, infused water, or natural fruit juices without added sugars not only hydrates the body effectively but also reduces toxin buildup. Consuming adequate hydration is essential for kidney filtering functions, flushing out toxins and supporting overall metabolic processes. Developing healthy beverage habits can significantly improve kidney health, reduce disease progression, and promote a vibrant, energetic life.
In conclusion, adopting a kidney-friendly diet involves a combination of reducing sodium, moderating protein intake, choosing healthy fats, balancing minerals like potassium and phosphorus, and avoiding harmful sugary drinks. By following these nutritional guidelines, individuals can greatly enhance their quality of life, slow the progression of kidney disease, and promote their overall health. Making mindful food choices, preparing meals at home, and consulting healthcare professionals for personalized advice are key steps toward achieving optimal kidney function and long-term wellness.