Comprehensive Lifestyle and Dietary Strategies for Managing Polymyalgia Rheumatica
This comprehensive guide explores effective dietary and lifestyle strategies to manage polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR). It emphasizes anti-inflammatory nutrition, proper hydration, and gentle exercise to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. The article highlights the importance of personalized approaches, considering foods to include and avoid, and discusses the potential benefits of specialized diets like keto, alongside conventional treatments. By adopting a holistic lifestyle plan, individuals with PMR can better control their condition, reduce flare-ups, and promote overall well-being through informed nutritional choices and physical activity.

In-Depth Nutritional Guidance and Lifestyle Modifications for Polymyalgia Rheumatica
Polymyalgia Rheumatica (PMR) is a chronic inflammatory disorder that predominantly affects older adults, especially those over the age of 50. Characterized by muscle stiffness and persistent pain, particularly in the shoulders, neck, upper back, and hips, PMR can significantly impair daily functioning and reduce quality of life. While medical treatment is essential, lifestyle choices, especially diet and physical activity, play a crucial role in symptom management and overall health improvement. This comprehensive guide explores various dietary practices, lifestyle modifications, and supplemental strategies to help those with PMR manage their condition effectively.
Understanding Polymyalgia Rheumatica and Its Challenges
PMR is an autoimmune-like inflammatory condition that causes swelling and pain in large muscle groups. Its exact cause remains unclear, but it is linked to inflammation markers released by the immune system. Symptoms often include severe morning stiffness, fatigue, and episodic flares which can last for months or years if unmanaged. While corticosteroids are the mainstay of treatment, long-term use of such medications can have side effects like osteoporosis, which emphasizes the importance of diet and lifestyle as complementary strategies.
Optimizing Diet for PMR: Nutritional Strategies for Symptom Relief
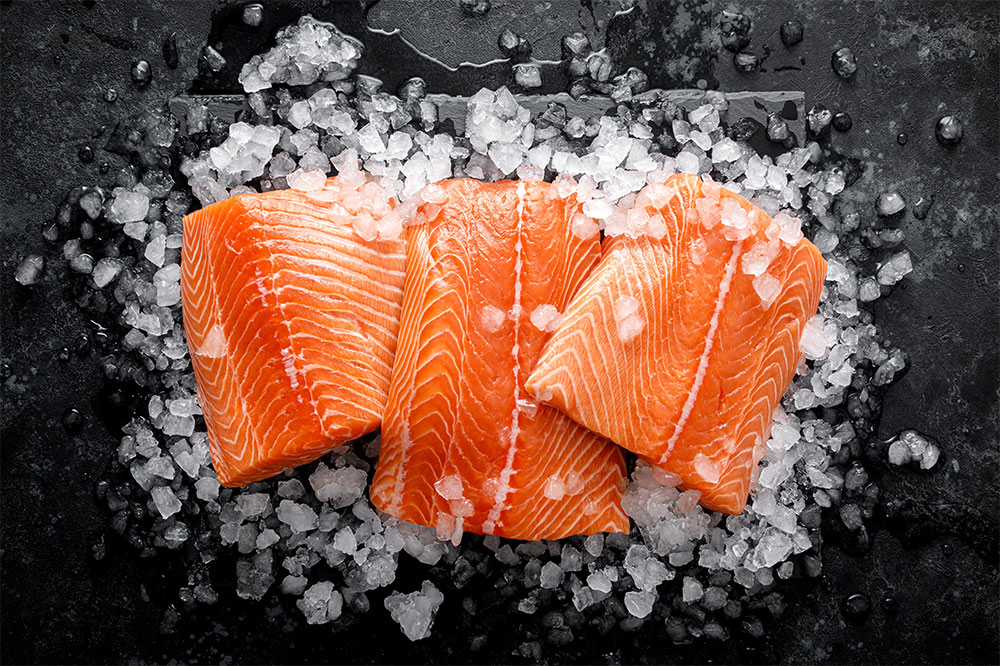
Since individual responses to dietary changes vary, it is advisable to maintain a food journal to track potential triggers and beneficial foods. An anti-inflammatory diet rich in nutrient-dense foods can help reduce systemic inflammation, support immune function, and alleviate some pain associated with PMR. Incorporating healthy fats, particularly those rich in omega-3 fatty acids, can have significant anti-inflammatory effects. These beneficial fats are found abundantly in fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, as well as in plant-based sources like walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseed. Consuming these regularly can help modulate inflammatory responses.
Rich in antioxidants and vitamins, fruits and vegetables such as berries, spinach, kale, oranges, and tomatoes can enhance immune function and diminish inflammatory processes. Foods high in vitamin D and calcium are also crucial, especially since corticosteroid treatment can lead to osteoporosis. Dairy products, leafy greens, fortified plant-based milks, and fatty fish contribute significantly to bone health.
Maintaining Proper Hydration for Optimal Joint and Muscle Function
Adequate hydration is fundamental in managing inflammation and supporting overall health. Patients should aim to drink between 2 to 3 liters of fluids daily, prioritizing water as the primary source. Infusing water with natural flavors like lemon or lime can make hydration more appealing. Some individuals find that moderate coffee consumption might confer mild anti-inflammatory benefits; however, it is important to listen to personal tolerance levels. Herbal teas such as ginger or chamomile can serve as soothing, caffeine-free alternatives that also support anti-inflammatory effects.
Considering Specialized Diets: The Keto Approach and Supplementation
The ketogenic diet, characterized by a high-fat, very low carbohydrate intake, has garnered attention for its potential health benefits, including inflammation reduction. While some proponents suggest that keto can benefit inflammatory conditions, scientific evidence specific to PMR remains limited. Patients contemplating such diets should undergo thorough evaluation and discuss with their healthcare provider or a registered dietitian to ensure safety and suitability. Always prioritize conventional treatments and lifestyle modifications supervised by medical professionals.
Foods to Minimize or Avoid to Prevent Flare-Ups
To prevent exacerbation of symptoms, individuals with PMR should limit or avoid foods known to promote inflammation. These include refined carbohydrates such as white bread and white rice, red meats which contain higher saturated fat, fried foods like French fries and fried chicken, as well as margarine and processed snacks high in trans fats. Additionally, foods rich in added sugars, such as sweets and sugary beverages, can trigger inflammatory responses and should be consumed sparingly. Emphasizing whole, unprocessed foods can significantly contribute to better symptom control.
Exercise and Physical Activity: Complementary Strategies for Symptom Management
Gentle, low-impact physical activity is highly recommended to improve joint mobility, muscle strength, and cardiovascular health. Activities such as walking, swimming, gentle cycling, or tai chi can be beneficial and are typically well-tolerated by individuals with PMR. Regular exercise has the added benefit of improving mood, reducing fatigue, and supporting bone density—particularly important given the risks associated with corticosteroid use. Consulting with a physical therapist or healthcare provider to develop a personalized and safe exercise regimen is essential to avoid injury and ensure gradual progression.
Holistic Approach for Long-Term Management
Combining nutritious anti-inflammatory foods, consistent physical activity, appropriate medications, and lifestyle adjustments cultivates a comprehensive management plan for PMR. It is important to monitor symptoms regularly, adjust dietary and activity plans as needed, and maintain open communication with healthcare professionals. As research continues, emerging therapies and nutritional insights may further enhance treatment options for individuals suffering from this challenging condition.
Ultimately, a proactive, holistic approach that emphasizes diet, exercise, and mental well-being can help mitigate symptoms, improve mobility, and enhance overall quality of life for those affected by polymyalgia rheumatica. Empowering patients with information and support for lifestyle modifications alongside conventional treatments offers a promising pathway to healthier living with PMR.