Comprehensive Dietary Approaches to Effectively Manage Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Discover comprehensive dietary strategies to effectively manage irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). This guide covers high-fiber and low-fiber diets, eliminating trigger foods, gluten-free options, and lifestyle tips for symptom relief. Learn how tailored nutrition combined with lifestyle changes can significantly improve gut health and enhance quality of life for IBS sufferers.

Comprehensive Dietary Approaches to Effectively Manage Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Maintaining a balanced and healthy diet is fundamental to overall well-being and plays a vital role in preventing a variety of health issues. Proper nutrition not only boosts your immune system but also accelerates recovery from ailments, enhances energy levels, and promotes optimal organ function. In today's fast-paced, stressful world, many individuals neglect proper nutritional habits, often leading to compromised health, emotional stress, and digestive disturbances. Skipping meals such as breakfast is a widespread habit, but this practice can negatively impact overall health by depriving the body of necessary nutrients and energy.
One of the key aspects of digestive health is ensuring your stomach and gut are functioning optimally. A well-maintained gastrointestinal (GI) system helps in preventing infections, reducing discomfort, and improving nutrient absorption. When your gut health is compromised, you become more susceptible to illnesses, food sensitivities, and chronic conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Recognizing and addressing these issues through proper dietary strategies is essential for improving quality of life.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome is a common yet complex disorder affecting millions worldwide. It is characterized by a range of gastrointestinal symptoms, including abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, diarrhea, and excess gas. The condition often arises due to irregular routines, stress, and dietary habits that disrupt gut function. IBS is also linked to immune system imbalances and sensitivities to certain foods, making dietary management a crucial aspect of treatment. While the exact cause remains unknown for many, understanding how food influences symptoms offers a practical way to control and alleviate this condition.
If you're suffering from IBS or digestive discomfort, the good news is that lifestyle and dietary modifications can significantly improve symptoms. By adopting targeted nutritional plans, you can promote gut healing, reduce inflammation, and restore normal bowel function. Here we explore comprehensive dietary strategies tailored for managing irritable bowel syndrome effectively:
High-Fiber Diet
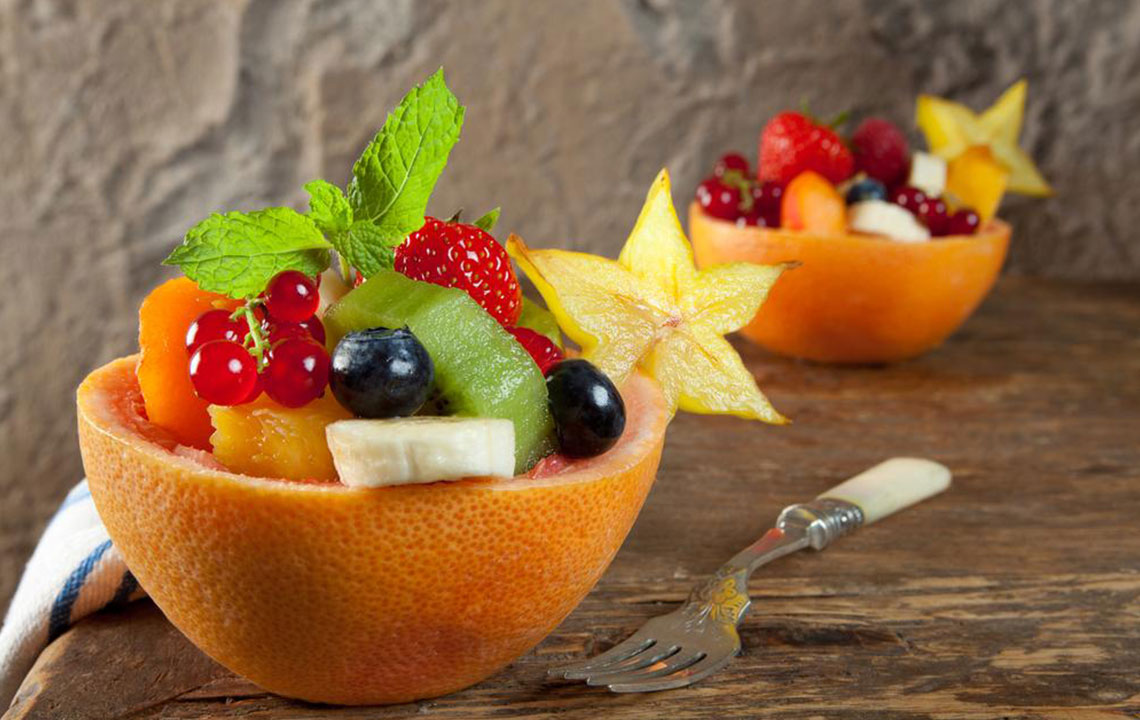
Incorporating high-fiber foods like fresh fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains helps add bulk to stool, which facilitates easier and more regular bowel movements. Fiber-rich foods stimulate peristalsis—the wave-like muscle contractions that move food through your digestive tract—leading to reduced constipation and abdominal discomfort. It is important, however, to increase fiber intake gradually to prevent gas and bloating, which can worsen IBS symptoms initially. A consistent intake of soluble fiber, found in oats, apples, carrots, and berries, is particularly beneficial for stabilizing bowel movements and promoting gut health.
Low-Fiber Diet
For individuals experiencing frequent diarrhea and bloating, a low-fiber diet can help minimize intestinal irritation. Foods that are easier to digest, such as bananas, white rice, cooked vegetables, and refined grains, decrease bowel load and reduce symptoms. Soluble fiber sources like apples, berries, and oats are preferable since they are gentle on the stomach and can help manage loose stools without causing excessive gas or cramping.
Gluten-Free Diet
Some people with IBS find that reducing or eliminating gluten-containing products, such as traditional wheat, barley, and rye, alleviates symptoms. Gluten sensitivity can trigger inflammation and disrupt intestinal flora, leading to pain, bloating, and irregular digestion. Transitioning to gluten-free foods—such as rice, corn, and gluten-free bread—may result in noticeable symptom relief. It’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional before making significant dietary changes, especially if gluten intolerance or celiac disease is suspected.
Elimination Diet
An elimination diet involves systematically removing common trigger foods—such as nuts, chocolates, caffeine, dairy, fried and fatty foods—for at least 12 weeks. Monitoring symptoms during this period helps identify specific food sensitivities or allergies that may exacerbate IBS. Once identified, these foods can be permanently avoided, leading to sustained symptom improvements. This approach requires careful planning and possibly guidance from a nutritionist to ensure nutritional adequacy.
In addition to these dietary modifications, integrating lifestyle changes can further enhance gut health. Adequate hydration is crucial—aiming for at least 8 glasses of water daily supports digestion and prevents constipation. Regular physical activity, such as walking, yoga, or gentle exercises, stimulates intestinal motility and reduces stress levels, which commonly influence IBS symptoms. Stress management techniques like meditation, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness can also have a positive impact on GI health.
It is equally important to avoid or limit foods and beverages known to aggravate IBS symptoms. These include cruciferous vegetables (such as broccoli, cauliflower), processed fats, dairy products in some individuals, alcohol, caffeinated drinks like coffee and energy beverages, and sweet chocolates. Keeping a symptom diary can help pinpoint specific triggers, enabling personalized dietary adjustments.
Persistent symptoms of IBS or other digestive issues should not be ignored. While dietary and lifestyle changes can dramatically improve your condition, it’s essential to consult healthcare professionals for proper diagnosis and treatment options. With dedication and the right approach, many individuals can lead normal, symptom-free lives. Starting with small, manageable dietary changes can lead to significant improvements within a month, providing relief and enhancing overall quality of life.
In conclusion, managing irritable bowel syndrome through diet involves understanding your body’s unique responses and tailoring your food choices accordingly. A combination of high-fiber and low-fiber diets, elimination plans, gluten avoidance, and healthy lifestyle practices can collectively empower you to take control of your gut health. Remember, proactive steps and expert guidance are key to making lasting improvements and maintaining a healthy digestive system.