Effective Dietary Strategies to Prevent and Manage Migraine Pain
Discover comprehensive dietary strategies to prevent and manage migraines effectively. Learn which foods to incorporate and avoid, and explore lifestyle tips to reduce migraine frequency and severity. This detailed guide provides practical advice for healthier living with migraines, emphasizing nutrition, hydration, and stress management for improved quality of life.

Effective Dietary Strategies to Prevent and Manage Migraine Pain
Migraines represent a particularly intense form of headache that can significantly impair daily activities and affect individuals' quality of life. Unlike common headaches, migraines tend to be more severe, often lasting several hours or even days, and come with additional symptoms such as nausea, sensitivity to light and sound, and visual disturbances. Although the precise mechanisms behind migraines remain elusive, it is well understood that various lifestyle and dietary factors can influence their occurrence and severity. Identifying and implementing effective nutritional habits can be a powerful tool in reducing the frequency and intensity of migraine attacks.
Understanding the relationship between diet and migraines begins with recognizing common triggers and protective foods. Certain foods and beverages can stimulate migraine episodes, while others possess properties that may help in alleviating symptoms or preventing attacks altogether. Therefore, building a balanced, supportive diet is crucial for individuals prone to migraines.
Dietary Tips to Combat Migraine Attacks
Load Up on Fresh Fruits and Vegetables: Including a variety of colorful produce in your meals ensures an ample intake of essential nutrients that support overall health. Fruits like berries, apples, and bananas are rich in antioxidants and magnesium, which have been linked to migraine relief. Vegetables such as spinach, kale, and broccoli provide vital vitamins and minerals that can stabilize nerve functions and reduce inflammation.
Limit Citrus Fruits: While citrus fruits are nutritious, they are also common migraine triggers for some individuals. If you notice that consuming oranges, lemons, or grapefruits exacerbates your symptoms, consider reducing their intake or avoiding them altogether.
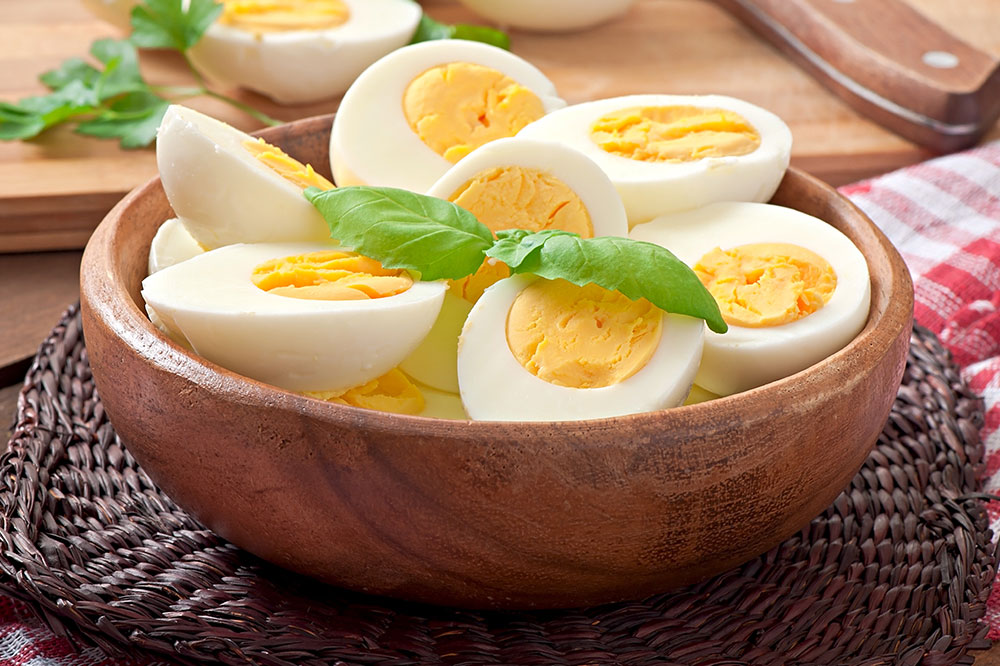
Opt for Vitamin B2-Rich and Fresh, Unprocessed Meats: Lean meats such as chicken and fatty fish like salmon are excellent sources of vitamin B2 (riboflavin). Studies suggest that higher levels of B2 may help decrease migraine frequency and severity by supporting energy production in brain cells.
Maintain Adequate Hydration: Drinking at least 8-10 glasses of water daily ensures optimal hydration, which is essential since dehydration is a common migraine trigger. Carry a water bottle with you and sip regularly throughout the day.
Eat Small, Frequent Meals: Skipping meals or experiencing prolonged fasting can lead to blood sugar drops, triggering migraines. Eat small portions every 3-4 hours to keep blood glucose levels steady, preventing hunger-induced attacks.
Incorporate Magnesium-Rich Foods and Gentle, Bland Foods: Brown rice, oats, bananas, and other magnesium-rich foods can help relax blood vessels and nerve pathways. When experiencing a migraine, bland foods like toast or crackers can soothe the stomach and reduce nausea.
Limit or Avoid Aged Dairy Products, Excessive Alcohol, and High Caffeine Intake: Aged cheeses, heavy alcohol consumption, and excessive caffeine are known migraine triggers. Monitoring and moderating these substances can significantly reduce attack frequency.
Additional Lifestyle Recommendations
Ensure Consistent Sleep Patterns: Irregular sleep or sleep deprivation can heighten migraine susceptibility. Maintain a regular sleep schedule and create a restful sleeping environment.
Reduce Stress and Practice Relaxation Techniques: Stress is a common migraine precipitant. Engage in activities such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises to manage tension effectively.
Monitor Food Triggers: Keep a migraine journal to identify specific foods or patterns that may trigger attacks, allowing for personalized dietary adjustments.
Conclusion
Managing migraines through diet involves strategic choices that can significantly diminish the frequency and severity of attacks. Emphasizing fresh fruits and vegetables, lean proteins, hydration, and small, regular meals forms the cornerstone of a migraine-friendly diet. Avoiding known triggers such as aged dairy products, alcohol, and excessive caffeine can further decrease attack risks. Along with these dietary modifications, maintaining adequate sleep, managing stress, and monitoring individual triggers are vital components of a comprehensive migraine management plan. If migraines persist or worsen, consulting a healthcare professional is essential to explore additional treatment options and ensure optimal health and well-being.