Comprehensive Home Care Tips for Effectively Managing Hematomas
This comprehensive guide offers effective home strategies for managing hematomas, emphasizing dietary tips, RICE treatment, and when to seek medical care. Learn how to speed up healing and reduce symptoms safely at home, ensuring prompt and effective recovery from minor hematomas with expert advice and practical tips.
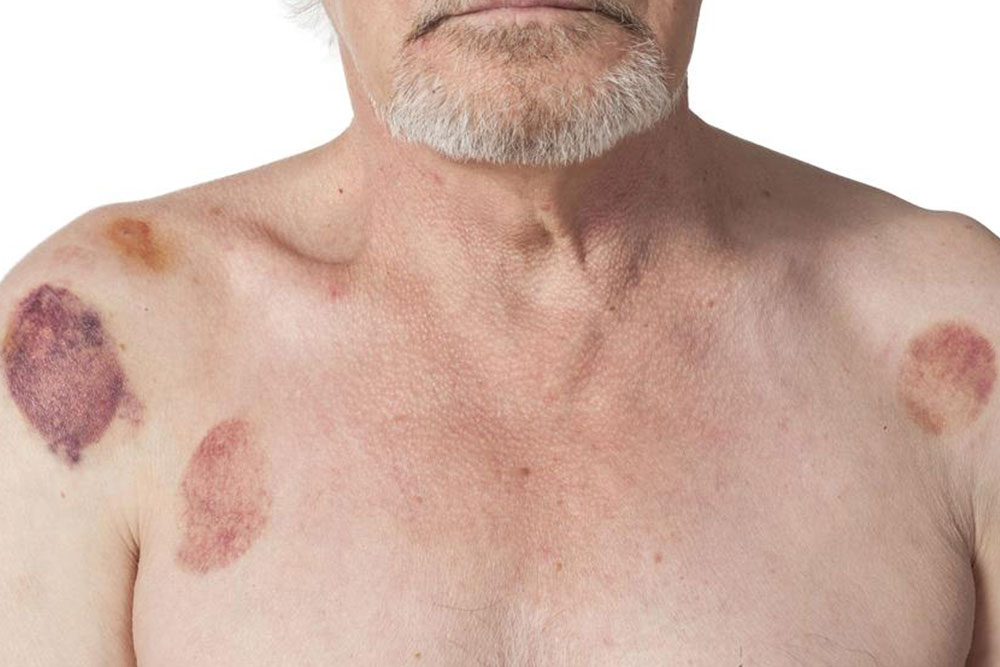
Comprehensive Home Care Tips for Effectively Managing Hematomas
Hematomas are localized collections of blood that form beneath the skin or within tissues following vascular injury, often resulting from blunt trauma or impact. Recognizing how to manage hematomas at home can significantly alleviate discomfort and promote faster healing, especially in minor cases. However, understanding when professional medical intervention is necessary is crucial to prevent complications. This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies, dietary recommendations, and home treatments that can help you handle hematomas safely and efficiently.
Understanding Hematoma Symptoms and Risks
Detecting early signs of a hematoma can ensure timely management and reduce the risk of further complications. Common symptoms include:
Severe or persistent pain localized to the affected area
Visible swelling or bulging
Discoloration or bruising that darkens over time
Weakness or numbness in the surrounding area
Headaches, especially if associated with head trauma
Redness or warmth around the affected zone
If symptoms intensify or if there are signs of infection, such as fever, pus, or increasing redness, immediate medical attention is necessary. While minor hematomas can often be managed at home, severe cases—such as large, rapidly expanding hematomas or those causing significant pain—require urgent medical evaluation and possibly surgical intervention.
Effective Home Remedies and Management Strategies
Managing a hematoma at home involves a combination of proper nutrition, physical care, and rest. Implementing these strategies can help manage symptoms and accelerate healing.
Proper nutrition is essential in supporting the body's natural healing processes. Consuming nutrient-rich foods that supply the right vitamins and minerals can significantly reduce recovery time and minimize bruising. Here are key dietary recommendations:
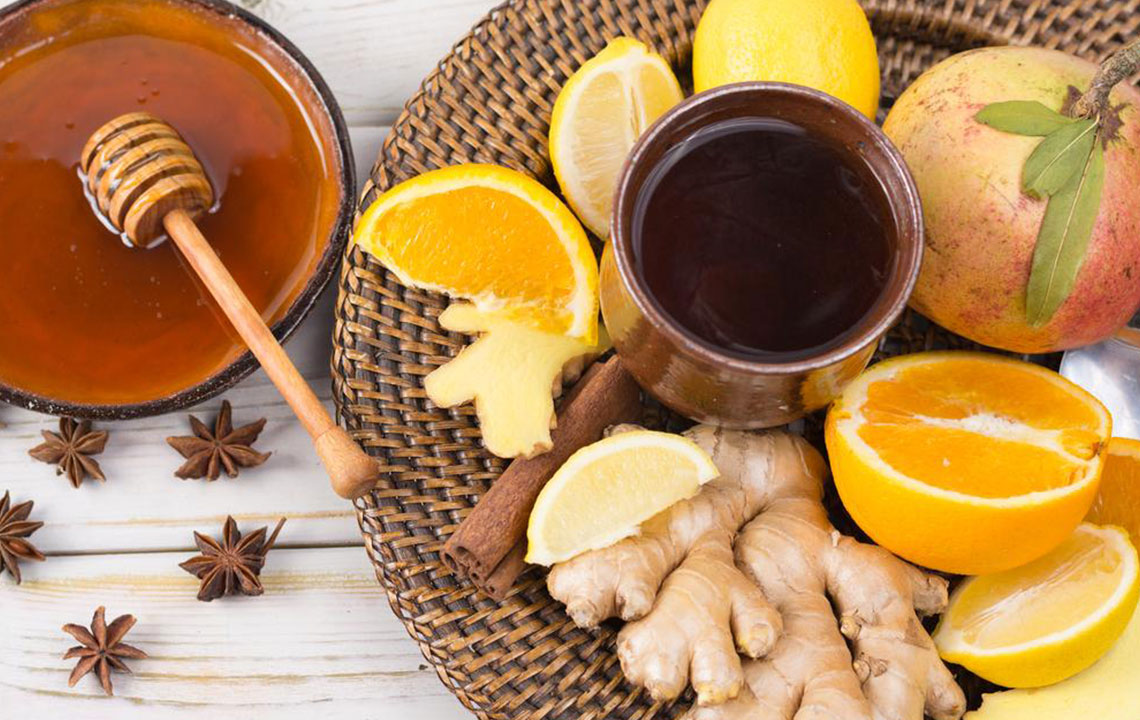
Vitamin C: An antioxidant that plays a vital role in restoring tissue integrity and reducing bruising. Incorporate citrus fruits such as oranges, lemons, and grapefruits, along with strawberries, papayas, bell peppers, broccoli, and pineapples.
Protein: Critical for repairing damaged tissues and promoting cell regeneration. Include lean meats like chicken and turkey, seafood like salmon and tuna, eggs, dairy products, and plant-based sources such as soy, quinoa, nuts, seeds, spinach, lentils, and beans.
Vitamin K: Important for blood clotting and promoting proper healing. Add spinach, kale, parsley, broccoli, dairy products, and eggs to your diet.
Alongside these dietary enhancements, staying well-hydrated facilitates detoxification and tissue repair. Drink plenty of herbal teas and fresh fruit juices while avoiding caffeine, alcohol, and sugary processed drinks, which can impede healing efforts.
Home treatment methods like RICE—Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation—are proven effective for minor hematomas. These techniques reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation, fostering a conducive environment for healing:
Rest: Limit movement and avoid strenuous activity around the affected area for 1-3 days to prevent further bleeding and aggravation.
Ice: Apply an ice pack wrapped in a cloth to the affected site for 15-20 minutes every couple of hours during the first 48 hours. This reduces pain, swelling, and internal bleeding. Avoid direct contact with skin to prevent frostbite.
Compression: Use an elastic bandage to gently compress the area, helping control swelling. Ensure the bandage is snug but not too tight, as excessive pressure can restrict blood flow and slow healing.
Elevation: Keep the injured limb elevated on pillows or cushions to decrease blood flow to the area, further reducing swelling and soreness.
For ongoing pain or swelling, over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or NSAIDs like ibuprofen can be used, but always consult a healthcare professional before medication use.
It is important to monitor the hematoma closely. If symptoms worsen or do not improve within a few days, seek medical care promptly. Remember, while home management can be effective for minor hematomas, professional medical assessment ensures proper diagnosis and care for more serious cases.
By combining dietary support, physical care, and rest, you can efficiently manage hematomas at home while reducing discomfort and promoting faster recovery. Always prioritize consulting healthcare providers, especially when symptoms are severe or persistent, to prevent further health issues.





