Comprehensive Guide to Mitral Regurgitation: Recognizing Symptoms and Engaging in Safe Exercise Practices
This comprehensive article explores mitral regurgitation, highlighting its symptoms, causes, and the importance of early diagnosis. It offers practical advice on safe exercises like walking, swimming, and yoga, which help strengthen the heart without causing strain. Understanding and managing this condition through lifestyle and medical intervention can improve quality of life and prevent severe complications. The article emphasizes the role of healthcare professionals in guiding treatment and safe physical activity for individuals with mitral regurgitation.

Comprehensive Guide to Mitral Regurgitation: Recognizing Symptoms and Engaging in Safe Exercise Practices
The human heart is a remarkable organ that tirelessly pumps blood, delivering oxygen and nutrients vital for survival. Maintaining optimal heart health is crucial for overall well-being, yet many individuals remain unaware of potential conditions that can affect cardiac function. One such condition is mitral regurgitation, a common yet often underestimated heart disorder that can develop gradually, especially with certain lifestyle factors. Understanding this condition, its symptoms, and how to exercise safely can significantly improve quality of life and prevent severe complications.
What is mitral regurgitation? The heart comprises four essential valves — the mitral, aortic, tricuspid, and pulmonary valves — each responsible for regulating blood flow through the chambers of the heart. The mitral valve, located between the left atrium and left ventricle, plays a vital role in ensuring unidirectional blood flow. When functioning properly, it opens to allow blood to flow into the left ventricle during heart relaxation and closes tightly during contraction to prevent backflow. However, in mitral regurgitation, this valve fails to close completely, resulting in blood leaking backward into the left atrium with each heartbeat. This backflow can lead to increased pressure in the atrium, congestion in the lungs, and eventual strain on the heart muscle, affecting overall cardiovascular efficiency.
Mitral regurgitation can develop due to various reasons, including age-related degeneration, infections such as endocarditis, congenital defects, or damage from a heart attack. Sometimes, lifestyle choices such as poor diet, lack of exercise, high blood pressure, or obesity increase the likelihood of developing this condition. Recognizing early symptoms and seeking timely medical advice are crucial steps in managing mitral regurgitation effectively. Left untreated, it can lead to complications like atrial fibrillation, heart failure, or pulmonary hypertension, which significantly impair quality of life.
Individuals diagnosed with mitral regurgitation may need to implement specific lifestyle modifications and consult healthcare professionals to adopt safe exercise routines and dietary habits. Symptoms to watch for include shortness of breath, especially during exertion or when lying flat, swelling in the legs and ankles, fatigue, rapid or irregular heartbeat, and episodes of dizziness or fainting. Early detection and intervention can prevent disease progression and improve long-term outcomes.
Once diagnosed, engaging in appropriate physical activities can help strengthen the heart and improve circulation. Below are some recommended exercises and lifestyle tips tailored for those with mitral regurgitation:
Walking — A low-impact exercise, walking is ideal for all fitness levels. It helps improve cardiovascular health without putting undue stress on the heart. Start with short walks around your home or neighborhood, gradually increasing duration and pace as tolerated. Consistency is key to benefiting from this activity.
Swimming — An excellent way to boost stamina and strengthen the heart muscles gently. Swimming provides a full-body workout with minimal joint impact, making it suitable for many individuals with heart issues. Always consult with your healthcare provider or a trained coach before starting a new swimming routine to ensure it aligns with your health status.
Yoga — Combining controlled movements, breathing exercises, and meditation, yoga can help reduce stress levels, improve flexibility, and enhance heart strength. Regular practice can lead to better energy management, mood stabilization, and improved cardiovascular function. Choose gentle yoga styles and avoid poses that strain the chest or increase blood pressure abruptly.
Cycling — Cycling, whether on a stationary bike or inline, can help manage blood pressure and cholesterol levels, both of which influence heart health. Begin with short, easy rides, paying attention to how your body responds. Always discuss with your healthcare provider before starting or modifying your cycling activities.
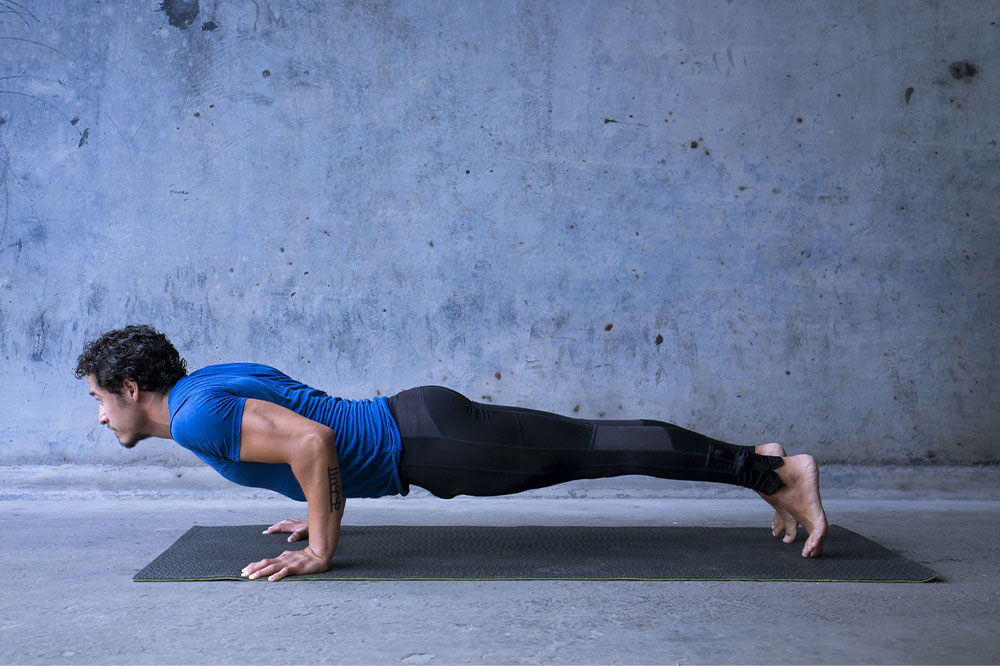
Strength training — Light resistance exercises, such as using resistance bands, bodyweight workouts, or light weightlifting, can support overall muscle tone and bolster heart function. These should be performed under professional supervision initially to prevent overexertion and injury. Gradually increase intensity as your strength and endurance build.
Stretching — Gentle stretching routines before and after workouts enhance muscle flexibility, prevent injuries, and promote circulation. Incorporate stretching into your daily routine for better muscle health and overall mobility.
Most of these exercises are accessible at home, requiring minimal equipment. However, it’s essential to consult your healthcare provider before initiating any new exercise regimen, especially if you have been diagnosed with a heart condition like mitral regurgitation.
Consistent physical activity offers numerous benefits for individuals with mitral regurgitation, such as reducing cardiac workload, enhancing blood circulation, increasing stamina, and boosting mental well-being. These activities can also help prevent disease progression or the need for surgical interventions in mild cases. For severe or symptomatic cases, surgical options like valve repair or replacement may be necessary. Ignoring symptoms and neglecting medical advice can lead to serious complications, emphasizing the importance of regular check-ups and personalized treatment plans.