Comprehensive Guide to Gout: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Management Strategies
This comprehensive guide explores gout, its causes, symptoms, and the latest treatment strategies. Learn how medication, diet, and lifestyle changes can effectively prevent flare-ups and manage this painful condition. Early diagnosis and proper management are essential for reducing long-term joint damage and improving quality of life. Discover practical tips on maintaining uric acid levels, dietary recommendations, and preventive measures to keep gout under control.

In-Depth Insights into Gout and Its Treatment Methods
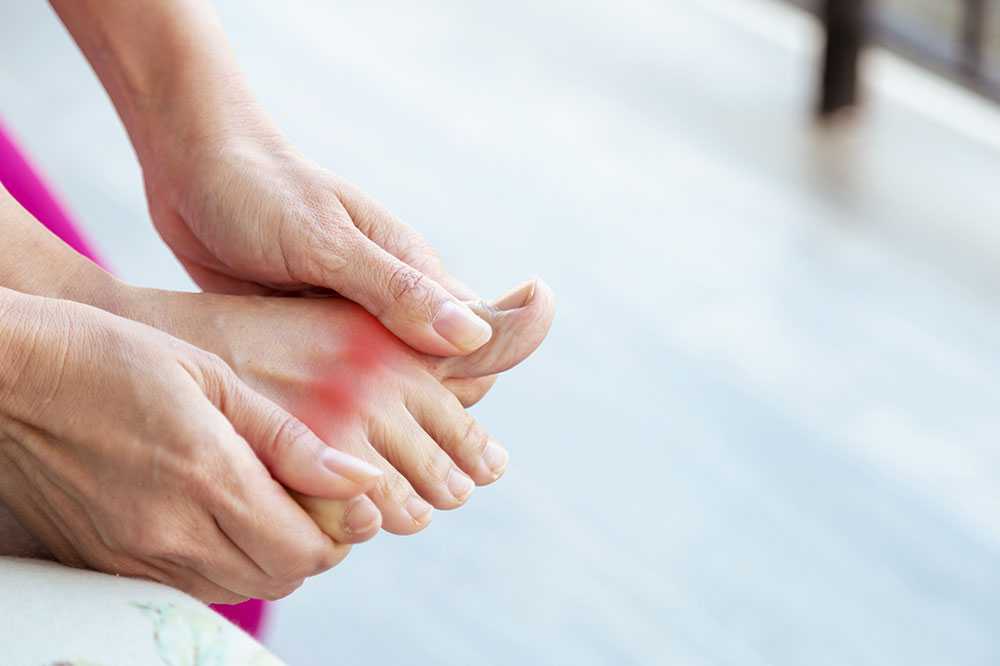
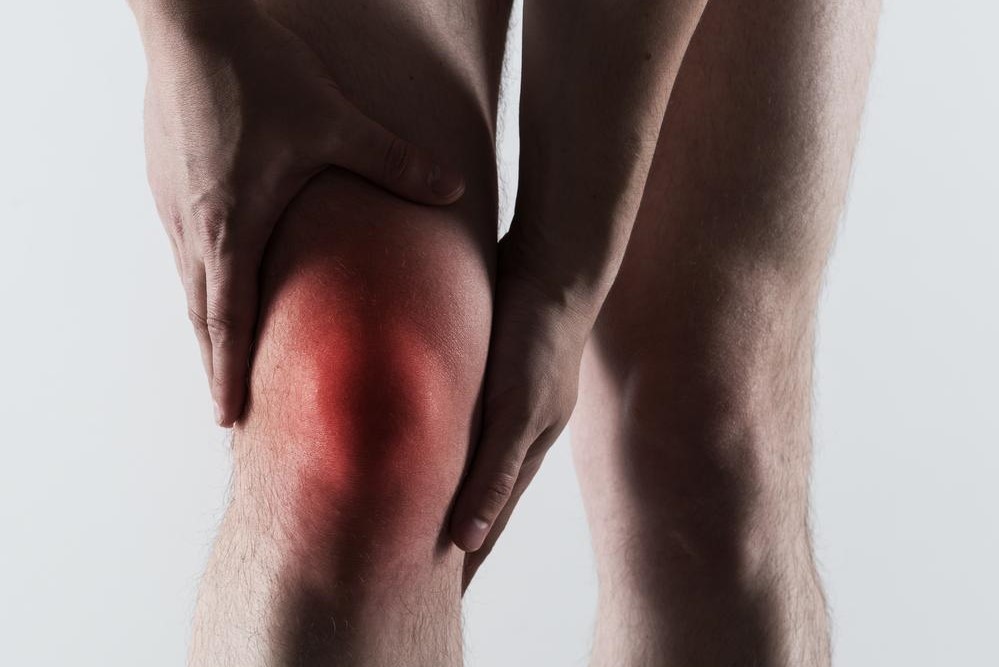
Gout is a prevalent form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by sudden and severe episodes of joint pain, swelling, redness, and warmth. It primarily affects a single joint at a time, with the big toe being a common initial site. Recognizing gout early and understanding its underlying causes are essential steps toward effective management. This article offers a thorough overview of gout, including its causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, treatment options, and preventive strategies, providing readers with valuable knowledge to take control of their health.
Gout is caused by the buildup of uric acid in the bloodstream, leading to the formation of sharp uric acid crystals within joints. The resulting inflammation causes intense pain and swelling that can range from mild discomfort to debilitating episodes. Recognizing the symptoms early and seeking appropriate medical advice are vital to prevent permanent joint damage and improve quality of life. Management of gout involves a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and dietary modifications tailored to reduce uric acid levels and prevent new attacks.
The core treatment approach for gout aims to lower serum uric acid levels, reduce inflammation, and control pain. Medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and colchicine are commonly prescribed during acute flare-ups to provide swift relief. Long-term management focuses on urate-lowering therapies, including allopurinol and febuxostat, which help reduce uric acid production. Regular monitoring of uric acid levels is essential for adjusting treatment plans and preventing future crises.
Diet and lifestyle play crucial roles in managing gout effectively. Patients are advised to avoid foods rich in purines, such as organ meats, shellfish, and certain fish varieties, which can increase uric acid production. Alcohol consumption, especially beer and spirits, should be limited or avoided since it interferes with uric acid excretion. Sugary foods and beverages, processed meats, and foods high in fructose are also linked to gout attacks. Instead, adopting a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and plenty of water helps promote uric acid excretion and maintain overall joint health. Maintaining a healthy weight, staying hydrated, quitting smoking, and exercising regularly are additional strategies to reduce the risk of gout episodes.
Prevention remains a key aspect of managing gout. Routine health check-ups, blood tests to monitor uric acid levels, and adherence to prescribed medication regimens help prevent recurring flare-ups. Being vigilant about early symptoms such as sudden joint swelling, warmth, and pain can lead to prompt treatment, minimizing long-term joint damage. Patients should consult healthcare professionals for personalized treatment plans and guidance tailored to their specific health conditions.
In summary, gout is a complex condition that requires a multifaceted management approach. Combining medical treatment with lifestyle and dietary modifications can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of attacks. By staying informed and proactive, individuals living with gout can lead healthier, more comfortable lives, preventing complications and maintaining joint integrity over time.