Comprehensive Guide to Milk Allergy in Young Children: Essential Knowledge for Parents
This comprehensive guide explores milk allergy in young children, emphasizing recognition, diagnosis, and management. It offers practical tips on breastfeeding, nutritional alternatives, dietary adjustments, medications, and allergy education. Understanding these facets helps parents ensure their child's health and well-being. The article highlights the importance of professional guidance and continuous monitoring for effective allergy management, with many children outgrowing the condition over time. A valuable resource for parents navigating this common but manageable childhood allergy.

Comprehensive Guide to Milk Allergy in Young Children: Essential Knowledge for Parents
Milk allergy remains one of the most common food allergies affecting infants and young children worldwide. It is a significant concern for parents and caregivers, as early detection and proper management can prevent complications and ensure the child's healthy development. This allergy primarily involves an immune response to proteins found in cow's milk, although it is important to distinguish between true milk allergy and lactose intolerance, which affects digestion rather than immune response.
Typically emerging during the early months or years of life, milk allergy symptoms can vary widely among children. The child's immune system perceives milk proteins as harmful invaders, leading to an allergic reaction. Since the gastrointestinal system is still maturing during infancy, the likelihood of developing such allergies is higher at this stage. While cow's milk is the primary culprit, breastfed infants may rarely experience allergic reactions from allergens transmitted through breast milk if the mother consumes dairy products.
Understanding the warning signs, early diagnosis, and effective management strategies are crucial for parents. This extensive guide aims to demystify milk allergy in children, offering practical tips, nutritional advice, and insights into medical interventions to help parents navigate this condition confidently.
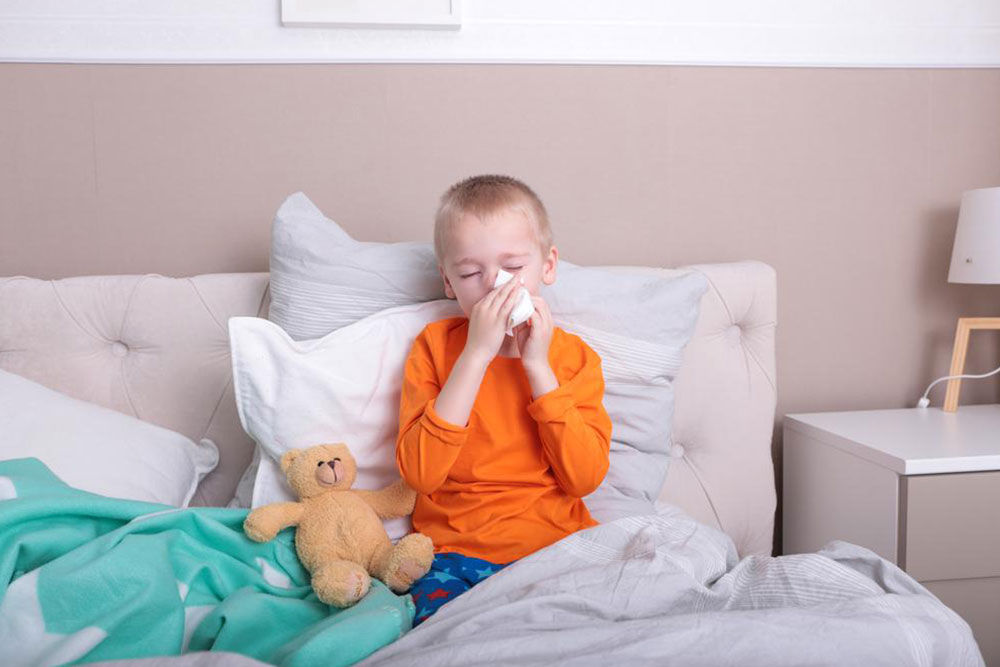
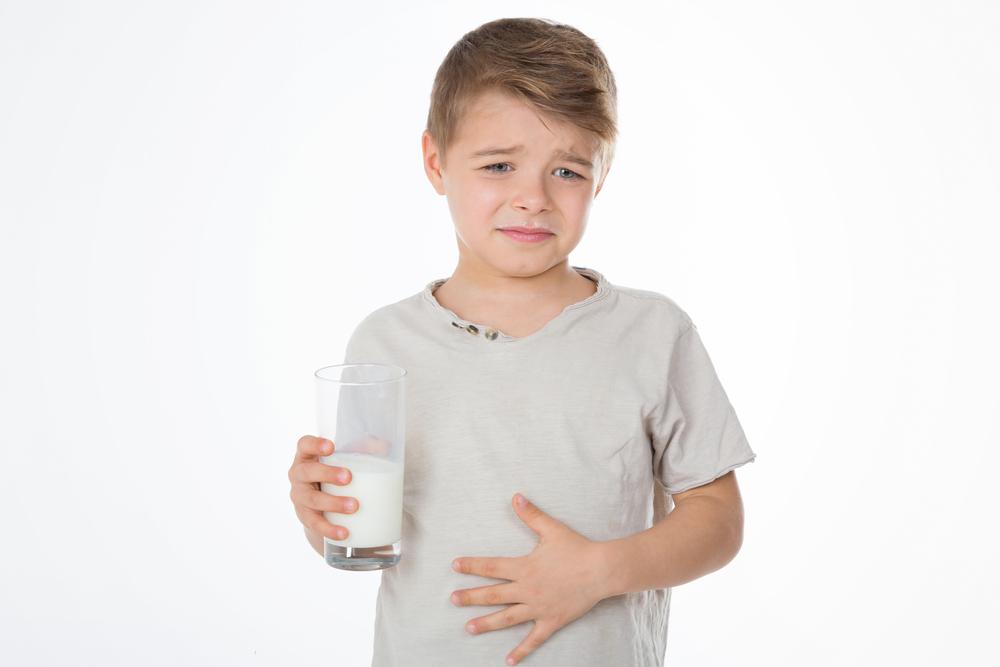
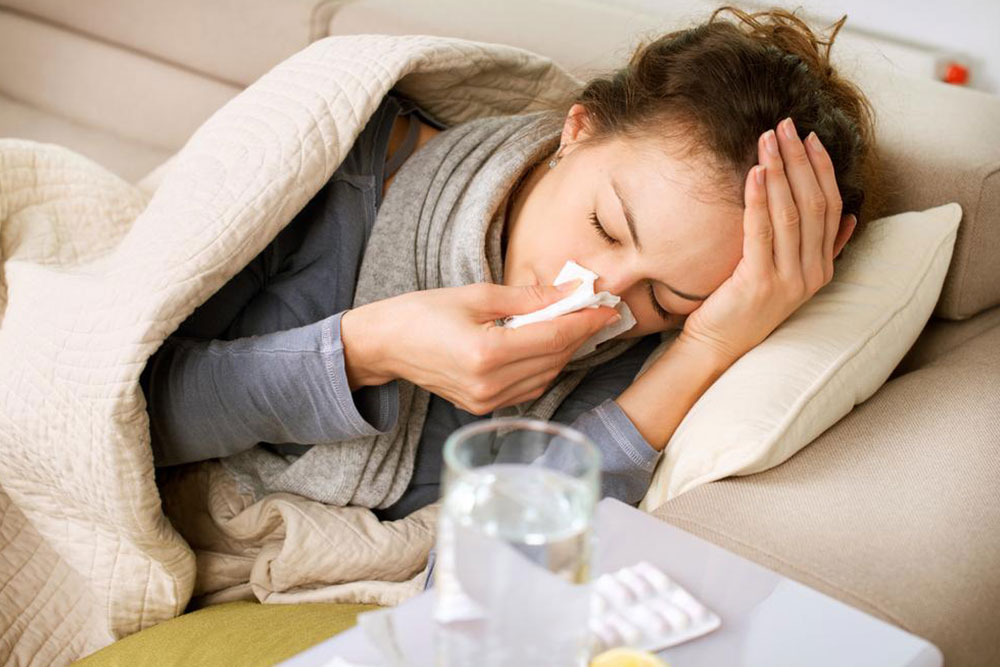
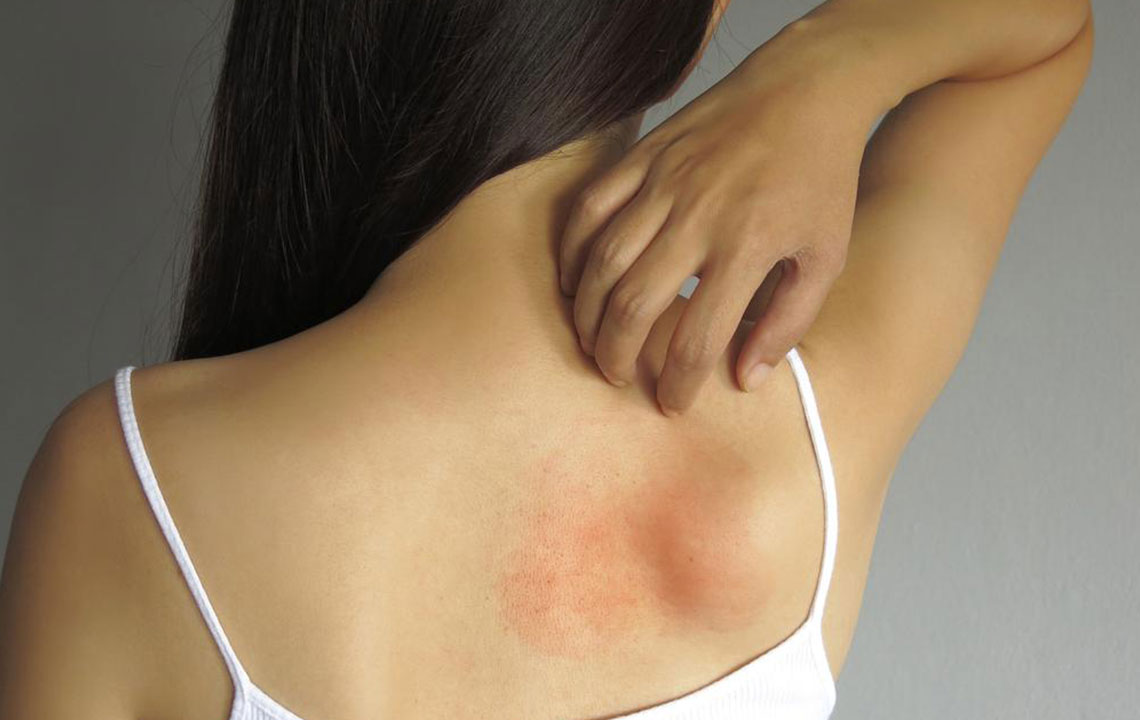
Recognizing the symptoms promptly can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes. Common signs include skin reactions such as hives and eczema, digestive problems like vomiting, diarrhea, or blood in stool, and respiratory issues such as wheezing or difficulty breathing. These manifestations typically develop within 30 minutes to a few hours after consuming milk or milk-containing products. However, some symptoms may be delayed, which underscores the importance of close monitoring and professional evaluation.
Effective Breastfeeding Strategies – For breastfeeding mothers, if the infant shows signs of milk allergy, a lactose-free or dairy-free diet can be beneficial. Ensuring adequate calcium intake through alternative sources or supplements is vital to support the mother's health. Introducing cow's milk should only occur under medical supervision, generally after reaching four months of age.
Choosing Suitable Nutrition Alternatives – For infants and young children unable to tolerate cow’s milk, healthcare professionals often recommend soy-based formulas, almond milk, or hypoallergenic formulas designed to minimize allergic reactions. The selection of appropriate alternatives depends on the child's specific allergies and nutritional needs, which should be evaluated by a pediatrician or allergist.
Managing Dietary Intake as Children Grow – As children transition to solid foods, limiting high-dairy products such as cheese, yogurt, and ice cream is prudent. Incorporating calcium-rich foods like nuts, seeds, beans, dark leafy greens, and fortified plant-based options helps meet nutritional requirements without provoking allergic reactions. Regular testing can help determine whether the allergy persists or diminishes over time.
Implementing Dietary Adjustments Safely – Any significant change in dietary habits should be guided by medical advice. Parents should avoid self-diagnosing or attempting desensitization without professional supervision, as accidental exposure to milk can lead to severe allergic responses.
Medicinal Treatments and Emergency Preparedness – In certain cases, antihistamines or prescribed allergy medications may relieve mild symptoms. For severe allergic reactions—known as anaphylaxis—carrying an epinephrine auto-injector is essential. Thankfully, many children outgrow milk allergy by school age or adolescence, particularly in mild cases.
Educational Awareness and Preventive Measures – Educating yourself, family members, and caregivers about milk allergy is crucial to avoid accidental ingestion. Reading food labels diligently, preparing allergen-free meals, and understanding cross-contact are vital steps in allergy management.
It is also worth noting that milk allergy is often confused with lactose intolerance, but they are distinct conditions. While lactose intolerance affects digestion due to the absence of lactase enzyme, milk allergy involves immune response to milk proteins. Diagnostic tests such as skin prick testing, blood tests for specific antibodies, or hydrogen breath tests can help clarify the diagnosis and inform treatment choices.
Overall, early intervention, proper nutritional planning, and ongoing medical supervision are keys to managing milk allergy in young children effectively. With appropriate guidance, most children adapt well, and many outgrow the allergy, facilitating a normal, healthy childhood without unnecessary dietary restrictions.