Comprehensive Nutritional Strategies for Hemophilia: Foods to Prioritize and Avoid
This comprehensive guide offers tailored nutritional advice for hemophilia patients, highlighting foods to include for bone health, blood regeneration, and immune support while identifying foods and substances to avoid that may increase bleeding risks. Proper diet management is essential for improving quality of life and minimizing complications associated with hemophilia.

Effective Dietary Approaches for Managing Hemophilia
Hemophilia is a hereditary bleeding disorder characterized by a deficiency in clotting factors, primarily factor VIII in hemophilia A. This deficiency leads to difficulties in blood clotting, resulting in prolonged bleeding episodes following injuries or internal bleeding. Patients with hemophilia must adopt tailored nutritional strategies that support their overall health and help minimize complications. Proper diet management plays a vital role in maintaining optimal health, reducing bleeding frequency, and supporting joint health. While there are no rigid dietary restrictions, understanding which foods to include and avoid can significantly improve quality of life for those affected by hemophilia.
Key Dietary Recommendations for Hemophilia Patients
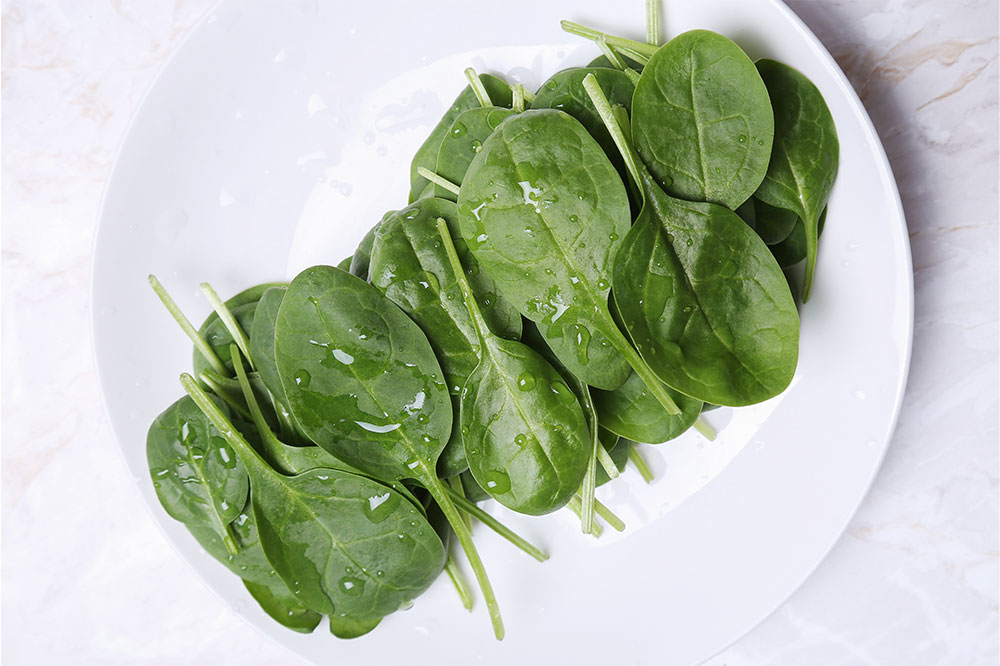
Prioritize Fruits and Vegetables
Incorporate a variety of colorful fruits and leafy green vegetables into your daily meals. Items such as spinach, kale, Swiss chard, broccoli, and bok choy are excellent sources of vital vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber. Fruits like strawberries, pears, apples, and oranges provide antioxidants that help reduce inflammation and promote overall health. These nutrient-rich foods support immune function, improve digestion, and help maintain balanced blood composition, which is especially crucial for hemophilia patients prone to bleeding.
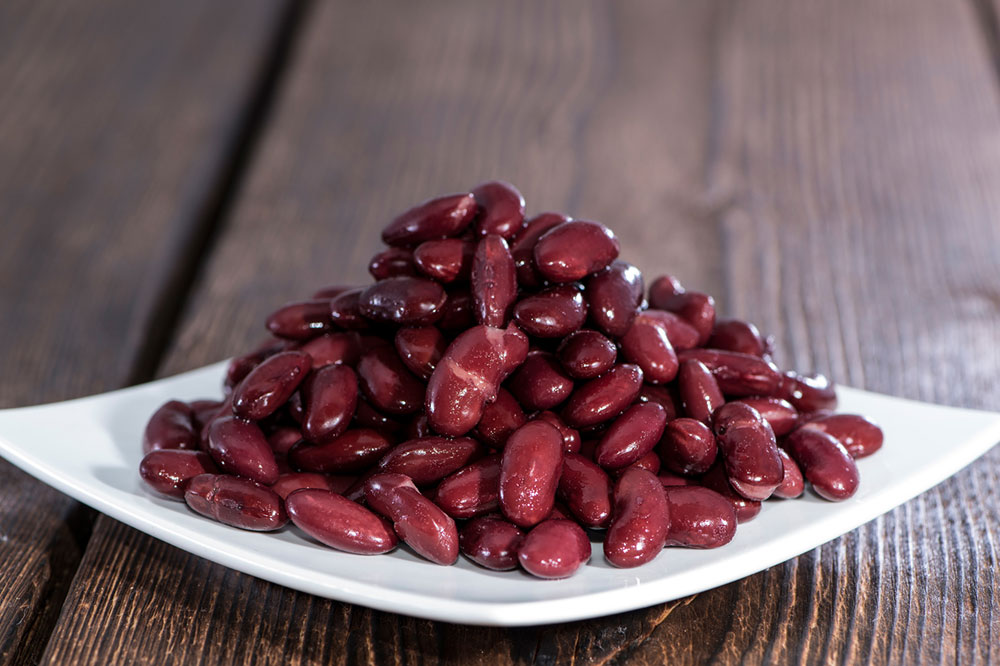
Calcium and Bone Strengthening Foods
Maintaining strong bones is vital for individuals with hemophilia, as joint bleeding and degenerative changes are common complications. Calcium-rich foods such as fortified plant-based and dairy products, orange juice, lean meats, poultry, nuts like almonds, and legumes like beans are essential. Adequate calcium intake helps prevent osteoporosis and supports joint stability. Proper bone health reduces the risk of fractures and joint deformities, which are significant concerns among hemophilia patients.
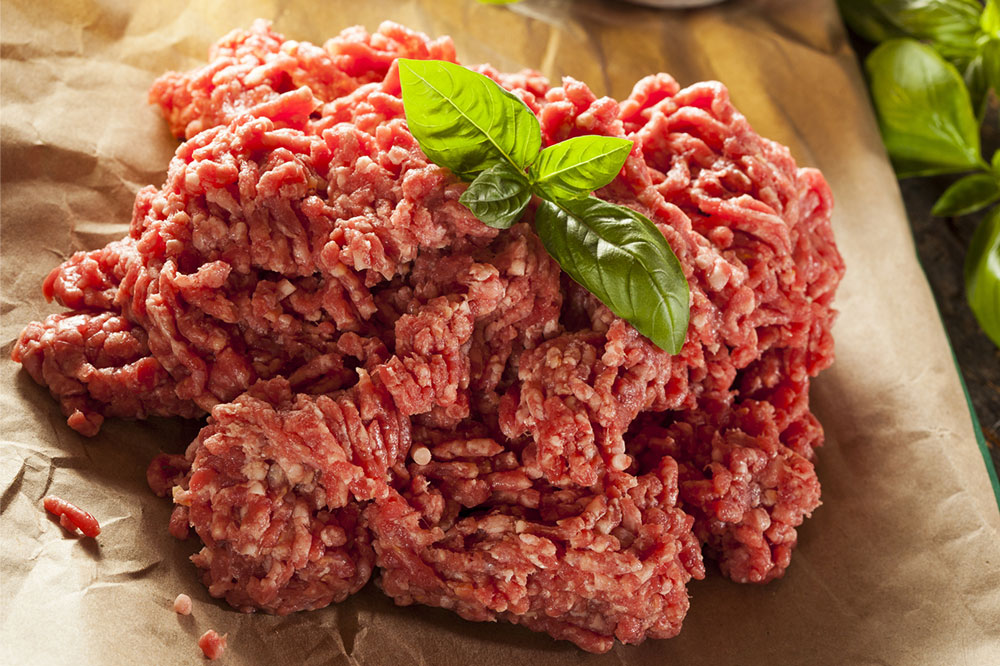
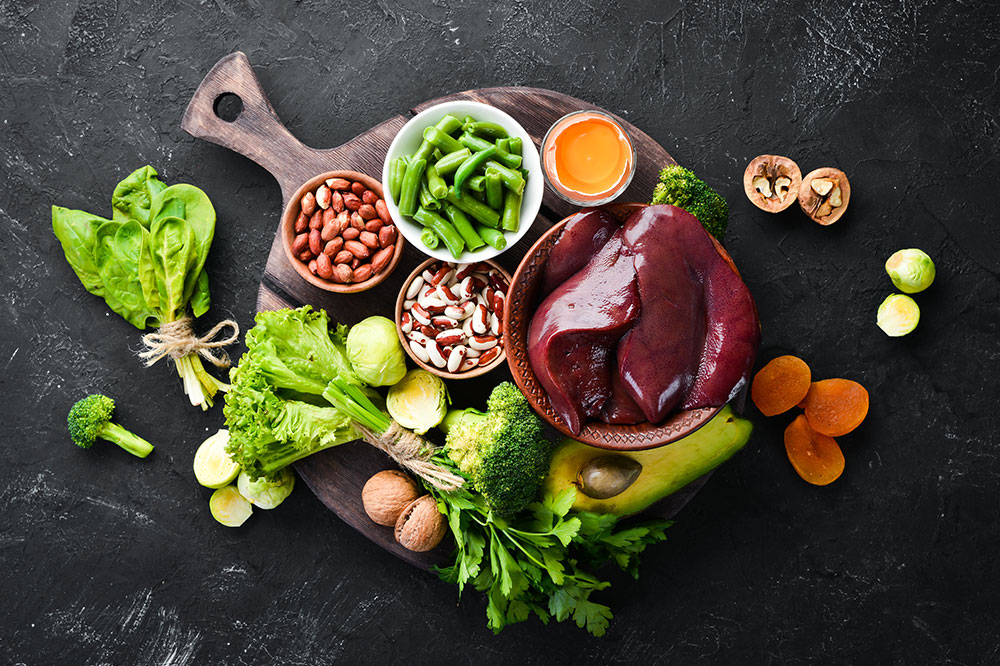
Iron and Blood Regeneration
Iron is a crucial element necessary for the production of healthy red blood cells. Hemorrhagic episodes can deplete iron stores, leading to anemia and fatigue. Include iron-rich foods like lean cuts of beef, chicken liver, seafood such as shellfish, fortified cereals, dried fruits like raisins and apricots, and nuts. These foods help replenish iron stores, support recovery, and improve oxygen transport throughout the body, which is vital during bleeding episodes or after surgeries.
Foods and Substances to Limit or Avoid
Fried, Greasy, and Fast Foods
Foods high in trans fats and saturated fats, such as deep-fried meats, fast-food items, chips, and processed snack foods, should be consumed sparingly. Excessive intake of unhealthy fats can lead to weight gain, cardiovascular issues, and exacerbate joint problems, all of which are detrimental for hemophilia patients. A balanced diet minimizing greasy and processed foods encourages better health and weight management.
Refined Sugar and Sweets
Limit intake of sugar-loaded products including baked sweets, candies, chocolates, sodas, and energy drinks. High sugar consumption can elevate triglyceride levels and promote inflammation, increasing cardiovascular risks. Opting for natural sweeteners or reducing sweet intake altogether supports better metabolic health and reduces the strain on the cardiovascular system.
Supplements and Herbal Remedies
Caution is advised with certain supplements and herbs. Hemophilia A patients should avoid fish oil and vitamin E supplements, which may interfere with platelet aggregation and increase bleeding tendencies. Additionally, herbs such as ginseng, garlic, ginkgo biloba, ginger, willow bark, and feverfew possess natural blood-thinning properties and can elevate bleeding risks. Prior consultation with healthcare providers is essential before starting any new supplement or herbal remedy to prevent adverse effects and ensure safe management.
In conclusion, adopting a well-balanced, nutrient-rich diet tailored to the needs of hemophilia patients can lead to improved health outcomes, fewer bleeding episodes, and enhanced quality of life. Regular check-ups and a collaborative approach with healthcare professionals ensure that dietary choices align with overall treatment plans. By focusing on support foods and avoiding potential bleeding triggers, individuals with hemophilia can better manage their condition and promote healthier living.