Comprehensive Guide to Protecting Yourself from Common Ear, Nose, and Throat (ENT) Infections
This comprehensive guide explores common ENT infections affecting the ears, nose, and throat. It covers symptoms, causes, and preventative strategies for conditions like ear infections, sinusitis, tonsillitis, and Meniere’s disease. Emphasizing early detection and proper treatment, the article highlights the interconnected nature of ENT regions and offers practical advice to maintain ear, nose, and throat health. Ideal for individuals seeking to understand and protect themselves from these prevalent infections, this guide provides detailed insight into managing and preventing ENT-related health issues effectively.
Comprehensive Guide to Protecting Yourself from Common Ear, Nose, and Throat (ENT) Infections
The human body’s immune system is resilient, yet it remains vulnerable to a wide variety of infections caused by external pathogens. Among the most common health issues affecting millions worldwide are ENT infections—those that target the ears, nose, and throat. These infections can range from mild discomforts to severe medical conditions that significantly impact quality of life. Understanding the various types of ENT infections, their causes, symptoms, and preventative measures is essential for early detection, effective treatment, and overall health preservation. Since the ear, nose, and throat are interconnected regions, an infection in one area can quickly spread or influence others, making vigilance and prompt action crucial for maintaining well-being.
Outer Ear and Middle Ear Infections – An Overview
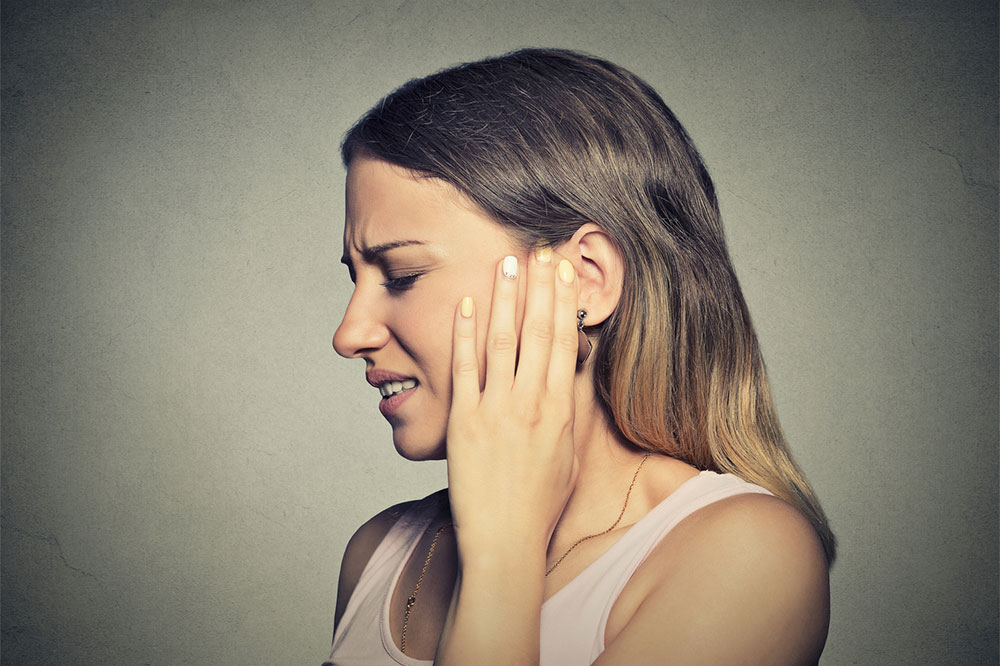
Infections affecting the outer and middle ear are among the most common ENT disorders, especially in children but also prevalent among adults. Outer ear infections, also known as otitis externa, involve inflammation of the ear canal. This condition can cause symptoms like itching, redness, swelling, tenderness, crusting, and discomfort. It often results from water-based bacteria or fungi multiplying in the moist environment of the ear canal, especially after swimming or exposure to humidity. Poor ear hygiene or injury to the ear canal can also contribute to these infections.
Middle ear infections, or otitis media, involve inflammation or infection behind the eardrum. These are typically caused by bacteria or viruses that ascend from the throat or nasal passages via the Eustachian tube. Symptoms often include ear pain, a sensation of fullness, temporary hearing loss, fever, dizziness, and sometimes fluid drainage. If untreated, middle ear infections can lead to complications like persistent hearing impairment or eardrum rupture, emphasizing the importance of timely medical intervention.
Inner Ear Disorders – Meniere’s Disease
Meniere’s disease is a chronic disorder affecting the inner ear, leading to vertigo, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), hearing loss, and a sensation of fullness or pressure in the affected ear. While the precise cause remains unclear, it is believed to involve abnormal fluid accumulation within the cochlea. This imbalance disrupts normal inner ear function, resulting in episodes of severe dizziness that can last for hours. Meniere’s disease can significantly impair daily life and increase fall risk due to vertigo. Management strategies include dietary modifications, medications, and, in some cases, surgical interventions.
Nosebleeds – Causes and Prevention
Nasal bleeding, commonly known as nosebleeds (epistaxis), occurs frequently in children and adults. Although often minor, recurrent nosebleeds should not be dismissed, as they might indicate underlying issues. Nosebleeds result from the rupture of fragile blood vessels in the nasal mucosa, which can be triggered by nose picking, vigorous blowing, dry air, allergies, or cold weather. To minimize risks, avoid inserting objects into the nostrils, keep the nasal passages moist with saline sprays, and avoid NSAIDs that thin the blood. If bleeding persists or is severe, medical attention is necessary to control the bleeding and identify underlying causes.
Sinusitis – Inflammation of the Sinus Cavities
Sinusitis refers to inflammation and swelling of the sinus cavities located around the nose, cheeks, and forehead. This condition often results from viral infections, bacterial infections, or allergies. Symptoms include nasal congestion, thick nasal discharge, post-nasal drip, facial tenderness, headache, and a sense of pressure around the face. Chronic sinusitis, lasting longer than twelve weeks, can significantly impair daily activities and may require medical management, including antibiotics, decongestants, or nasal corticosteroids. Preventative measures involve maintaining good nasal hygiene, avoiding known allergens, and managing upper respiratory infections promptly.
Throat Infections – Pharyngitis and Tonsillitis
Pharyngitis, commonly known as sore throat, affects the pharynx and can be caused by viral or bacterial infections. Symptoms include redness, swelling, pain during swallowing, fever, and general malaise. When bacterial, especially streptococcus, it is classified as strep throat and requires antibiotics for eradication. Tonsillitis involves inflammation of the tonsils, presenting with severe throat pain, difficulty swallowing, and sometimes fever. It can be viral or bacterial and, in recurrent cases, might necessitate surgical removal of the tonsils (tonsillectomy). Recognizing early signs of these infections facilitates prompt treatment and prevents potential complications such as abscess formation or rheumatic fever.
Since the ENT region is intricately connected, infections in one area can propagate rapidly to adjacent structures, amplifying health risks. Symptoms such as persistent cold, sinus pressure, ear pain, or sore throat should never be ignored. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to preventing complications, improving recovery times, and maintaining optimal health. Practicing good hygiene, avoiding irritants, and seeking medical advice at the onset of symptoms can make a significant difference in managing and preventing ENT infections effectively.