Comprehensive Guide to Advanced Breast Cancer: Causes, Treatments, and Support Strategies
This comprehensive guide explores advanced breast cancer, highlighting its causes, diverse treatment strategies including chemotherapy, radiation, hormone, targeted therapies, and the importance of supportive care. Emphasizing personalized treatment plans, the article provides insights into managing side effects and improving patient quality of life. As research advances, new therapies offer hope for better outcomes in metastatic breast cancer. Learn about the latest approaches and holistic support strategies to navigate this complex disease effectively.

Comprehensive Guide to Advanced Breast Cancer: Causes, Treatments, and Support Strategies
Advanced breast cancer, also known as metastatic breast cancer, is a term used when malignant cells originating from the breast have spread beyond the primary tumor site to other parts of the body. This spread, known as metastasis, often involves critical organs such as the lymph nodes, lungs, liver, brain, or bones. Although current treatments cannot often eradicate the disease completely, they aim to control its progression, manage symptoms effectively, and improve the overall quality of life for those affected. Understanding this complex condition is vital for patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals striving to develop the most effective management plans.
One of the most important aspects of managing advanced breast cancer involves recognizing that the disease's behavior varies greatly depending on factors like tumor size, location, molecular characteristics, and the patient’s overall health. Treatments are carefully tailored to address these individual differences, focusing on extending survival, alleviating symptoms, and maintaining functionality. The main goal is not always to cure but to control the disease and improve the patient's day-to-day experiences.
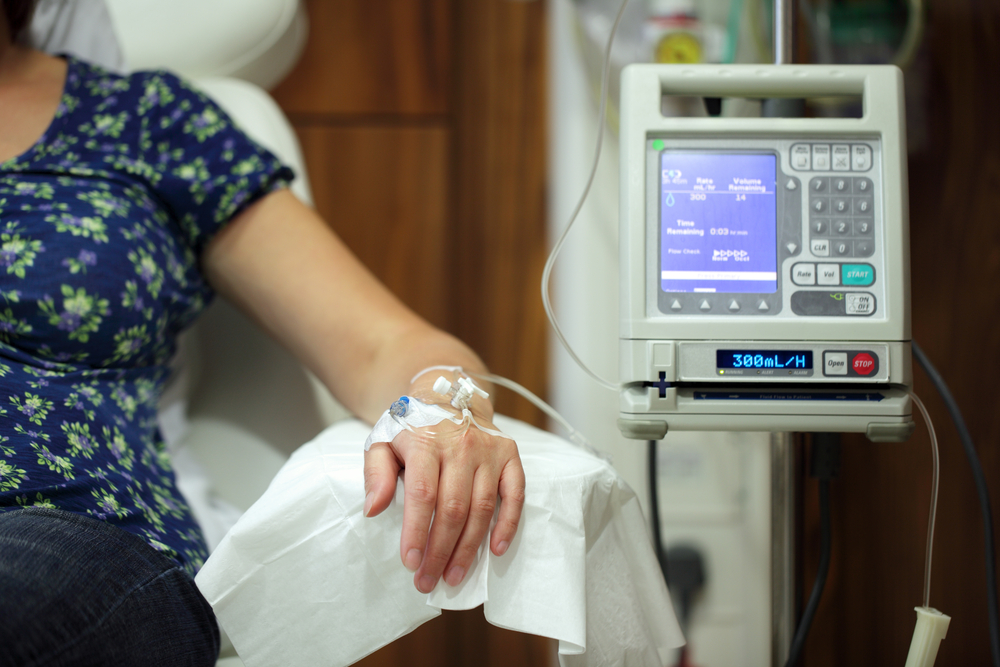
Various treatment modalities are employed in managing advanced breast cancer, and often, a combination of therapies is used to optimize outcomes. These approaches are influenced by the tumor’s characteristics, the extent of metastasis, previous treatments, and the patient’s preferences. Below is an in-depth look into the most common and effective treatment options:
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy involves the use of potent drugs that circulate throughout the body to target and kill rapidly dividing cancer cells. It is usually employed in advanced stages where systemic disease dissemination has occurred. Chemotherapy can be administered intravenously or orally, and the choice of drugs depends on the specific cancer subtype, previous treatments, and the patient’s overall condition.
Radiation Therapy: This treatment involves directing high-energy rays precisely at tumor sites or metastatic lesions to reduce tumor size, alleviate pain, and control symptoms. Radiation therapy can be used in specific areas such as the brain or bones, where metastases cause significant discomfort or functional impairment.
Hormone Therapy: For hormone receptor-positive breast cancers, hormone therapy is vital. It works by blocking the effects of hormones like estrogen and progesterone, which fuel the growth of certain breast cancer cells. This approach can be highly effective and often has fewer side effects compared to chemotherapy, making it a cornerstone in managing hormone-sensitive advanced breast cancers.
Surgical Interventions: While surgery is less common in metastatic disease, it can be performed to remove specific tumors when feasible or to alleviate symptoms caused by primary tumors, such as ulceration or bleeding. Surgical procedures may also be part of a palliative approach to improve quality of life.
Targeted Therapy: Advances in cancer research have led to the development of targeted drugs that specifically inhibit molecular pathways critical for cancer growth. These therapies—such as HER2 inhibitors or CDK4/6 inhibitors—offer precision treatment options that can be more effective and have a different side effect profile compared to traditional therapies.
Combination therapies are common, emphasizing personalized treatment plans based on tumor biology, progression rate, and patient health status. Moreover, ongoing clinical trials continually explore new drugs and methods, providing hope for improved outcomes and even potential cures in the future.
Beyond direct cancer treatments, supportive care is essential. This includes addressing nutritional needs, managing pain and fatigue, providing psychological counseling, and supporting mental and spiritual wellbeing. Such holistic care helps patients maintain dignity, comfort, and resilience throughout their journey.
It’s important to be aware that all treatments carry potential side effects, which can impact healthy tissues and overall health. These effects can be temporary but sometimes persist long-term. Open communication with healthcare providers, regular monitoring, diagnostic tests, and timely adjustments to treatment protocols are crucial for optimal management and minimizing adverse effects.
In summary, advanced breast cancer management is a complex, evolving field that combines multiple treatment modalities tailored to individual patient needs. Advances in targeted therapies and supportive care continue to improve survival rates and quality of life, offering hope and a better future for those facing this challenging diagnosis.