Comprehensive Lifestyle Approaches to Rapidly Lower Cholesterol Levels and Improve Heart Health
Discover comprehensive lifestyle strategies to rapidly lower cholesterol levels. This guide covers essential dietary changes, physical activity, quitting smoking, and alcohol moderation to help improve heart health naturally. Implementing these proven approaches can significantly reduce cardiovascular risks and promote overall wellness. Learn how nutritious eating, regular exercise, and healthy habits are key components in achieving optimal cholesterol balance. Suitable for anyone seeking quick and sustainable ways to manage their heart health effectively.

Effective Strategies for Quickly Reducing Cholesterol and Enhancing Cardiovascular Wellness
High cholesterol levels are a common concern for many individuals aiming to maintain optimal heart health. Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance naturally produced by the liver, crucial for various bodily functions including cell membrane integrity, hormone synthesis, and nerve function. Despite its essential roles, excess cholesterol, particularly low-density lipoprotein (LDL or "bad" cholesterol), can accumulate in artery walls, leading to atherosclerosis, Heart attacks, and strokes. Therefore, understanding effective lifestyle modifications to lower cholesterol is vital for reducing cardiovascular risks and promoting overall well-being.
This comprehensive guide explores proven approaches that can swiftly and sustainably improve your cholesterol profile through diet, exercise, and behavioral changes. Adopting these strategies can not only help lower LDL levels but also elevate HDL ("good" cholesterol), providing a balanced approach to heart health management.
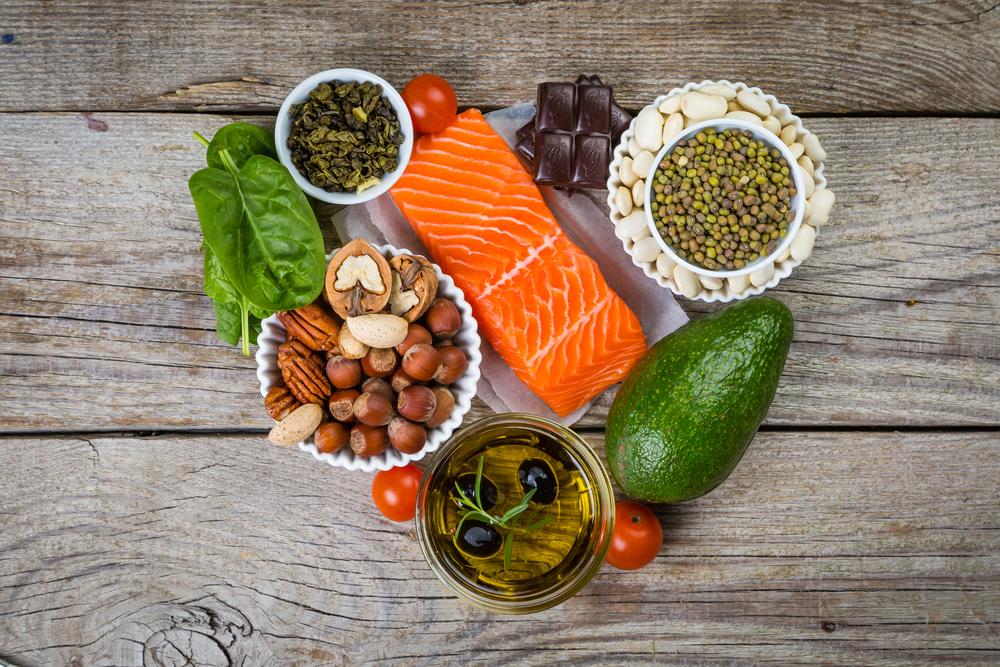
Adopt a Heart-Healthy Diet for Cholesterol Management
Reduce Saturated Fats: Source primarily from full-fat dairy products, red meats, and processed foods. Cutting back on these fats can significantly decrease LDL cholesterol levels.
Eliminate Trans Fats: Present in partially hydrogenated oils found in baked goods, fried foods, and snack foods. Avoiding trans fats is crucial since they not only raise LDL but also lower HDL cholesterol.
Incorporate Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Foods such as fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, sardines, as well as walnuts, flaxseeds, and herring. These fats are known to reduce inflammation and have protective effects against heart disease, even if they don't directly lower LDL cholesterol.
Prioritize Soluble Fiber: Found in oats, barley, beans, lentils, apples, oranges, and Brussels sprouts, soluble fiber helps reduce cholesterol absorption in the bloodstream.
Increase Fruit and Vegetable Intake: Rich in antioxidants, fiber, and essential nutrients, fruits and vegetables contribute to lowering cholesterol and improving arterial health.
Utilize Whey Protein: Derived from dairy, whey protein complements a healthy diet by lowering both LDL cholesterol and blood pressure levels.
Achieving and Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Maintaining an optimal weight is pivotal in cholesterol management. Excess weight, especially around the abdomen, is associated with higher LDL levels and lower HDL levels. Through balanced eating and regular physical activity, individuals can shed excess pounds, leading to improved lipid profiles.
Quit Smoking to Boost HDL Levels
Smoking cessation is essential for heart health. Smoking reduces HDL cholesterol, which plays a protective role by helping to clear LDL cholesterol from arteries. Both active and passive smoking negatively impact HDL levels, increasing cardiovascular risk.
Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Exercise is one of the most effective ways to improve cholesterol levels. Activities such as brisk walking, jogging, cycling, swimming, or aerobics for at least 150 minutes per week or 30 minutes daily can significantly raise HDL cholesterol. Vigorous workouts three times a week further enhance cardiovascular health and lipid profiles.
Practice Responsible Alcohol Consumption
While moderate alcohol intake might slightly increase HDL levels, excessive drinking contributes to high blood pressure, obesity, and other health problems. If you choose to drink, do so in moderation—generally up to one drink per day for women and up to two for men—to avoid adverse effects.
In summary, these lifestyle strategies, combined with medical supervision and prescribed medications when necessary, can lead to meaningful reductions in cholesterol levels. Making consistent, health-conscious choices can result in healthier arteries, decreased risk of cardiac events, and an overall improved quality of life.