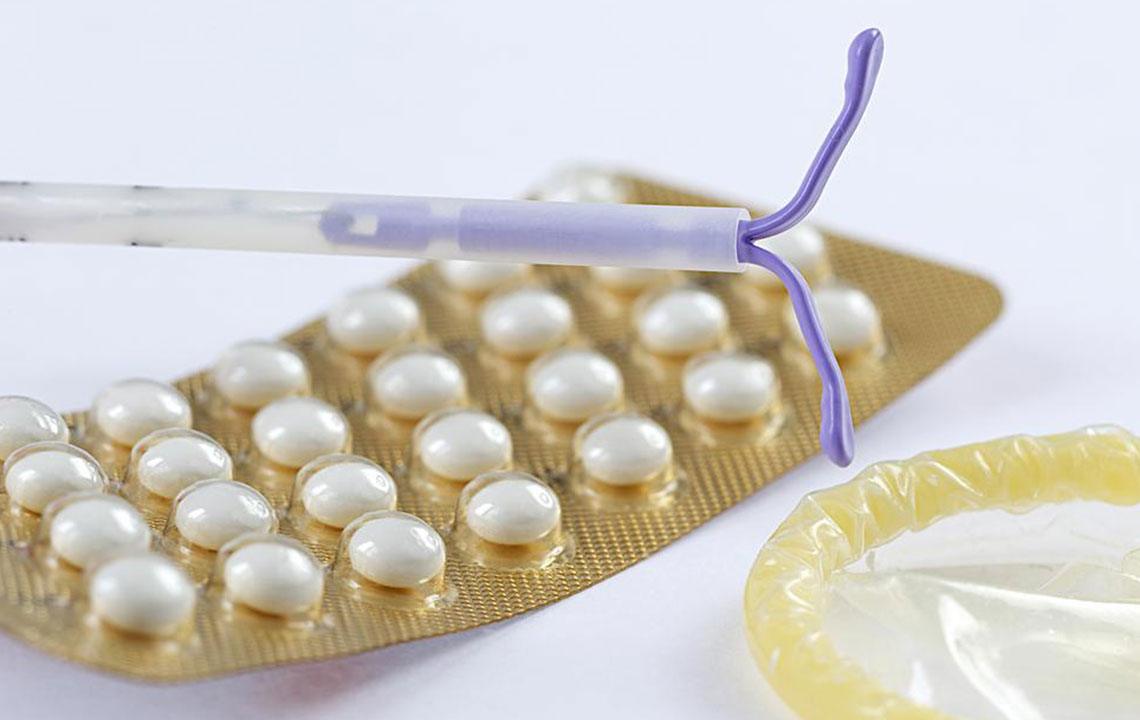
Comprehensive Guide to the Top Three Contraceptive Methods for Effective Family Planning
This comprehensive guide explores the top three contraceptive methods—oral contraceptives, barrier devices, and implants—providing detailed insights to help individuals and couples make informed decisions about family planning. Learn about effectiveness, usage, benefits, and considerations for each method to choose the best option for your reproductive health and lifestyle.
Comprehensive Guide to the Top Three Contraceptive Methods for Effective Family Planning
In today's rapidly advancing world of reproductive health, contraceptive methods have seen remarkable improvements, offering individuals and couples a wider range of safe, reliable, and convenient options to plan their families. Choosing the right contraceptive method is a highly personal decision that depends on various factors such as health conditions, lifestyle, convenience, and future family planning goals. Understanding the most commonly used contraceptive methods is essential for making informed choices and achieving effective family planning. This guide explores the top three contraceptive options: oral contraceptives, barrier devices, and contraceptive implants, providing in-depth information on each method to help you decide which is best suited to your needs.
Contraceptive methods are designed to prevent pregnancy while minimally impacting everyday life. Over the years, these methods have been refined to enhance safety, efficacy, and user comfort. Today, people have access to both reversible and long-acting contraceptives, allowing flexibility in family planning. It's important to consult with healthcare professionals when selecting a method to ensure it aligns with individual health, preferences, and future reproductive plans.
Among the wide variety of contraceptives available today, the three most popular and widely used are oral contraceptives, barrier methods like condoms, and hormonal implants. Each of these options has unique advantages and considerations, which makes understanding their mechanisms and effectiveness crucial for making an educated decision. Let’s delve into these methods in detail.
Oral Contraceptives: The Pill for Convenient Birth Control
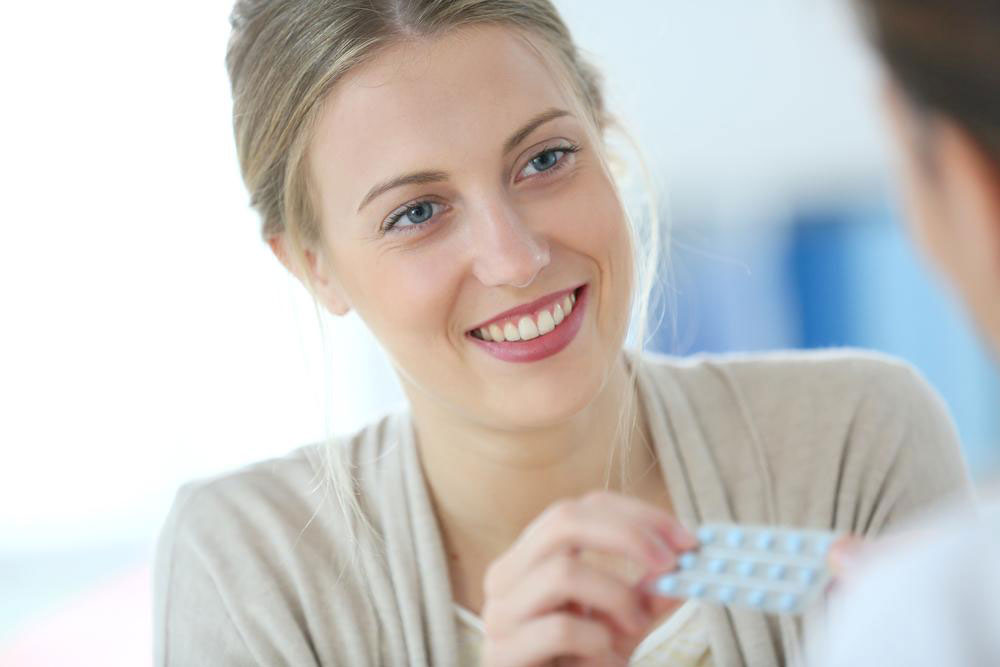
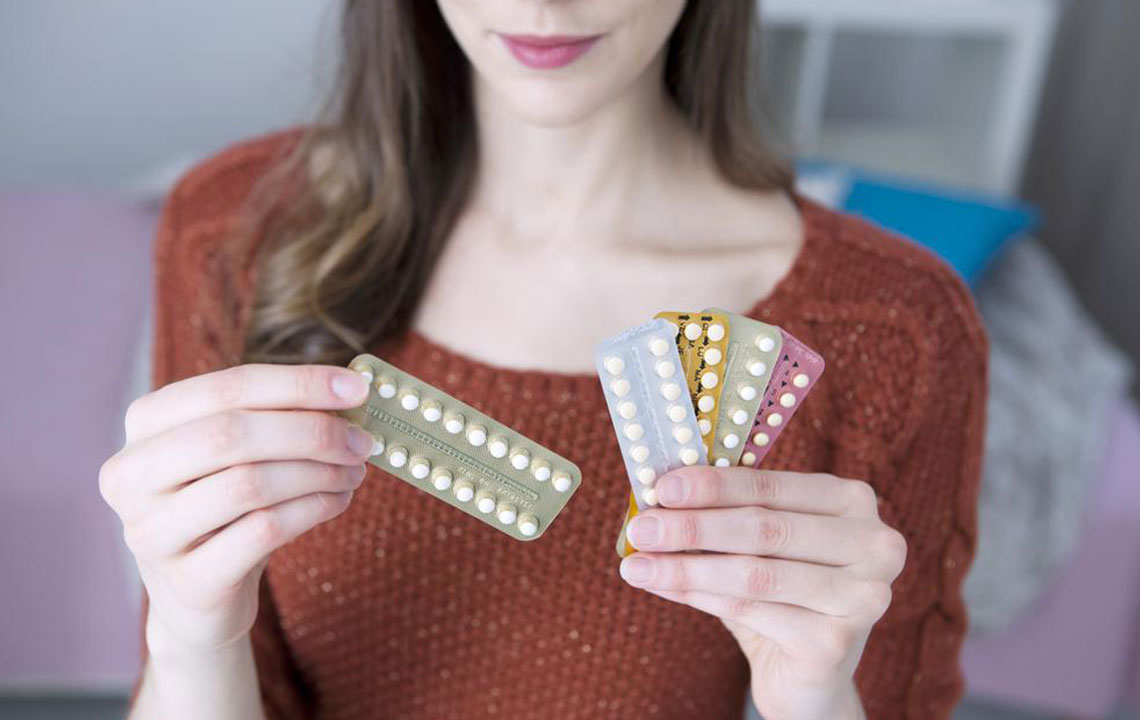
Oral contraceptives, commonly known as birth control pills, are one of the most trusted and widely used methods of preventing pregnancy. These pills contain synthetic hormones—either progestin alone or a combination of estrogen and progestin—that work by inhibiting ovulation, which is the release of an egg from the ovaries. Without ovulation, fertilization cannot occur, thus preventing pregnancy. The convenience and high efficacy rate of oral contraceptives have contributed to their popularity among women worldwide.
Availability: Birth control pills are available by prescription from healthcare providers. They come in various formulations and dosages tailored to individual needs, including options for those who cannot tolerate estrogen or have other health considerations.
Effectiveness: When taken perfectly, oral contraceptives boast over 99% effectiveness in preventing pregnancy. However, typical use, which may involve missed doses or inconsistent intake, reduces effectiveness slightly. Consistency is key to ensuring optimal protection.
Advantages: Besides preventing pregnancy, oral contraceptives can regulate menstrual cycles, reduce menstrual pain, and improve acne in some women. They are discreet and do not interfere with sexual activity.
Limitations: Birth control pills do not protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Some women may experience side effects such as nausea, weight changes, mood shifts, or spotting between periods. It’s essential to have medical consultation to determine suitability and discuss potential risks.
Who should consider this method: Women in good health seeking a reliable, reversible form of contraception who can adhere to daily pill schedules.
Barrier Devices: Easy-to-Use Protection with Added STI Prevention
Barrier methods are physical or chemical barriers that prevent sperm from reaching the egg. Among them, condoms are the most accessible and commonly used form of contraception worldwide. They are simple to use, affordable, and readily available at pharmacies without a prescription.
How they work: Condoms are sheath-like coverings designed to fit over the penis during sexual intercourse. They trap semen, preventing sperm from entering the vagina and reaching the uterus, thus preventing fertilization.
Effectiveness: When used correctly every time during intercourse, condoms are about 98% effective. However, with typical use, effectiveness drops slightly due to possible breakage or incorrect application.
Additional benefits: One of the key advantages of condoms is their barrier against sexually transmitted infections (STIs), including HIV, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and syphilis. This dual protection makes them a unique and essential choice for sexual health.
Limitations: Some users may find condoms reduce sensation or cause allergic reactions, particularly latex allergies. It’s important to choose the right type, such as latex-free options if sensitivities exist.
Who should consider this method: Individuals and couples seeking a non-hormonal, easy, and cost-effective option that also offers STI protection.
Contraceptive Implant: Long-Acting Reversible Contraception
The contraceptive implant, often marketed under the brand name Nexplanon, is a small, flexible rod about the size of a matchstick that is inserted under the skin of the upper arm by a healthcare professional. It provides long-term birth control with high efficacy and minimal maintenance.
How it works: The implant releases a steady, low dose of progestin hormone, which prevents pregnancy primarily by thickening cervical mucus, thereby blocking sperm movement. Additionally, it inhibits ovulation in some women.
Duration of protection: The implant offers protection for up to four years, making it a highly convenient option for women who seek long-term contraception without daily or monthly attention.
Reversibility: One of the major advantages of the implant is its reversibility. Removal by a healthcare provider at any time restores fertility fairly quickly, allowing women to conceive once the implant is removed.
Effectiveness and safety: The implant boasts over 99% effectiveness at preventing pregnancy. Side effects may include irregular bleeding, changes in menstrual flow, or hormonal side effects, but serious complications are rare.
Who should consider this method: Women looking for a long-term, reversible contraception that requires minimal maintenance and has a high success rate.
Conclusion: Making Informed Choices in Family Planning
Choosing the right contraceptive method is a deeply personal decision that should be made based on individual health status, lifestyle, and reproductive goals. Consulting healthcare professionals can help determine the most suitable option tailored to your needs, whether it’s a daily pill, a barrier device, or a long-acting implant. By understanding the benefits and limitations of each method, you can confidently make choices that support your well-being and family planning objectives.
Remember, no contraceptive method is one-size-fits-all. Regular medical advice and check-ups are essential to ensure continued effectiveness and to address any concerns or side effects. Family planning is a significant journey that benefits from knowledge, communication, and professional guidance, ensuring safe, effective, and satisfying outcomes for you and your loved ones.