Comprehensive Guide to Identifying Early Signs of Neuropathy and Taking Action
Neuropathy is a common nerve disorder with diverse symptoms. Early signs include tingling, numbness, muscle weakness, and organ-related issues. Recognizing these symptoms early and consulting a neurologist can prevent severe complications, improving quality of life. This comprehensive guide explains the key indicators and necessary steps for effective management and prevention of neuropathy, emphasizing timely medical intervention to safeguard nerve health and overall well-being.

Comprehensive Guide to Identifying Early Signs of Neuropathy and Taking Action
Neuropathy, also known as peripheral neuropathy, is a condition characterized by damage or dysfunction of the peripheral nerves — the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. It is a common neurological disorder that can affect individuals of all ages, though it is more frequently diagnosed in people over the age of 55. The significance of early recognition of neuropathy symptoms cannot be overstated since early intervention can prevent the progression of nerve damage and lower the risk of severe complications. This detailed guide aims to educate readers about the critical signs of neuropathy, the potential symptoms to watch for, and the steps you should take if you suspect you have this condition.
Neuropathy manifests with a wide range of symptoms that can sometimes be confusing or mimic other ailments. Its presentation varies depending on which nerves are affected, whether sensory nerves, motor nerves, or autonomic nerves that control functions like heart rate, digestion, and bladder functions. While it commonly occurs in older adults, younger individuals, including those with certain medical conditions like diabetes, autoimmune diseases, or vitamin deficiencies, are also at risk.
The symptoms of neuropathy are diverse and may appear gradually or suddenly. Recognizing these early signs is essential for timely diagnosis and management, which can significantly improve the patient's quality of life. Symptoms can range from mild tingling to severe pain, muscle weakness, or even organ dysfunction. Ignoring these signs may lead to worsening conditions, increased discomfort, or complications affecting one’s overall health.
Major Indicators of Neuropathy You Should Not Miss
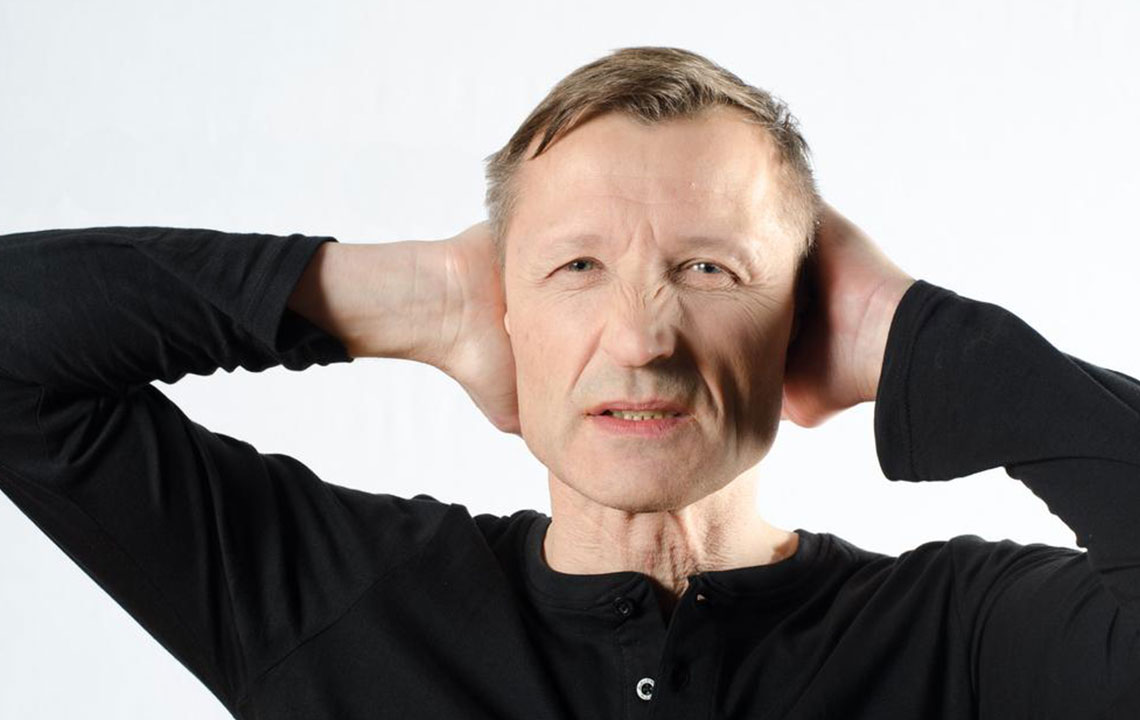
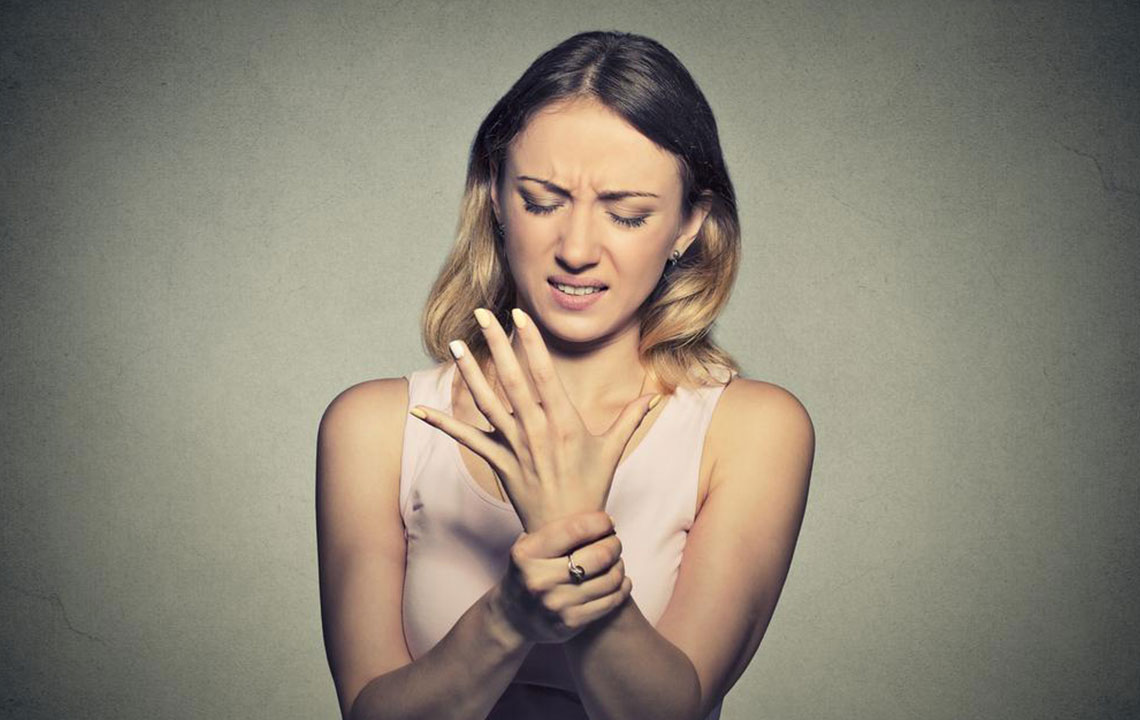
Sensory Symptoms: These are among the earliest symptoms and often include tingling sensations, burning feelings, numbness, or a pins-and-needles sensation, particularly in the extremities such as hands and feet. Patients may describe these sensations as crawling or itching and may notice increased sensitivity to touch or temperature changes.
Muscle Weakness and Motor Difficulties: As neuropathy progresses, there may be noticeable muscle weakness, twitching, cramps, and difficulty controlling specific movements. People might experience frequent falls, clumsiness, or problems with coordination, which can significantly impair daily activities.
Autonomic Nerve-Related Symptoms: The autonomic nervous system regulates involuntary bodily functions. Damage to these nerves can lead to digestive issues like constipation or diarrhea, abnormal heart rhythms causing dizziness or fainting, bladder dysfunction such as incontinence or retention, as well as sexual dysfunction. Excessive sweating or inability to sweat normally can also occur.
Why Recognizing These Signs Early Matters
If you observe any of these symptoms, it is imperative to seek medical advice promptly. Early diagnosis by a neurologist allows for intervention strategies that can halt or slow nerve degeneration. Treatments may include medications, physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, and managing underlying conditions like diabetes or vitamin deficiencies. Addressing symptoms early can prevent long-term damage, decrease pain, restore function, and improve overall quality of life.
Additional Factors and Risk Elements
Understanding the risk factors associated with neuropathy can further aid in prevention. These include chronic illnesses such as diabetes mellitus, autoimmune diseases like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis, infections, exposure to toxins, nutritional deficiencies (particularly B vitamins), and alcohol abuse. Additionally, certain medications, especially chemotherapy drugs, can cause nerve damage as a side effect.
Preventive Measures and When to See a Doctor
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is vital in preventing neuropathy. This includes controlling blood sugar levels if diabetic, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, ensuring a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, and avoiding nerve-toxic substances. Regular check-ups can help catch underlying health issues early. If you experience persistent numbness, tingling, weakness, or organ-related symptoms, consult a healthcare professional immediately. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are key to managing neuropathy effectively.
Taking note of these symptoms and seeking medical advice promptly can make a significant difference in managing neuropathy. Early intervention can prevent further nerve damage, alleviate symptoms, and improve overall health outcomes. Don't ignore the warning signs—your nerves need proper attention and care.