Comprehensive Guide to Surgical Treatments for Ptosis Correction
This detailed guide explores effective surgical options for ptosis correction, offering insights into various procedures, recovery tips, and cost considerations. Learn how modern ophthalmic surgeries can restore both vision and appearance for individuals suffering from drooping eyelids, ensuring improved quality of life and confidence.

Exploring Effective Surgical Options for Drooping Eyelids
Ptosis, commonly known as drooping eyelids, is a condition that can either be congenital—present at birth—or acquired later in life due to various factors such as aging, injury, or neurological issues. According to recent studies, approximately 11.5% of adults worldwide experience some degree of eyelid droop, which can sometimes lead to visual impairment or aesthetic concerns. Fortunately, advancements in ophthalmic surgery have made it possible to effectively correct ptosis, restoring both function and appearance. The surgical approach is particularly suitable for adults, offering long-lasting results and significant improvements in quality of life. This comprehensive article delves into the nature of ptosis and elaborates on the main surgical methods used to correct this condition, providing valuable insights for patients and practitioners alike.
Understanding Ptosis and Its Causes
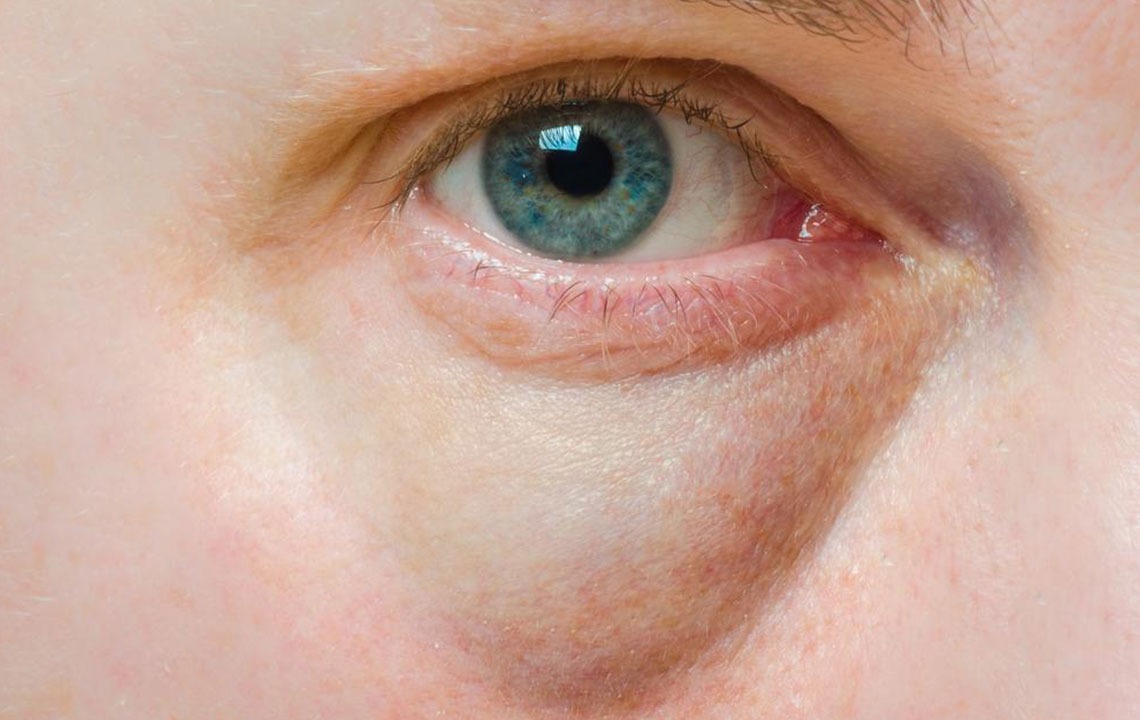
Palpebral ptosis, or drooping eyelids, occurs when the muscles responsible for lifting the eyelids—primarily the levator palpebrae superioris—fail to function correctly. This malfunction leads to sagging eyelids that may obscure the visual field and affect facial aesthetics. Ptosis can be classified into two types: congenital, present at birth due to developmental issues with the eyelid muscles, and acquired, developing over time due to aging, trauma, neurological conditions, or muscle weakness. Acquired ptosis is more common among adults and often worsens gradually. The severity of eyelid droop varies, with some patients experiencing mild sagging while others face significant obstruction of vision.
Drooping eyelids can affect one or both eyes, affecting vision, appearance, or both. Several factors influence the choice of surgical method, including the extent of ptosis, muscle strength, and patient-specific anatomical considerations. The goal of surgical correction is to elevate the eyelid to a normal or near-normal position, thereby improving visual function and facial symmetry.
Surgical Approaches to Correct Ptosis
There are various surgical procedures tailored to different types and severities of ptosis. The choice of procedure depends on the patient's specific condition, muscle strength, and overall health. Here, we explore the most common surgical techniques used worldwide for ptosis correction:
External Approach Surgery
This method is predominantly used when the levator muscle retains some functional strength. It involves making an external incision along the natural eyelid crease, allowing precise access to the eyelid muscles and tissues.
Anesthesia: Typically, local anesthesia with sedation is administered to ensure patient comfort during the procedure.
Incision and Dissection: The surgeon carefully makes an incision along the eyelid's natural crease. This approach minimizes visible scarring, as the scar integrates seamlessly into the eyelid fold.
Muscle Reattachment: The levator muscle or its aponeurosis (tendon-like extension) is repositioned or tightened by attaching it to the tarsal plate, lifting the eyelid.
Intraoperative Adjustment: During surgery, the surgeon may request the patient to look in specific directions to fine-tune eyelid positioning for optimal function and aesthetic harmony.
This approach often yields excellent cosmetic outcomes, with scars hidden naturally within the eyelid crease. It is considered the first-line surgical treatment for moderate to severe ptosis when the levator function is adequate.
Frontalis Sling Technique
This procedure is indicated when the levator muscle is too weak or absent to facilitate eyelid elevation, often seen in congenital ptosis or severe cases of acquired ptosis.
Anesthesia: Usually performed under general anesthesia, especially in children or patients who prefer unconscious sedation.
Sling Placement: A synthetic or autologous sling material, such as silicone, fascia lata, or mersilene, is used to connect the eyelid to the frontalis muscle (forehead muscle). This allows the forehead muscles to lift the eyelids, compensating for poor levator function.
Procedure: The sling is threaded through small incisions made in the eyelid and forehead, creating a support system that lifts the eyelid with brow movements.
Postoperative Considerations: Some patients experience eyelid asymmetry or lagophthalmos (incomplete eyelid closure), which usually resolves over several months with proper eyelid care and lubricants to prevent dryness.
This technique is especially beneficial for bilateral ptosis with weak levator muscles, providing functional and aesthetic improvements.
Internal or Transcutaneous Surgery
This approach involves shortening or tightening the eyelid muscles from inside the eyelid, often used when the levator muscle is partially functional but lax.
Anesthesia: Depending on the case, local or general anesthesia is administered.
Procedure: The surgeon inverts the eyelid, accesses the levator or Muller’s muscle, and shortens or tightens the tissue to elevate the eyelid to the desired position.
Advantages: The internal approach results in minimal visible scarring and preserves eyelid aesthetics while providing effective lift.
Cost and Financial Planning for Ptosis Surgery
The cost for eyelid correction surgery varies significantly based on the procedure type, surgeon expertise, geographic location, and specific patient needs. On average, the expenditure ranges from $3,000 to $6,000 per eyelid, with bilateral procedures often costing between $6,000 and $12,000. These costs cover surgeon fees, anesthesia, facility charges, and post-operative care. It’s crucial for patients to explore insurance coverage options, as in some cases, ptosis correction may be deemed medically necessary if it impairs vision.
Postoperative Care and Recovery Tips
Proper aftercare is essential to ensure optimal healing and long-lasting results. Patients can typically expect some swelling, bruising, and mild discomfort in the initial days following surgery. Applying cold compresses can reduce swelling, and keeping the head elevated helps minimize bruising. Patients should avoid rubbing their eyes or applying makeup until fully healed. Protecting the eyes from environmental irritants like soaps, shampoos, and dust is vital. Limiting screen time and ensuring sufficient rest aid in recovery. Following the surgeon’s instructions for medication and hygiene guarantees the best possible outcomes.
In conclusion, surgical correction of ptosis offers a safe and effective solution for individuals experiencing eyelid drooping. With various techniques tailored to different needs, patients can achieve improved vision, enhanced facial aesthetics, and higher self-confidence. Consulting with an experienced ophthalmic surgeon is essential to determine the most suitable approach based on individual circumstances and functional requirements.