Comprehensive Guide to Seasonal Influenza Prevention and Vaccination Strategies
This comprehensive guide explains the importance of seasonal influenza vaccination, details about the quadrivalent flu vaccine Fluarix Tetra, and essential preventive measures to protect yourself and your community during flu season. Learn about how the vaccine works, recommended timing, potential side effects, and additional tips for staying healthy during peak influenza periods.

Understanding Influenza and How to Protect Yourself This Season
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is a highly contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses. Unlike bacterial infections, the flu is viral, meaning antibiotics are ineffective for treatment. Instead, managing influenza involves alleviating symptoms such as fever, muscle aches, fatigue, and sore throat. The most effective prevention method is receiving an annual influenza vaccine. With the flu virus constantly evolving, regular vaccination provides the best immunity against circulating strains each season.
Influenza remains a significant public health concern worldwide, especially during the colder months when transmission rates increase. The seasonal flu can lead to severe health complications, including pneumonia, bronchitis, and even hospitalization or death in vulnerable populations such as the elderly, young children, pregnant women, and those with underlying health conditions. Therefore, understanding the importance of vaccination and proper preventive measures is crucial for individual and community health.
The quadrivalent inactivated influenza vaccine, widely used during flu season, is marketed under the name Fluarix Tetra. This vaccine offers protection against four major circulating strains of the influenza virus: H1N1, H3N2, and two B lineages. It is designed to stimulate the immune system to produce specific antibodies, equipping your body to fight the influenza viruses more effectively.
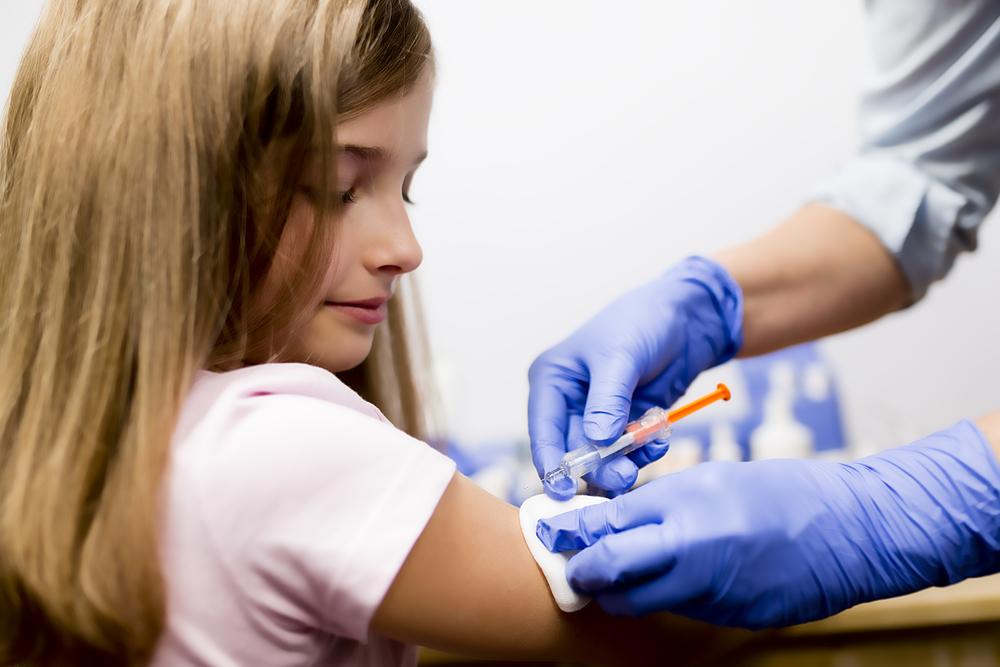
Each dose of the Fluarix Tetra vaccine contains 15 micrograms of hemagglutinin (HA) protein per virus strain. Hemagglutinin is a surface protein on the influenza virus that plays a key role in viral attachment to host cells. The presence of this protein in the vaccine helps your immune system recognize and respond quickly to actual infections. The vaccine is administered via intramuscular injection, typically into the deltoid muscle in the upper arm or into the thigh for young children.
The vaccine works by prompting your immune system to develop antibodies that neutralize the influenza viruses. This process offers active immunity, meaning your body is prepared to combat future infections during the flu season. It is recommended to receive this vaccination annually, ideally starting in October each year, before the peak of flu activity. The timing ensures optimal protection during the months when influenza transmission is most intense.
Before getting vaccinated, consulting with a healthcare professional is advised, especially if you have allergies, chronic health conditions, or a history of adverse reactions. Like all vaccines, Fluarix Tetra may cause mild side effects such as temporary soreness at the injection site, fatigue, or a mild fever. Less commonly, some individuals might experience reactions like rash, dizziness, or allergic responses. Serious adverse events are rare. The vaccination process involves a standard intramuscular injection, which is a quick and generally well-tolerated procedure.
In addition to vaccination, practicing good hygiene—such as frequent handwashing, wearing masks in crowded places, and covering your mouth when coughing or sneezing—further reduces the risk of contracting or transmitting influenza. Staying informed about local flu activity and following public health advice are also vital components of an effective seasonal prevention strategy. Overall, annual vaccination remains the cornerstone of influenza prevention and helps protect not only yourself but also those around you, especially the vulnerable populations.