Comprehensive Strategies for Relieving Back Muscle Discomfort and Preventing Future Injury
This comprehensive article explores effective strategies for managing back muscle discomfort, emphasizing the importance of understanding causes, employing initial treatments like cold and heat therapy, engaging in safe exercise, and adopting lifestyle modifications for prevention. It highlights the significance of professional consultation for personalized care and discusses warning signs requiring urgent medical attention. The article aims to empower individuals to alleviate back pain, improve mobility, and prevent future episodes through evidence-based practices and ergonomic adjustments, promoting overall spinal health.

Comprehensive Strategies for Relieving Back Muscle Discomfort and Preventing Future Injury
Back muscle discomfort is an extremely prevalent issue affecting people of all ages, occupations, and lifestyles. It can significantly impair daily functional activities, reduce productivity, and diminish overall quality of life. Whether the discomfort is caused by sudden strains, chronic poor posture, or minor injuries, understanding effective management and prevention techniques is vital for maintaining spinal health and ensuring mobility. This comprehensive guide delves into the various causes of back muscle pain, diagnostic considerations, and evidence-based strategies to alleviate discomfort and prevent its recurrence.
Understanding the root causes of back muscle discomfort is crucial as it dictates the appropriate treatment approach. Common causes range from muscular overexertion and strains to structural issues such as herniated discs, inflammation in spinal joints, fractures, and improper or awkward movements like prolonged crouching or twisting. Lifestyle factors, including poor posture during prolonged sitting, repetitive lifting, or inadequate ergonomic setups at work, also contribute significantly. Early recognition of symptoms such as muscle stiffness, limited range of motion, sharp or dull pain radiating to hips, thighs, or shoulders helps tailor effective interventions.
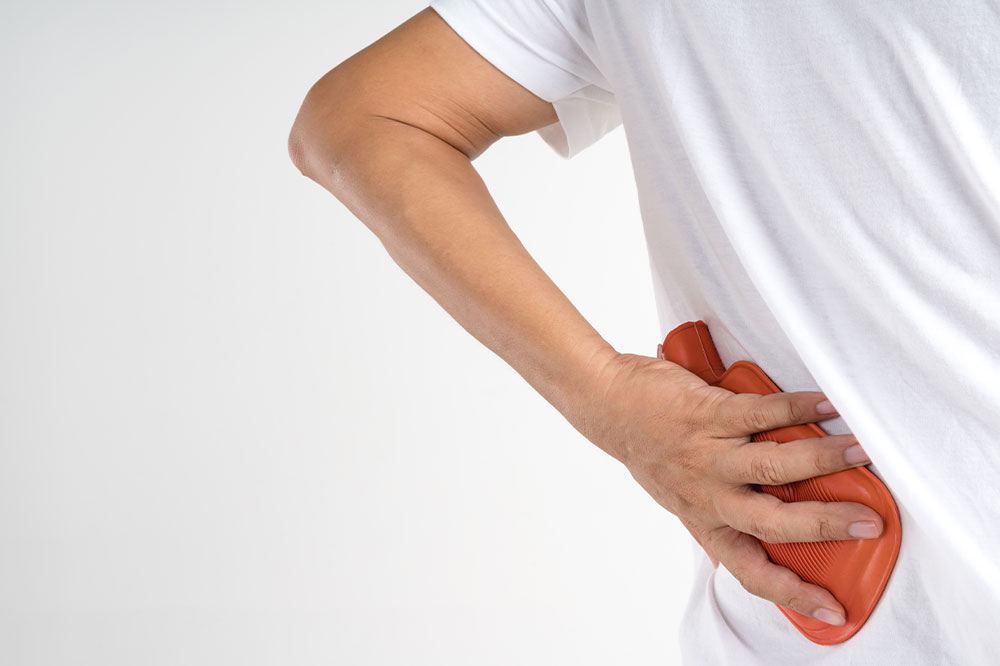
When managing back muscle discomfort, a multifaceted approach yields the best outcomes. Immediate relief often involves applying cold therapy—using ice packs for 20 to 25 minutes every three hours during the initial stages of injury. Cold therapy helps reduce inflammation and swelling, thereby alleviating pain. As inflammation diminishes, transitioning to heat therapy, such as warm compresses, hot baths, or heating pads, can relax tight muscles and improve blood flow, facilitating healing. It’s important to combine these modalities with gentle stretching exercises to maintain mobility and prevent stiffness. Exercise regimens should be supervised by healthcare providers or physical therapists to avoid aggravating the condition.
Medications, notably non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can provide temporary pain relief but should be used judiciously under medical supervision to avoid adverse effects. In certain cases, muscle relaxants may be prescribed to ease severe spasms. Additionally, physical therapy plays a vital role in restoring muscle strength, improving flexibility, and correcting posture-related issues that contribute to muscle strain. Techniques such as massage, ultrasound therapy, and targeted strengthening exercises enhance recovery and diminish the chances of future episodes.
Adopting lifestyle modifications is key to preventing back discomfort. Ergonomic assessments of workspaces, proper lifting techniques, maintaining a healthy weight, and engaging in regular low-impact physical activity like swimming, walking, or yoga can fortify back muscles and improve spinal stability. Postural awareness during daily activities—such as sitting, standing, or sleeping—is essential. Moreover, educating oneself on body mechanics and employing proper ergonomics can significantly reduce undue strain on the back.
In addition to treatment and prevention, recognizing warning signs that necessitate immediate medical attention is vital. Symptoms such as persistent numbness, weakness, loss of bowel or bladder control, or severe unrelenting pain may indicate serious underlying conditions like nerve compression or fractures, requiring urgent medical evaluation. Consulting healthcare professionals—including general practitioners, orthopedists, or neurologists—ensures a precise diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
In conclusion, managing back muscle discomfort involves a combination of timely interventions, lifestyle adjustments, and preventive practices. By understanding causes, employing appropriate therapies, and maintaining awareness of proper body mechanics, individuals can reduce pain, enhance mobility, and prevent future episodes of back discomfort. Prioritizing spinal health through education and proactive measures is key to a pain-free and active lifestyle.