Comprehensive Guide to Becoming a Certified HVAC Technician
Discover comprehensive pathways to becoming a certified HVAC technician. This guide covers educational requirements, technical training, apprenticeships, licensing, and ongoing education essential for a successful career in HVAC. Learn how to develop your skills and gain industry-recognized certifications in this dynamic field, ensuring steady employment and professional growth in the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning industry.

Comprehensive Guide to Becoming a Certified HVAC Technician
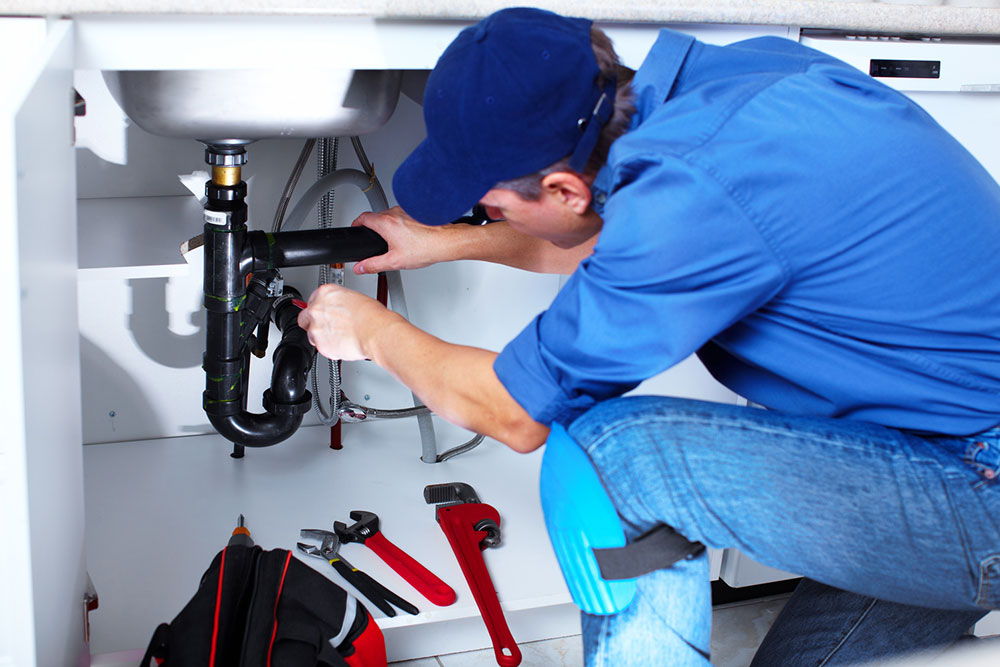
Embarking on a career as a Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) technician opens doors to a dynamic and in-demand field. HVAC technicians are essential professionals responsible for installing, maintaining, and repairing climate control systems in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. Their expertise ensures indoor comfort and air quality, making their skills highly valued across numerous industries. This detailed guide explores the various pathways to achieving certification and establishing a successful career in HVAC, covering educational requirements, training options, practical experience, and licensing procedures.
Foundational Educational Requirements
Starting your journey to become an HVAC technician begins with a solid educational foundation. A high school diploma or equivalent is the minimum requirement for entry into technical training programs. During high school, students should focus on relevant subjects such as physics, chemistry, and mathematics, which provide a critical understanding of the principles underlying HVAC systems. Courses in computer science can also be beneficial, considering the increasing integration of smart technology and automation in HVAC systems.
Beyond traditional classroom education, vocational classes related to mechanical drawing, electronics, blueprint reading, and technical math can give aspiring technicians a head start. These classes develop practical skills and technical knowledge that serve as building blocks for advanced HVAC training and certification.
Formal Educational Programs
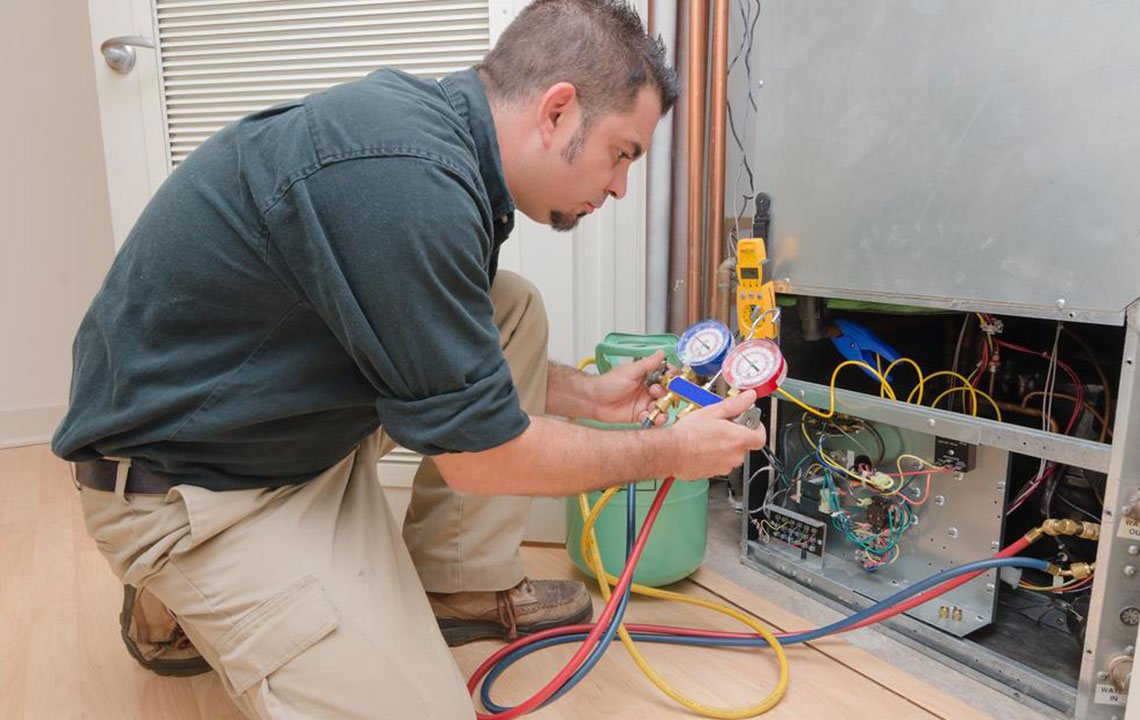
Once basic education is complete, prospective HVAC technicians can enroll in specialized training programs offered by vocational schools, trade colleges, and technical institutes. These programs typically range from six months to two years and are designed to provide comprehensive knowledge of heating, ventilation, air conditioning, and refrigeration systems. Coursework often includes electrical principles, gas and refrigerant properties, furnace and boiler operation, plumbing, hydraulics, ductwork design, and safety protocols. Many programs incorporate hands-on training and practical internships, offering students valuable real-world experience in a controlled environment. These internships may involve working with actual HVAC systems, assisting with repairs, and learning industry-standard tools and techniques.
On-the-Job Training and Apprenticeships
While classroom education provides essential theoretical knowledge, practical experience is crucial for skill development. Entry-level positions allow new technicians to work under the supervision of experienced professionals, assisting with routine tasks such as small repairs, system inspections, and basic installations. This on-the-job training not only reinforces classroom learning but also helps develop troubleshooting skills and familiarity with industry equipment.
For more immersive learning, apprenticeships offer a structured pathway to becoming a fully licensed HVAC technician. Apprenticeships, often organized through local trade associations or union programs, typically last between three to five years. During this time, apprentices earn wages while receiving practical training, gradually progressing from basic tasks to more complex projects. Successful completion of an apprenticeship program often results in certifications that are recognized industry-wide and serve as a stepping stone toward independent work.
Licensing, Certification, and Continuing Education
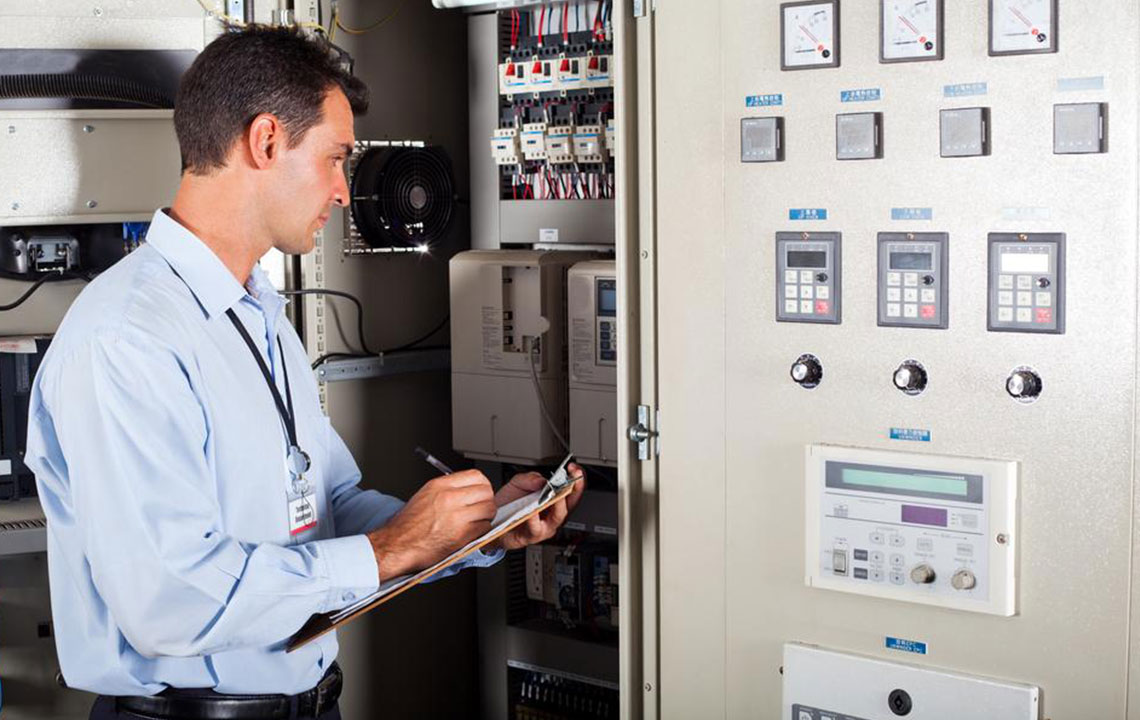
To operate legally and independently as an HVAC technician, obtaining appropriate licensing and certification is essential. Licensing requirements vary by region and may involve passing examinations that test knowledge of safety standards, electrical codes, refrigerant handling, and system troubleshooting. Certifications such as the EPA 608 Certification for refrigerant handling are mandatory in many areas and are generally required to work on specific types of equipment.
Continuing education is vital to stay updated with advancements in HVAC technology, environmental regulations, and new system designs. Industry associations, manufacturers, and vocational institutes often offer advanced courses and specialty certifications in areas like building automation, energy management, and green HVAC systems. Lifelong learning ensures technicians remain competitive and capable of implementing innovative solutions for clients.
In conclusion, becoming a certified HVAC technician involves a combination of formal education, hands-on experience, apprenticeships, and licensure. This pathway not only guarantees technical proficiency but also fosters career growth in a sector with consistent demand and opportunities for specialization. Whether you’re just starting or seeking to advance your existing skills, understanding these pathways can help you achieve your professional goals efficiently and successfully.