Comprehensive Guide to Treating Age Spots: Effective Strategies and Expert Tips
Learn about effective strategies to treat age spots, including topical treatments and medical procedures. This comprehensive guide covers causes, diagnosis, and expert-recommended options to improve skin appearance. Discover how to safely manage age spots for a more even and youthful skin tone.
Comprehensive Guide to Treating Age Spots: Effective Strategies and Expert Tips
Age spots, medically known as liver spots or solar lentigines, are a common dermatological concern, especially among individuals over the age of 40. These pigmentation changes are characterized by flat, brown, or black spots that appear on the skin, particularly in areas frequently exposed to sunlight. While they are generally harmless, many seek to reduce their appearance for cosmetic reasons. This comprehensive guide explores the causes, diagnosis, and a wide array of treatment options available to effectively address age spots, helping you make informed decisions about managing this skin condition.
Understanding the Causes of Age Spots
Age spots develop due to an increase in melanin production within certain areas of the skin, often triggered by prolonged sun exposure over the years. The primary culprit is ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun, which accelerates skin aging and stimulates excess melanin synthesis. As skin ages naturally, its ability to regenerate diminishes, making pigmentation issues more prominent. Other contributing factors include genetic predisposition, repeated tanning—whether natural or artificial—and exposure to environmental pollutants.
Age spots tend to be more prevalent in individuals with fair skin, although people of all skin types can develop them. Areas highly exposed to the sun, such as the face, hands, shoulders, chest, and forearms, are especially prone to discoloration. These spots vary in size, shape, and color, ranging from light brown to dark brown or black. Despite their cosmetic concern, age spots are generally painless and do not cause medical problems; however, distinguishing them from other pigmented lesions, including potential skin cancers, is crucial for skin health.
How Are Age Spots Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of age spots involves a thorough clinical examination by a qualified dermatologist. Visual assessment provides initial insights, but doctors may perform additional tests to confirm the diagnosis or rule out other skin conditions. In certain cases, a biopsy might be necessary, especially if the spots have irregular borders, color variation, or rapid changes, to exclude malignancies like melanoma or other pigmented lesions. Proper diagnosis is essential to ensure appropriate treatment and monitor any unusual changes in skin pigmentation.
Effective Treatment Options for Age Spots
Although age spots are benign and do not pose health risks, many individuals opt for treatment to improve their skin’s appearance and restore confidence. Today, there are numerous options ranging from topical creams to advanced dermatological procedures. Treatment effectiveness depends on various factors, including skin type, age, the number and size of spots, and personal preferences. Consulting with a dermatologist is crucial for selecting a safe and effective treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
Topical Treatments: Gradual Lightening Solutions
One of the first lines of attack against age spots involves topical medications. These creams and ointments are designed to inhibit melanin synthesis and promote skin renewal. Common ingredients include hydroquinone, which acts as a skin lightening agent, retinoids like tretinoin that accelerate cell turnover, and other agents such as kojic acid or vitamin C derivatives. Regular application coupled with diligent sun protection can lead to noticeable fading over several weeks or months.
It’s important to note that topical treatments might cause side effects like dryness, redness, peeling, or irritation, especially in sensitive skin. Proper usage instructions and consistency are key to achieving desired results while minimizing adverse effects. During treatment, daily application of broad-spectrum sunscreen is essential to prevent further pigmentation and protect newly exposed skin.
Medical Procedures for Targeted Removal
For more significant or stubborn age spots, medical interventions offer faster and sometimes more dramatic results. These procedures are performed by dermatologists or qualified skin specialists and often require multiple sessions. Each method has its own mechanism and potential risks, so professional guidance is vital to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Below are some of the most popular treatments for age spots:
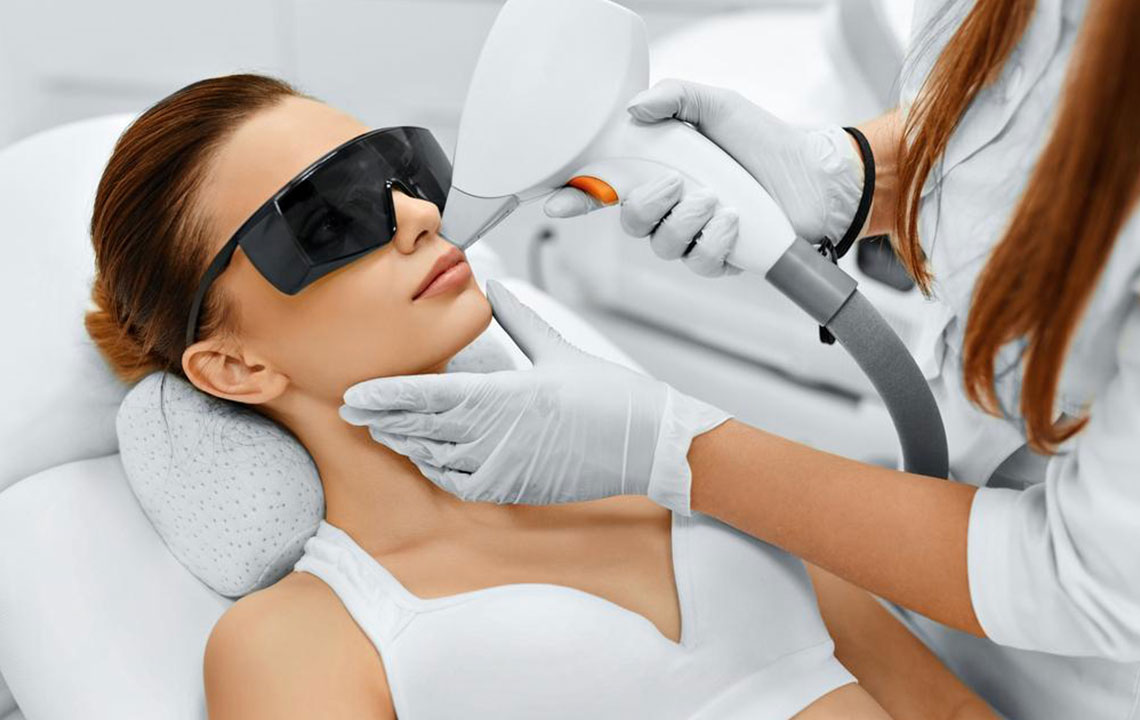
Laser and Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) Therapy: These advanced technologies target melanin-producing cells without damaging the surrounding tissue. By emitting focused light, they break down pigmented deposits, leading to gradual lightening of spots. Typically, two to three sessions are needed, spaced several weeks apart. Post-treatment care involves diligent sun protection to prevent recurrence, as remaining pigmentation can reactivate with UV exposure.
Cryotherapy: In cryotherapy, liquid nitrogen is applied directly onto the age spots, causing localized freezing. This destroys the excess pigment cells, which are then reabsorbed as the skin heals. Ideal for small, isolated spots, this method can produce rapid results but might cause temporary discomfort, pinpoint scarring, or temporary discoloration. Follow-up care includes avoiding traumatic skin injury and safeguarding against sun exposure.
Chemical Peel: Chemical solutions containing acids such as glycolic acid or trichloroacetic acid remove the damaged outer skin layers, promoting regeneration of new, clearer skin. Multiple sessions may be necessary for optimal results. This method requires diligent post-procedure skin care and sun protection. Potential side effects include redness, peeling, and in some cases, permanent skin discoloration if not performed correctly.
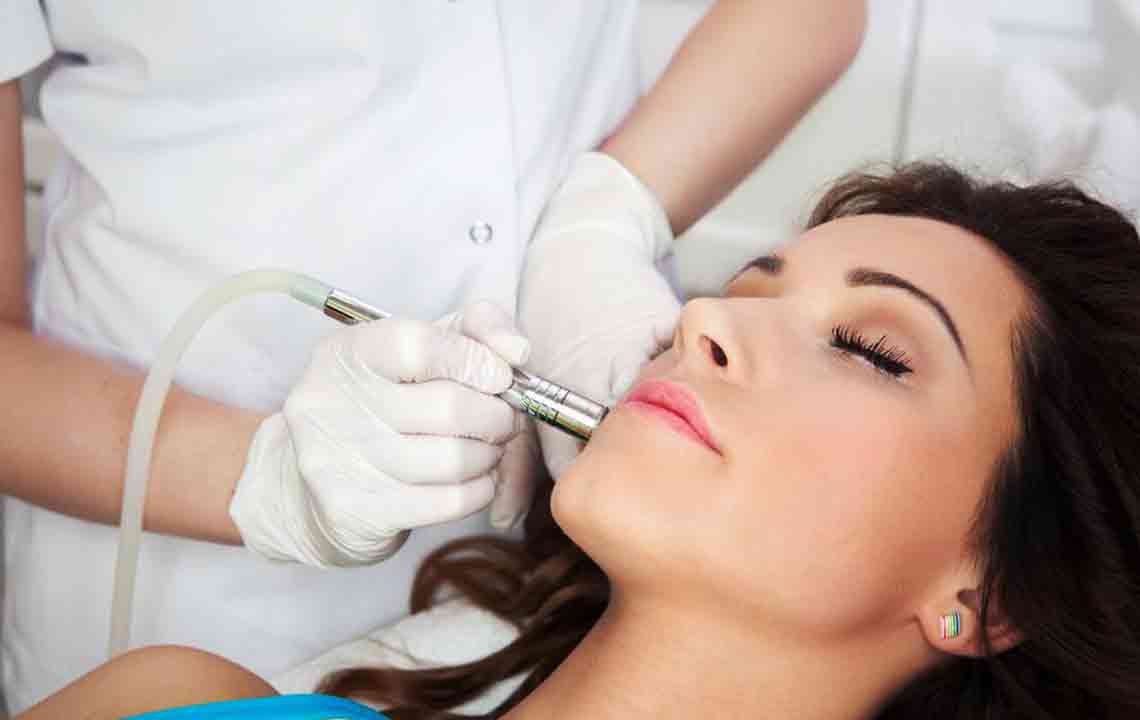
Additional cosmetic procedures like microdermabrasion and dermabrasion are also available for superficial skin resurfacing. These methods involve exfoliating the skin to improve pigmentation and texture but are generally considered cosmetic and might not be covered by insurance.
Before opting for any treatment, consulting with a licensed dermatologist is essential. They can evaluate your skin condition, discuss potential risks, and customize a treatment plan that aligns with your aesthetic goals and skin health.
Maintaining results requires adhering to sun protection measures, including wearing broad-spectrum sunscreen daily, avoiding peak sunlight hours, and wearing protective clothing. Consistent skin care and regular dermatological check-ups help prevent the reappearance of age spots and ensure your skin remains healthy and vibrant.