Comprehensive Guide to Female Tubal Ligation: Key Facts and Considerations
Female tubal ligation is a trusted permanent contraception method offering long-term sterilization for women. This detailed guide covers the procedure, reversibility, risks, and key considerations to help women make informed reproductive choices. Understanding all aspects of tubal ligation ensures that women can weigh their options carefully, considering future family plans and health implications before proceeding with this irreversible sterilization method.
Comprehensive Guide to Female Tubal Ligation: Key Facts and Considerations
Female tubal ligation remains one of the most reliable and widely chosen permanent contraception methods for women seeking long-term sterilization. Often referred to as getting their tubes tied, this surgical procedure offers women freedom from daily contraceptive methods and alleviates worries about unwanted pregnancies. Typically performed after childbirth or during minimally invasive surgery, tubal ligation provides a dependable solution for women who are certain about not wanting children in the future. However, despite its high effectiveness, there are several factors, risks, and considerations women should evaluate carefully before deciding to undergo this procedure.
This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on the intricate details of female tubal ligation, including the procedural steps, potential reversibility, risks involved, and important personal considerations. Understanding these aspects can help women make informed choices aligned with their reproductive goals and life plans.
Procedure Overview
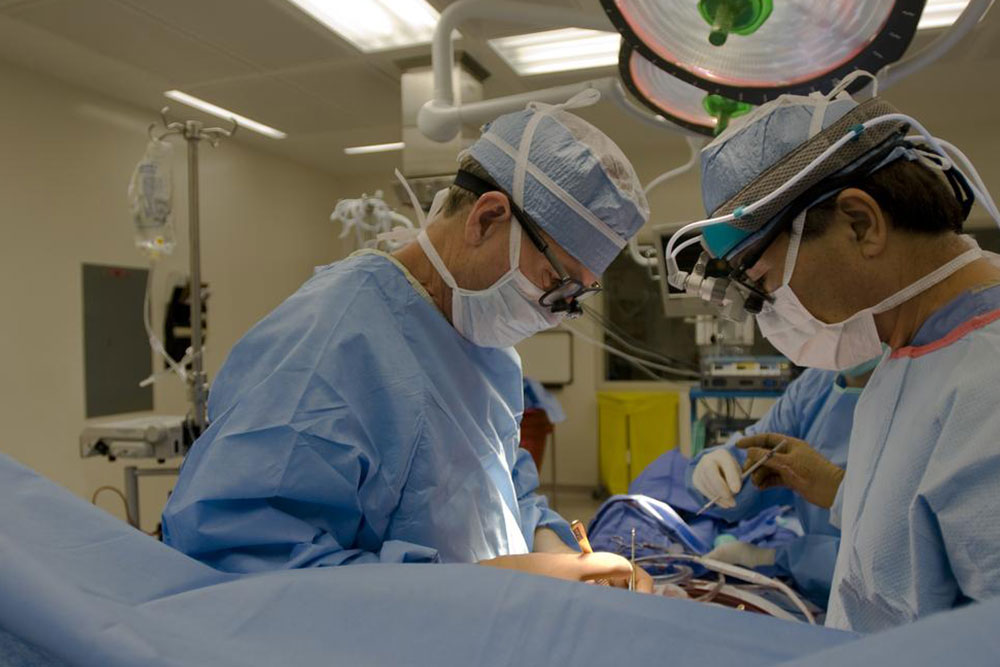
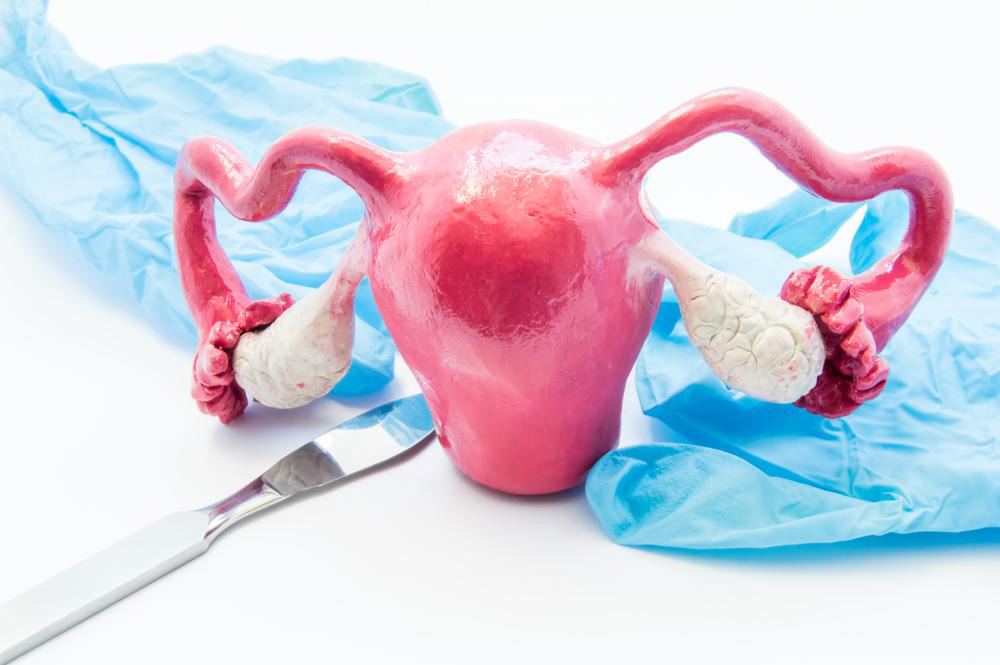
Tubal ligation is a surgical procedure that involves closing or blocking the fallopian tubes to prevent eggs from meeting sperm, effectively stopping fertilization. During the operation, a gynecologic surgeon typically makes small incisions in the abdomen or uses laparoscopy to access the tubes. The tubes are then sealed using clips, rings, electrocoagulation, or sharply cut and sealed, depending on the method chosen. This process creates a physical barrier, preventing conception and rendering pregnancy highly unlikely.
Reversibility and Future Pregnancy
Although tubal ligation is considered a permanent method, reversibility is sometimes possible through surgical procedures. However, rejoining the tubes or removing blockages is complex, expensive, and success depends heavily on the method used initially. Women considering reversal should consult with a reproductive specialist to assess their individual viability. For women who later change their minds, assisted reproductive technologies like in-vitro fertilization (IVF) offer alternative options, bypassing the fallopian tubes entirely. While IVF can be effective, success rates vary based on individual circumstances, age, and health factors.
Possible Risks and Side Effects
Like any surgical procedure, tubal ligation carries potential risks, although serious complications are relatively rare. Common mild side effects include pain, swelling, dizziness, or minor bleeding at the incision sites. More serious, but infrequent, issues can involve infections, damage to surrounding organs, or anesthesia reactions. It’s crucial to monitor symptoms post-surgery and consult a healthcare provider if abnormal signs such as severe abdominal pain, abnormal vaginal bleeding, or signs of infection occur. Moreover, while rare, pregnancy can still occur after tubal ligation, particularly if the tubes become damaged or re-opened, which increases the risk of ectopic pregnancy—a potentially life-threatening condition requiring prompt medical attention.
Is Tubal Ligation Right for You?
Deciding on tubal ligation involves careful consideration of personal, emotional, and future family planning goals. Women in their twenties or those who have not yet experienced major life changes may wish to think twice, as regret can occur later if circumstances change—such as a new partner, remarriage, or a desire for children. It’s important to discuss thoroughly with your partner, family, and healthcare provider your motivations and expectations before opting for permanent sterilization.
External social pressures, relationship issues, or expectations that tubal ligation will solve relationship problems are not advisable reasons for this procedure. Additionally, tubal ligation does not protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs), so barrier methods are still necessary if STI prevention is a priority. If you are contemplating a reversal in the future or remain unsure about permanent sterilization, it’s wise to explore all options and understand that reversal procedures are not always successful and can involve additional costs and risks. Making an informed, well-considered decision is crucial to ensure the procedure aligns with your reproductive desires and overall health.
In conclusion, female tubal ligation is a highly effective form of permanent contraception suitable for women certain they do not wish to conceive in the future. Understanding the procedure, potential risks, and the possibility of future pregnancy options is vital before making this significant decision. Engaging in open discussions with healthcare professionals, considering personal circumstances, and weighing the pros and cons will help you make a choice that best fits your life's goals and health needs.