Comprehensive Guide to Shingles: Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, and Treatment Strategies
Shingles is a painful viral infection caused by reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus. This comprehensive guide explains its causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment options, emphasizing the importance of vaccination and early medical intervention to avoid complications and ensure swift recovery.

Comprehensive Guide to Shingles: Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, and Treatment Strategies
Shingles, medically known as herpes zoster, is a common viral infection that can cause significant discomfort and pain. It primarily manifests as a painful rash, which often appears on the torso, but it can also affect other parts of the body, including the face, neck, and eyes. Understanding the underlying causes, recognizing early symptoms, and knowing effective prevention measures are crucial for managing this condition and reducing the risk of complications.
Shingles occurs when the varicella-zoster virus— the same virus responsible for chickenpox—reactivates after lying dormant in the nervous system. Many individuals who have had chickenpox earlier in life harbor the virus quietly within their nerve tissues. Later in life or when their immune defenses are compromised, this dormant virus can become active again, leading to shingles. Factors such as aging, weakened immune systems due to illness, stress, certain medications, and other health conditions can contribute to the risk of reactivation.
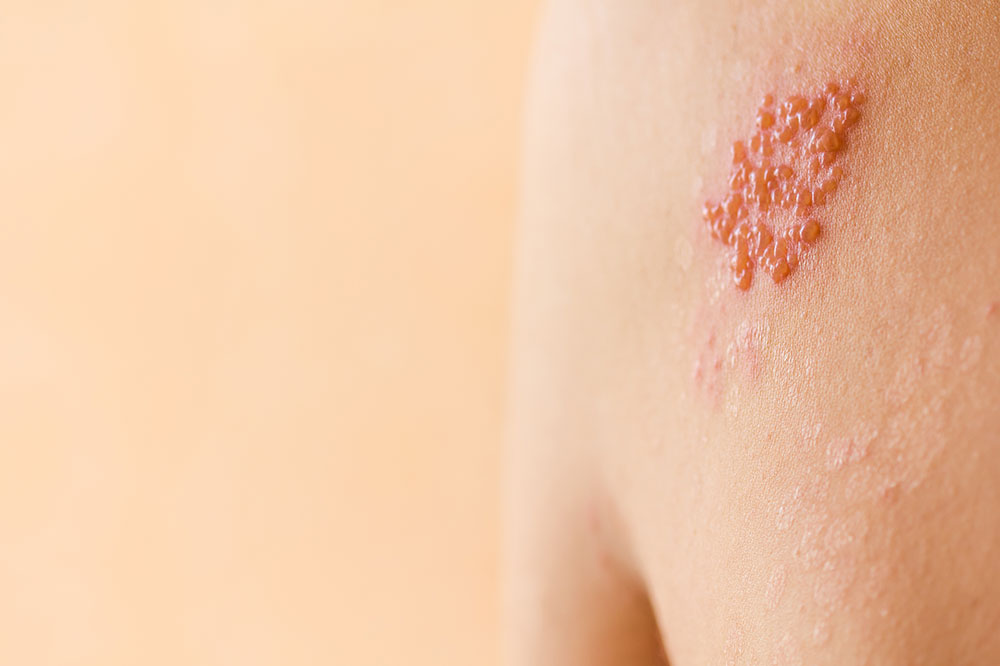
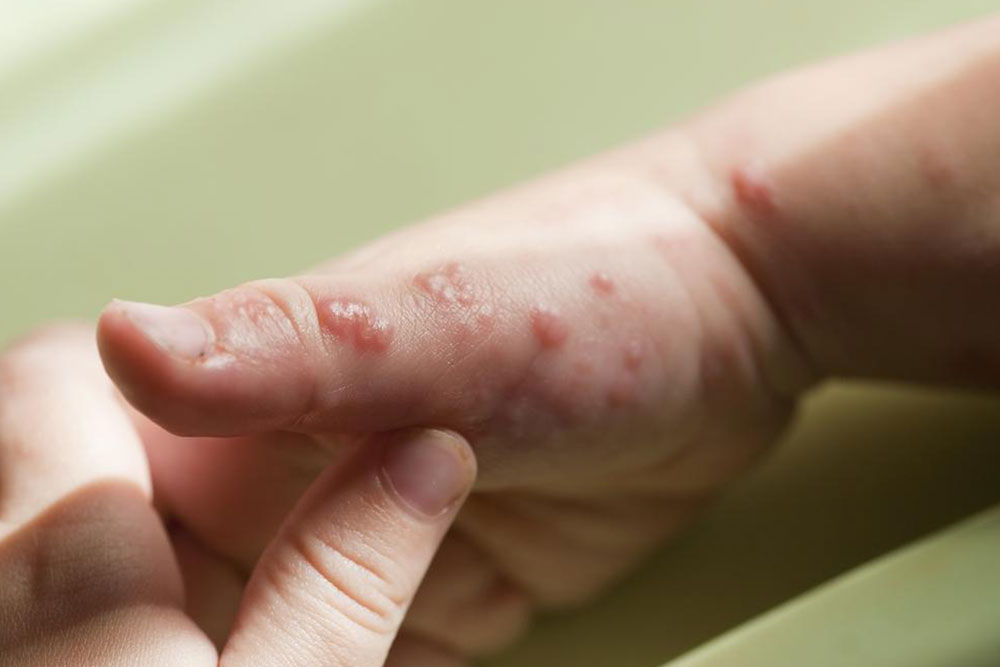
The symptoms of shingles often begin with localized pain, tingling, or a burning sensation along a nerve pathway. This discomfort can precede the appearance of the skin rash by a few days. When the rash appears, it typically manifests as clusters of fluid-filled blisters on a red base, usually confined to one side of the body. Some people also experience fever, fatigue, headache, and sensitivity to light during the early stages of infection.
While shingles is not generally life-threatening, it can lead to severe complications in some cases. The most common complication is postherpetic neuralgia, a persistent nerve pain that lasts weeks or months after the rash has healed. Other serious but rare complications include vision loss if the infection affects the eye, neurological problems, or skin infections. Therefore, prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential.
Prevention is a key aspect in managing shingles risk. Vaccination offers significant protection; the shingles vaccines, such as Shingrix, are recommended especially for older adults as they substantially reduce the incidence and severity of shingles and related complications. In addition to vaccination, maintaining a healthy immune system through balanced nutrition, regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management can help lower the risk.
Exact treatment for shingles involves antiviral medications like acyclovir, valacyclovir, or famciclovir, which are most effective when started early in the course of the illness. These medications can lessen the severity of symptoms, shorten the duration of the rash, and decrease the likelihood of complications. Pain management, including over-the-counter analgesics, prescribed pain relievers, or topical agents, can alleviate discomfort. In some cases, corticosteroids are used to reduce inflammation. Additionally, keeping the affected skin clean and avoiding scratching helps prevent secondary infections.
Awareness and education about shingles are crucial, especially for vulnerable groups such as the elderly or immunocompromised individuals. If you notice symptoms suggestive of shingles, seek medical attention promptly to get appropriate antiviral therapy and reduce the risk of long-term nerve pain.
In summary, shingles is a preventable and manageable condition with timely medical intervention and preventive vaccination. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options can significantly improve quality of life for those affected and help prevent serious complications. Protecting yourself through vaccination and a healthy lifestyle is the best way to reduce your risk of developing shingles and experiencing its associated discomforts.