Understanding the Common Causes of Upper Arm Discomfort and How to Address Them
Upper arm discomfort can stem from various causes, including muscle strain, shoulder injuries, or fractures. Recognizing symptoms early and consulting healthcare professionals ensures proper diagnosis and effective treatment. This comprehensive guide covers common causes and management strategies to help alleviate pain and promote recovery.
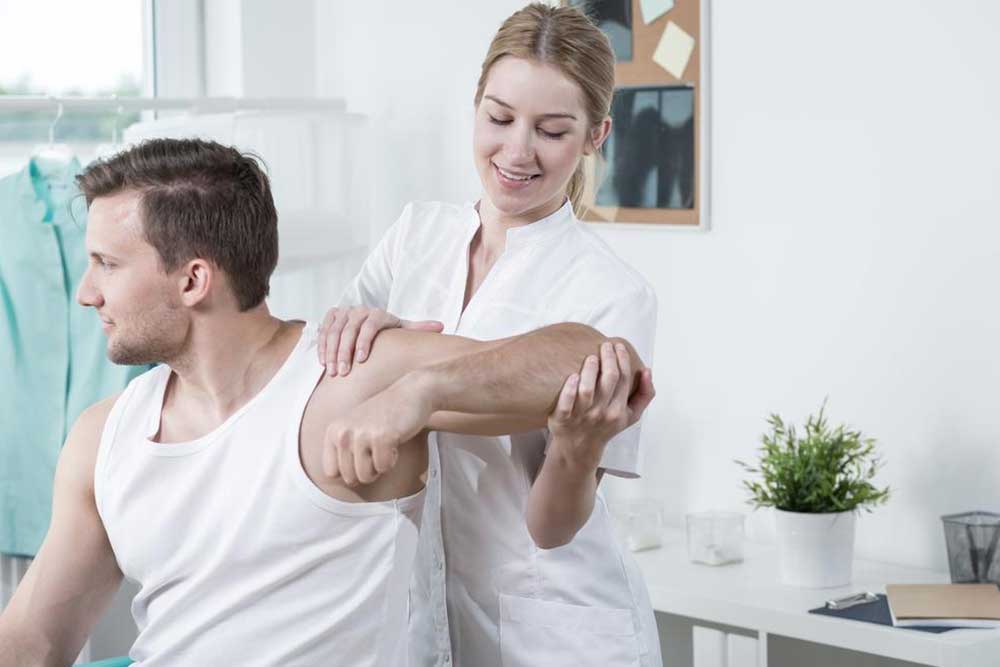

Comprehensive Overview of Upper Arm Pain Causes and Management Strategies
Upper arm discomfort can significantly impact your daily life, affecting your ability to perform routine tasks and engage in physical activities. Whether the pain is sudden or persistent, understanding its underlying causes is crucial for effective treatment and recovery. While some cases of arm pain are straightforward, such as injuries from heavy lifting, others might be linked to more complex health issues that require medical attention. This extensive guide explores the primary reasons behind upper arm discomfort, providing insights into symptoms, causes, and preventive measures to help you manage and mitigate pain effectively.
Muscle Strain and Overexertion
One of the most common causes of upper arm pain is muscle strain resulting from overexertion or overstretching. This condition occurs when the muscles are subjected to stress beyond their capacity, often during strenuous physical activity, heavy lifting, or repetitive motions. Muscle fibers may develop tears or microtears, leading to pain, swelling, and decreased mobility. The severity of muscle strain can vary from minor discomfort to significant tears that require longer recovery periods.
When muscle fibers are overstressed, they respond with inflammation and pain that can appear immediately or after a delay. Severe tears can cause sharp, intense pain, making movement difficult and sometimes immobilizing the arm temporarily. Rest and proper rehabilitation are essential in such cases, as continuing physical activities can exacerbate the injury and prolong recovery. Applying ice packs, elevating the arm, and avoiding strenuous activity are recommended initial steps. Physical therapy and specific exercises may be necessary to restore strength and flexibility in the affected muscles.
Muscle tears caused by overexertion often lead to immediate or delayed pain in the upper arm, emphasizing the importance of proper warm-up before physical activity. Complete tears usually necessitate medical intervention, ranging from conservative treatments to surgical procedures, depending on severity. Accurate diagnosis through physical examination and imaging studies helps tailor the most effective recovery plan.
Injuries to the Shoulder and Surrounding Structures
Damage or inflammation originating from shoulder injuries frequently result in pain radiating down to the upper arm. Conditions such as rotator cuff tears, shoulder impingement, or bursitis can cause discomfort and restrict movement. Continuing to use the shoulder when injured can worsen inflammation and prolong healing time. Rest, ice, anti-inflammatory medications, and physical therapy are vital in managing shoulder-related pain, preventing further damage, and restoring function.
Humerus Fractures and Bone-Related Issues
Fractures of the humerus, the upper arm bone, are often mistaken for muscle strain but typically cause much more severe pain and swelling. These injuries usually occur due to falls, direct blows, or during sports activities involving overhead movements like baseball or softball. Symptoms include intense pain, swelling, bruising, and inability to move the arm normally. Fractures require prompt medical assessment, imaging, and treatment, which can involve casting, bracing, or surgical fixation depending on the break's severity.
Additional Potential Causes of Upper Arm Pain
Several other factors may contribute to discomfort in the upper arm, warranting consideration and medical evaluation:
Blood clots forming in the veins of the upper arm (deep vein thrombosis)
Infections affecting the humerus or surrounding tissues
Cardiac-related issues like heart attacks or angina that radiate pain to the arm
Presence of benign or malignant tumors within the humerus
If you experience persistent, severe, or worsening pain, it is crucial to seek healthcare advice. A comprehensive medical assessment, including diagnostic imaging and laboratory tests, can identify the exact cause and guide appropriate treatment strategies. Early intervention not only alleviates discomfort but also prevents potential complications such as nerve damage, chronic pain, or systemic health issues.