Comprehensive Guide to Air Filters and Air Purifiers: How to Choose the Best Indoor Air Quality Solution
This comprehensive guide explains the differences between air filters and air purifiers, covering various types, applications, advantages, and limitations. Learn how to select and combine these devices to improve indoor air quality, especially if you have allergies or pollution concerns. Equip yourself with knowledge to create healthier indoor environments using the right technology for your needs.

Key Differences Between Air Filters and Air Purifiers: A Complete Guide
Maintaining pristine indoor air quality is a top priority for many homeowners and office environments. The quality of the air we breathe indoors significantly impacts our health, comfort, and overall well-being. To achieve healthier indoor environments, it’s crucial to understand the distinctions between two common air cleaning devices: air filters and air purifiers. While both serve the purpose of cleaning the air, their technologies, applications, and effectiveness differ remarkably. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of air filters and purifiers, their functionalities, advantages, and limitations, empowering you to make informed choices for improved indoor air quality.
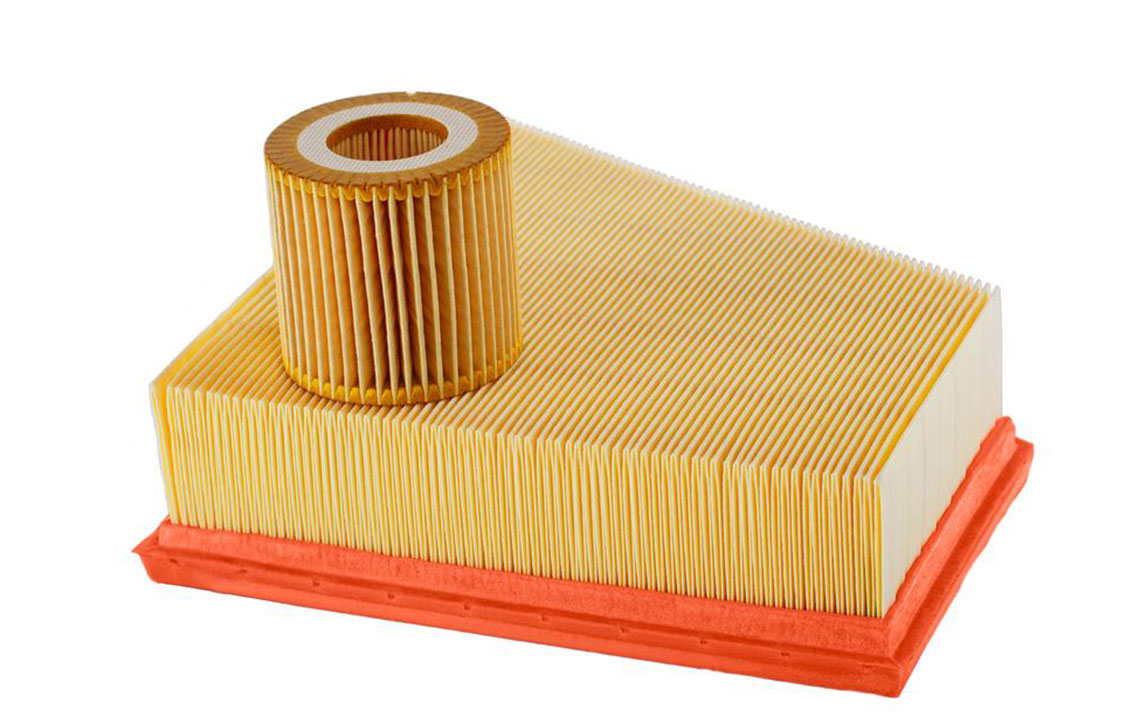
Understanding Air Filters: Types and Functions
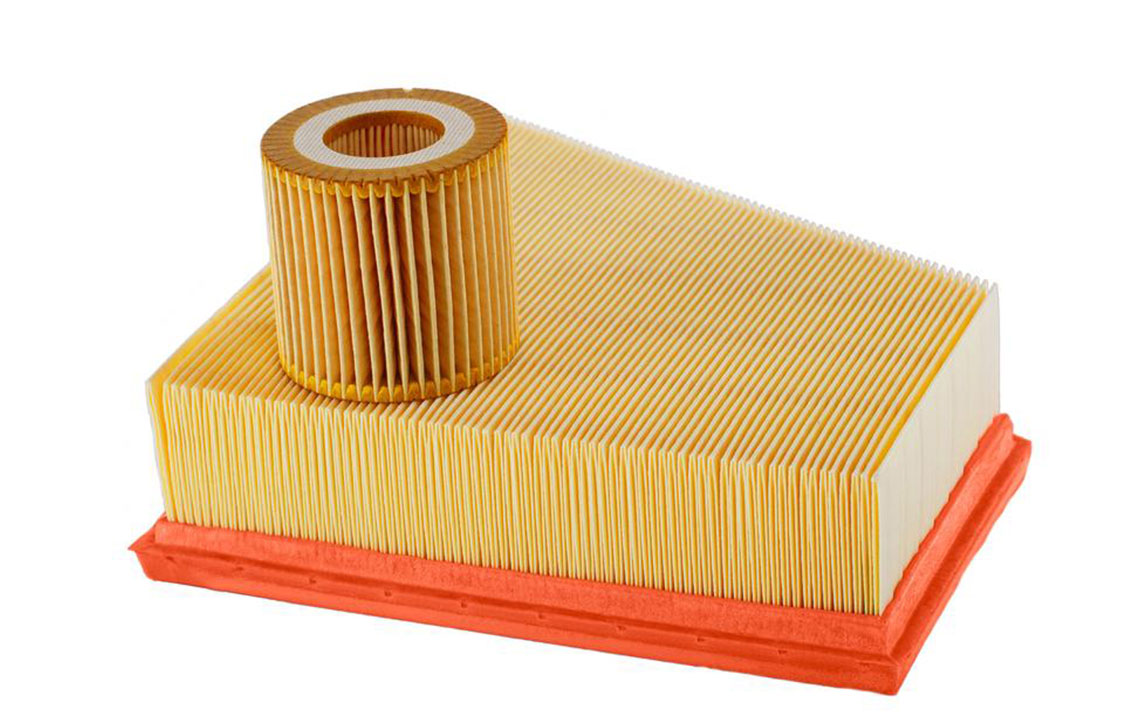
Air filters are integrated into heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems or used as standalone units. They function primarily by trapping particulate matter within the filter material as air passes through. These filters are essential for reducing airborne dust, pollen, mold spores, pet dander, and bacteria, contributing to a cleaner and healthier indoor environment.
Common Types of Air Filters
HEPA Filters (High-Efficiency Particulate Air)
HEPA filters are renowned for their exceptional efficiency, capable of trapping 99.97% of particles as small as 0.3 microns. They are extensively used in hospitals, laboratories, and homes to combat allergens and microscopic pollutants. Installing a HEPA filter in your HVAC system or using portable HEPA air cleaners can significantly reduce the presence of airborne allergens, mold spores, and bacteria.
Fiberglass Filters
These are disposable filters made from layered fiberglass materials, often electrostatically charged to improve particle capture. They are cost-effective and commonly found in residential furnaces. However, they tend to have lower filtration efficiency and are mainly designed to protect the HVAC system rather than provide comprehensive air purification.
Activated Carbon Filters
Utilizing porous activated carbon, these filters excel at absorbing gases, odors, and chemical pollutants. They are often used as pre-filters or in combination with other filters to eliminate unpleasant smells from pets, cooking, smoke, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). For optimal air quality, integrating activated carbon filters into your air filtration system is highly recommended.
Washable or Reusable Filters
Made from durable materials that can be cleaned and reused, washable filters offer a cost-effective and eco-friendly alternative. They require regular maintenance and are suitable for dust and larger particle collection but may have lower filtration efficiency compared to high-grade filters like HEPA.
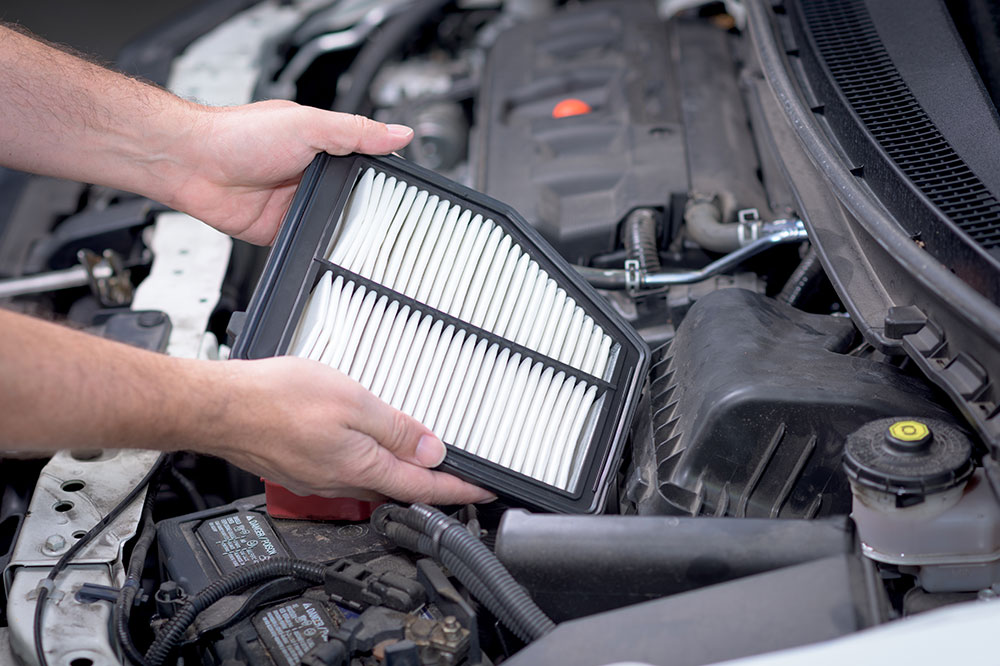
Where and Why Are Air Filters Used?
Air filters are essential components in central HVAC systems, where they maintain air quality during air circulation throughout homes, offices, or industrial premises. They trap particulate pollutants such as dust, pet hair, pollen, mold spores, and bacteria, significantly improving indoor air hygiene. Regularly changing or cleaning filters ensure efficient operation and consistent air quality.
However, despite their benefits, filters are primarily designed for particulate removal and do not actively remove gases, odors, or microscopic pathogens unless combined with specific media like activated carbon or UV sterilization modules.
Advantages and Limitations of Air Filters
**Advantages:** Effective at capturing large to small particles, improve HVAC system longevity, cost-effective over time, easy to install and replace.
**Limitations:** May produce noise due to fan operation, possible ongoing replacement costs, limited in removing gaseous pollutants or viruses, less effective against ultrafine particles and volatile chemicals.
Understanding Air Purifiers: Technologies and Benefits
Air purifiers are standalone devices engineered to actively eliminate airborne contaminants through advanced technologies beyond simple filtration. They are particularly effective at improving indoor air quality by targeting microscopic pollutants, odors, gases, and pathogens that filters alone might miss.
Types of Air Purifiers
UV Light Purifiers
Utilize ultraviolet (UV-C) light to sterilize bacteria, viruses, and mold spores, rendering them harmless. UV purifiers are effective in healthcare settings and homes concerned about microbial pollution, especially during flu seasons or outbreaks.
Activated Carbon Purifiers
Employ activated charcoal to absorption of chemical fumes, odors, and VOCs, making them ideal for smokers, cooking areas, or environments with chemical pollutants.
Ionic Purifiers
Generate negatively or positively charged ions to attach to airborne particles. These ions cause particles such as bacteria, fungi, and dust to settle on surfaces or be captured on collector plates. Ionic purifiers are typically quiet and low-maintenance.
HEPA Purifiers
Many standalone air purifiers incorporate HEPA filters for particulate removal while combining other technologies for broad-spectrum air cleaning. These units are portable and suitable for individual rooms.
Applications and Advantages of Air Purifiers
Air purifiers are invaluable in reducing allergens like pet dander, dust mites, mold spores, and airborne pathogens. They are particularly beneficial for allergy sufferers, asthma patients, and in environments where air hygiene is crucial. Some units can also lessen VOCs and odors, creating fresher indoor atmospheres.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Air Purifiers
**Pros:** Highly effective against microscopic allergens, operate quietly, portable, easy to use, and often more affordable than comprehensive HVAC upgrades.
**Cons:** Struggle with large particles like dust and pet hair unless equipped with powerful filters, limited airflow coverage unless multiple units are used, and some models may produce ozone as a byproduct, which can be harmful.
Comparing Air Filters and Purifiers: Which Should You Choose?
While both devices aim to improve indoor air quality, their operating mechanisms and ideal applications differ. Filters focus predominantly on trapping particles in your HVAC system, making them suitable for ongoing, whole-house filtration. Purifiers actively neutralize airborne germs, odors, and microscopic pollutants, providing targeted relief and enhanced air quality.
Combining both systems offers the most comprehensive approach. Using high-efficiency filters within your HVAC system along with portable air purifiers in various rooms can significantly elevate your indoor air environment. This strategy is especially recommended during allergy seasons or in situations with high pollution levels.
If you suffer from allergies, asthma, or have concerns about airborne contaminants, selecting a combination of HEPA filters and advanced purifiers tailored to your needs can substantially improve your indoor living space. Ensuring proper maintenance and regular replacement of filters and purifiers will maximize their effectiveness and contribute to long-term health benefits.