Comprehensive Guide to Advanced Melanoma: Risks, Treatment Options, and Self-Care Strategies
This comprehensive article explores advanced melanoma, detailing risks, current and emerging treatments, and practical self-care tips. It emphasizes early detection for better outcomes and provides insights into innovative therapies in clinical trials. Suitable for patients, caregivers, and health professionals, the guide aims to increase awareness and promote proactive management of metastatic melanoma to improve survival and quality of life.

Comprehensive Guide to Advanced Melanoma: Risks, Treatment Options, and Self-Care Strategies
Understanding what constitutes advanced melanoma: risks, treatment methods, and patient self-care tips
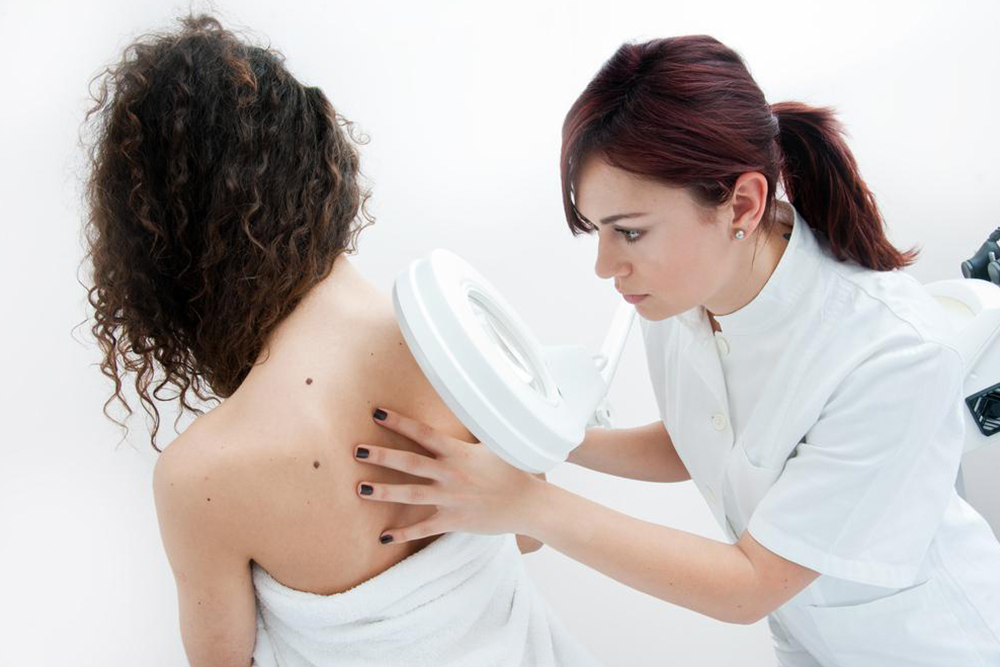
When melanoma, a serious form of skin cancer, progresses beyond the superficial layers of the skin and spreads to other parts of the body, it is classified as advanced or metastatic melanoma. This stage of melanoma involves the spread of malignant cells to internal organs and tissues, including the liver, lungs, brain, lymph nodes, and subcutaneous tissues. Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the risk factors associated with advanced melanoma are essential steps toward early detection and effective management. Symptoms may include swollen lymph nodes, unexplained weight loss, swelling of the liver, persistent headaches, palpable lumps under the skin, bone pain, ongoing cough, and reduced appetite. Once melanoma reaches an advanced stage, treatment options become more complex, often requiring a combination of therapies. Timely medical intervention upon noticing skin changes or related symptoms can significantly improve treatment outcomes.
Factors that elevate the risk of developing melanoma
While excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight or artificial sources like tanning beds remains the primary cause of melanoma, several other factors can increase an individual's risk of developing this aggressive skin cancer. These include:
Use of indoor tanning devices, including tanning lamps and booths
Having numerous moles, especially atypical or dysplastic moles
Fair skin with a tendency to freckle, light-colored eyes, and blond or red hair
A family history of melanoma or other skin cancers
Genetic mutations that predispose to cancer development
Inherited conditions such as Li-Fraumeni syndrome, Werner syndrome, xeroderma pigmentosum, retinoblastoma, or hereditary breast and ovarian cancers
Age over 40, as the risk increases with advancing years
Compromised immune system, whether due to medical conditions or immunosuppressive medications
Recognizing these risk factors aids in early screening and proactive lifestyle adjustments to mitigate melanoma development.
Current therapeutic options available for advanced melanoma
Medical science has developed several effective treatment modalities for combating advanced melanoma, often used in combination based on disease severity and progression. These include:
Surgical excision of primary tumors and affected lymph nodes, especially in the early stages of metastasis
Chemotherapy, which involves drugs to kill cancer cells, though its role in melanoma is now often adjunctive
Targeted therapies that focus on specific genetic mutations within melanoma cells, such as BRAF inhibitors
Immunotherapy, which employs the body's immune system to recognize and attack melanoma cells, including checkpoint inhibitors
Radiation therapy to destroy cancerous tissues and control symptoms
The choice and combination of treatments are personalized, depending on the extent of disease spread, patient health status, and molecular characteristics of the tumor. Advances in targeted and immunotherapies have significantly improved survival rates and quality of life for many patients.
Cutting-edge therapies and ongoing research efforts in advanced melanoma treatment
The scientific community continually explores innovative solutions through clinical trials, aiming to improve outcomes and develop less invasive, more effective treatments. Some emergent therapies under investigation include:
Reflectance confocal microscopy (RCM) and other advanced diagnostic tools for early and precise detection
Immune checkpoint inhibitors that rejuvenate the immune response against melanoma cells
Development of melanoma-specific vaccines to bolster immune defenses
Drugs targeting specific genetic mutations, such as those affecting the BRAF gene
Trials and studies are crucial in validating these approaches, potentially leading to new standards of care in the near future.
Effective self-care and supportive strategies for individuals with advanced melanoma
Managing advanced melanoma requires not only medical treatment but also comprehensive self-care practices to promote physical and emotional well-being. Here are some recommended strategies:
Building a support network and maintaining open communication – Navigating the emotional challenges of metastatic cancer can be overwhelming. Connecting with family, friends, support groups, or mental health professionals offers comfort and guidance. Resources from organizations like the American Cancer Society and the American Melanoma Foundation provide valuable assistance.
Nutrition and hydration – Side effects from treatments such as fatigue or nausea can impair nutrition. Consuming a balanced diet rich in lean proteins, whole grains, healthy fats, fruits, and vegetables can help sustain energy levels. Staying well-hydrated is equally important for recovery and overall health.
Physical activity and adequate rest – Light exercises like yoga, walking, or gentle stretching can reduce stress and improve mood. Ensuring sufficient restful sleep through relaxing routines such as listening to calming music or journaling can enhance recovery.
Regular skin checks are vital. Observing changes in moles or new skin lesions warrants prompt medical evaluation for early detection and treatment. Because early-stage melanoma can often be cured with appropriate intervention, staying vigilant and proactive significantly impacts prognosis. In advanced stages, personalized treatment plans aim to control disease progression, alleviate symptoms, and improve quality of life. Early detection remains the cornerstone of effective melanoma management, emphasizing the importance of routine skin examinations and prompt medical attention for any suspicious skin changes.