Comprehensive Guide to Accelerating Cold Sore Healing and Management
This comprehensive guide offers effective strategies for managing cold sores, including medications, natural remedies, and lifestyle tips. Understanding symptoms, triggers, and prevention helps shorten healing time and reduce discomfort. Proper hygiene, early treatment, and healthy habits are key to maintaining comfort and preventing outbreaks. Suitable for those experiencing recurrent cold sores or seeking proactive management options, this detailed guide aims to enhance quality of life through informed care and natural support methods.

Comprehensive Strategies to Accelerate Cold Sore Healing and Effective Management
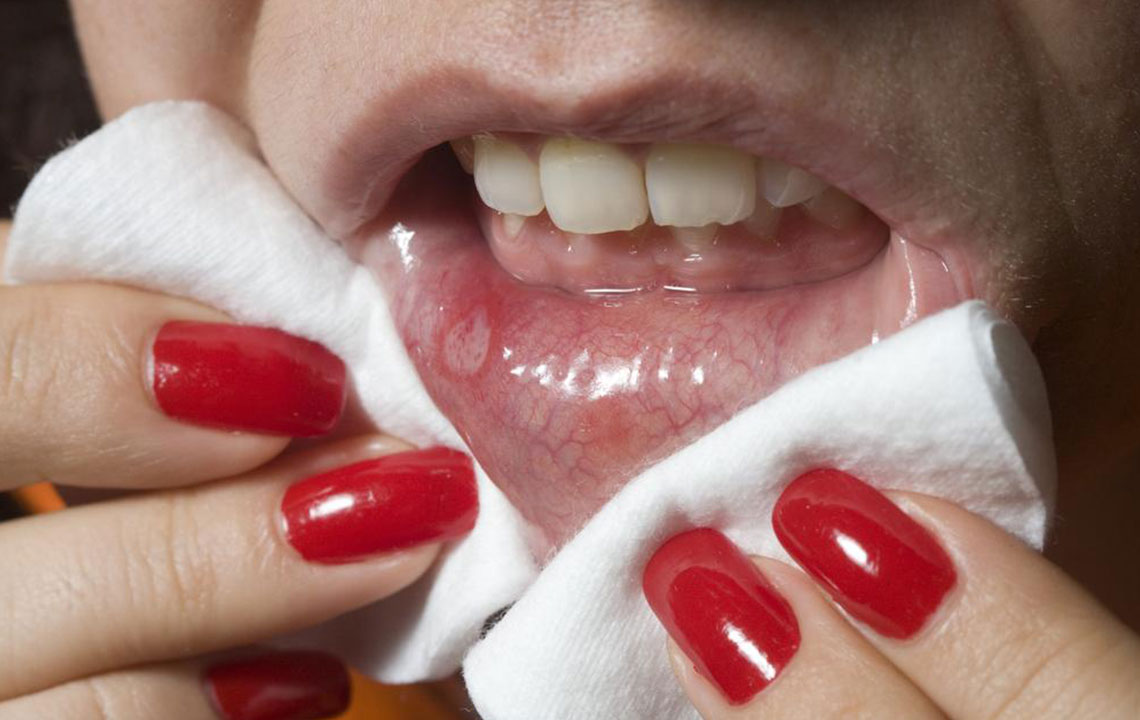
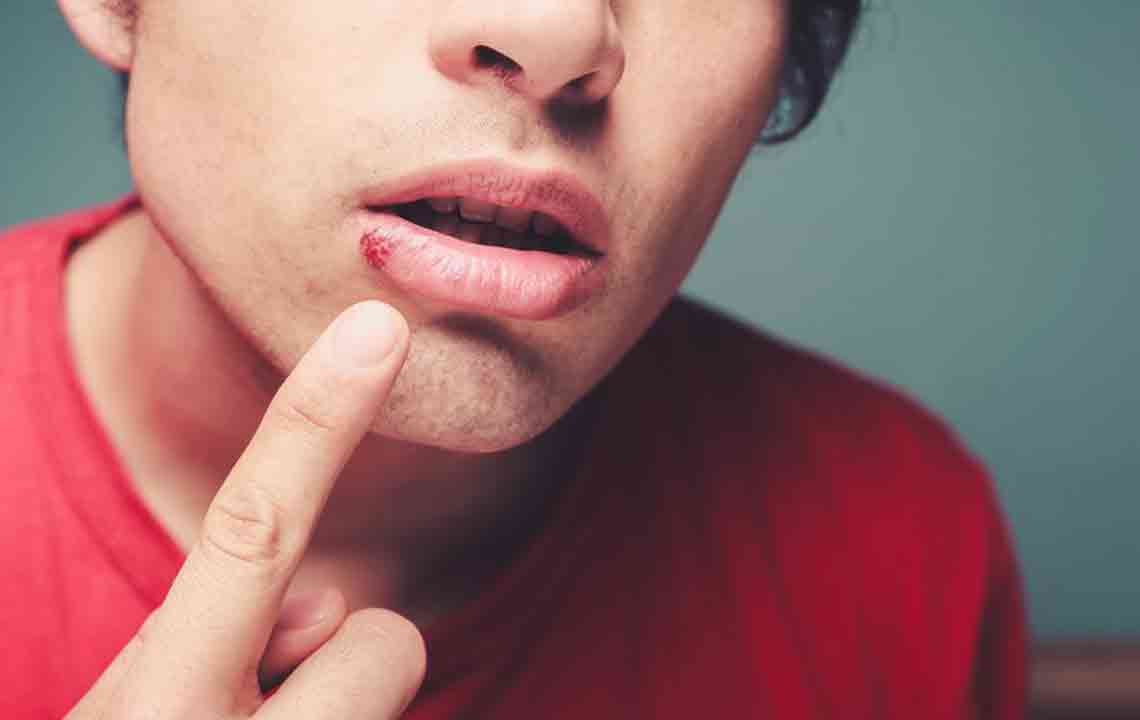
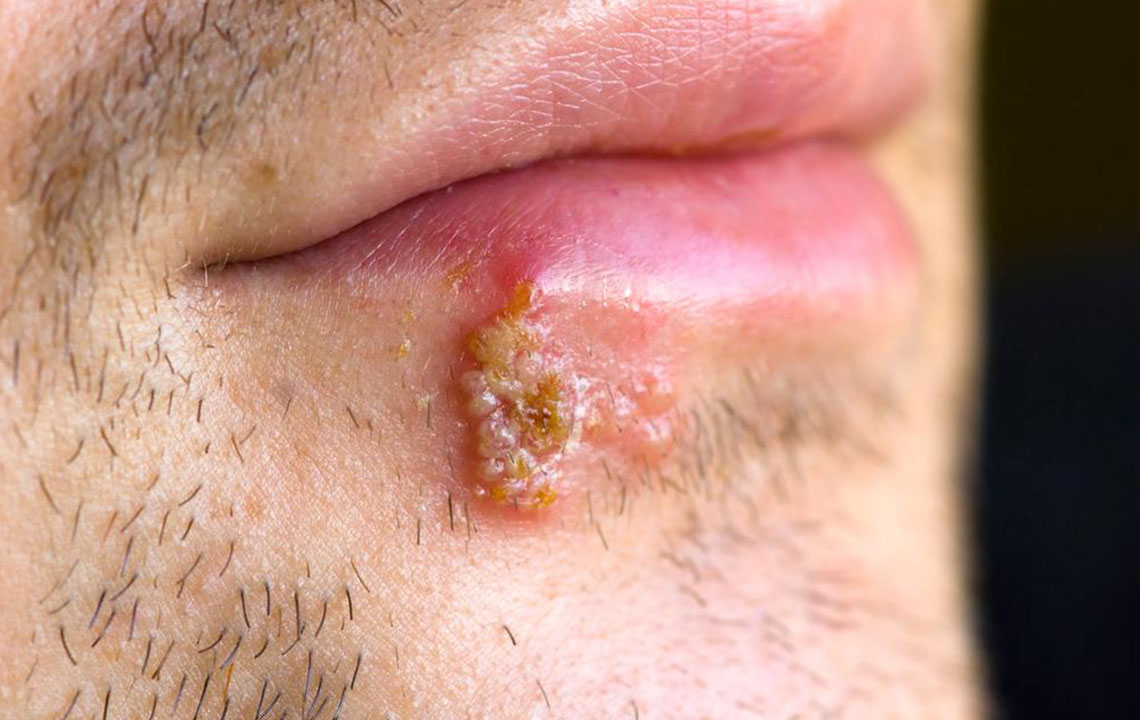
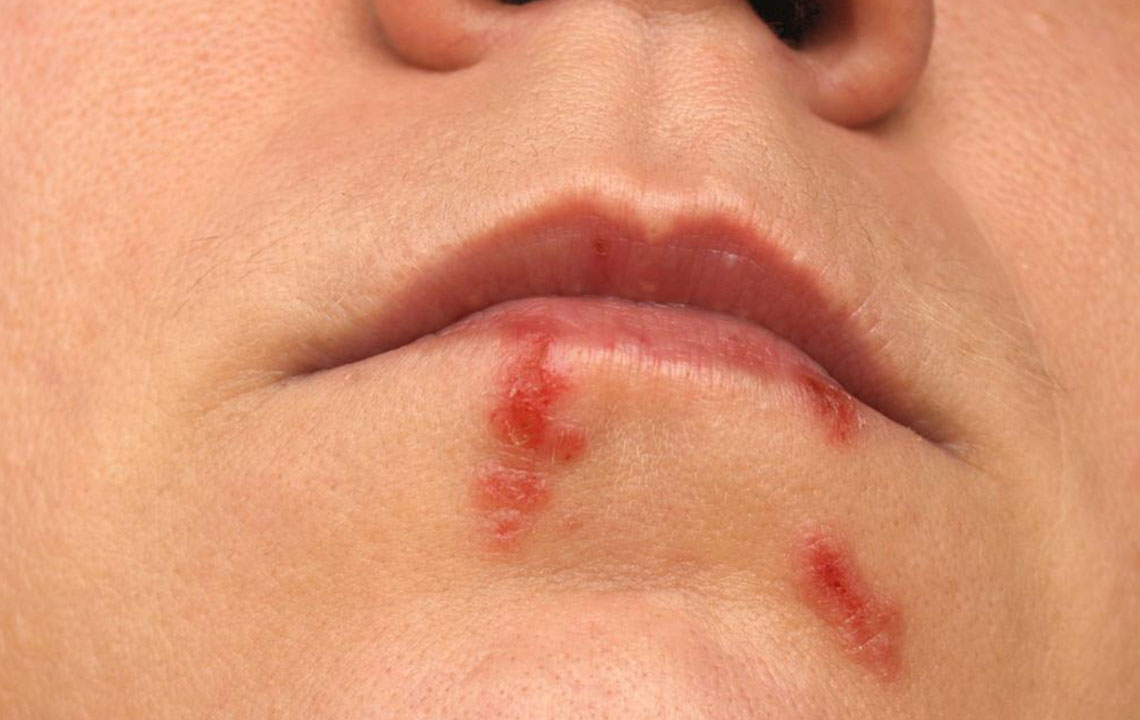
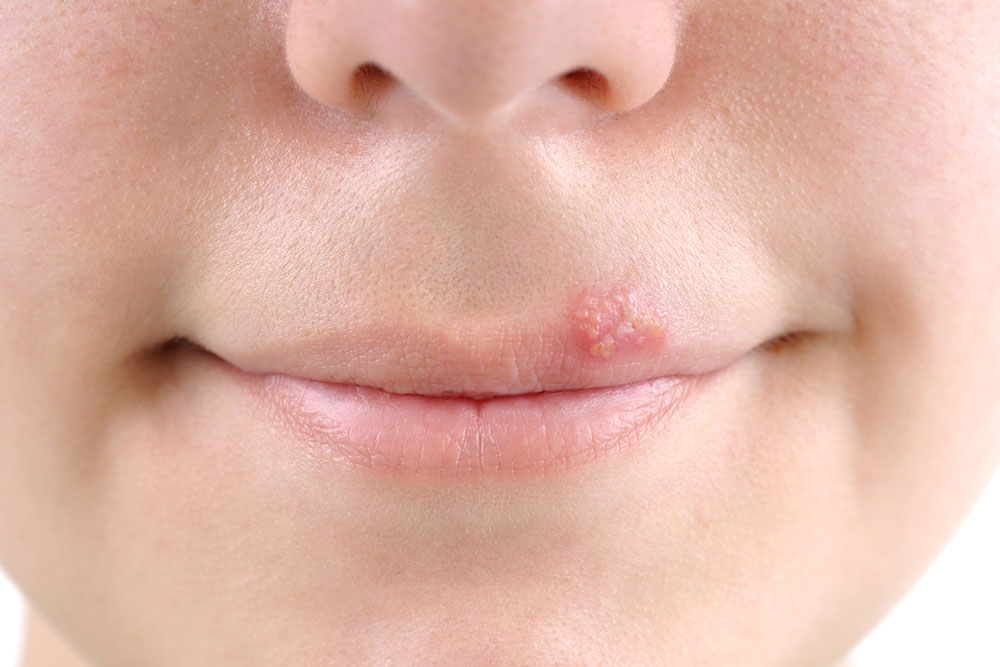
Cold sores, also known as oral herpes, manifest as painful, unsightly blisters that typically emerge around the lips, portions of the mouth, and sometimes inside the mouth itself. These outbreaks are caused by the Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV), predominantly HSV-1, although HSV-2—more commonly associated with genital herpes—can occasionally be responsible for oral infections. Once an individual is infected, the virus establishes a latent presence in nerve cells, remaining dormant but capable of reactivating periodically. Many people will experience at least one outbreak during their lifetime, with symptoms varying in severity and frequency. Understanding the nature of cold sores, their causes, symptoms, and effective treatment strategies can significantly reduce discomfort and shorten healing time, improving quality of life.
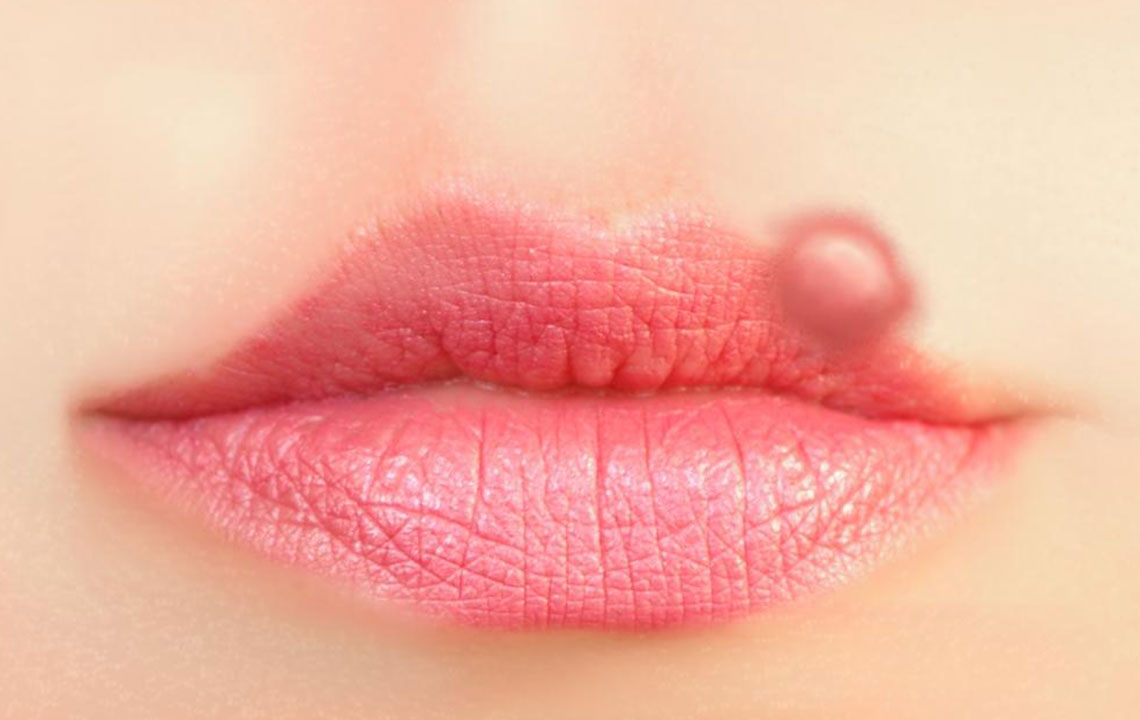
Cold sores typically start as small, fluid-filled blisters that can be tender or itchy. These blisters often cluster together and may break open, resulting in oozing sores that eventually scab over, forming crusted lesions. The incubation period—the time from virus exposure to the appearance of symptoms—is usually around 2 to 12 days. During the initial outbreak, symptoms are often more severe, sometimes accompanied by systemic signs such as fever, muscle aches, and swollen lymph nodes, especially in first-time infections. Subsequent outbreaks can vary in intensity, often triggered by factors such as stress, fatigue, hormonal changes, illness, or exposure to sunlight.
From a medical standpoint, cold sores are contagious and can spread through direct contact with infected saliva, skin lesions, or sharing items such as towels, utensils, or lip balm. The contagious period often extends from the first appearance of symptoms until the sore fully heals, which generally takes 7 to 10 days. The risk of transmission is highest when sores are visibly broken or oozing, but the virus can also spread when no sores are visible due to viral shedding.
While cold sores usually resolve on their own without intervention, certain measures can expedite healing and reduce discomfort. For individuals with weakened immune systems, children, or those with recurrent outbreaks, proactive management is even more critical. If the virus spreads to the eyes (ocular herpes), it can cause conjunctivitis or keratitis, potentially leading to vision problems, while spread to the central nervous system can result in severe complications like encephalitis. Therefore, prompt medical attention is necessary if symptoms worsen or if there is eye involvement.
To effectively manage cold sore outbreaks, maintaining good hygiene is essential. Keep the affected area clean with gentle washing using soap and water, and avoid touching or picking at the sores to prevent secondary bacterial infections. Avoid sharing personal items such as towels, razors, lip balms, and utensils to minimize spreading the virus to others. Over-the-counter (OTC) medications, including topical creams like docosanol and acyclovir, can reduce pain, healing time, and frequency of outbreaks when applied at the first sign of symptoms. Oral antiviral medications such as valacyclovir or famciclovir may be prescribed by healthcare providers for severe or recurrent cases.
Preventive strategies play a pivotal role in minimizing the occurrence of cold sores. Sun exposure is a well-known trigger; using lip balms with SPF and limiting sun exposure can help avoid outbreaks. Maintaining a healthy immune system through adequate nutrition, hydration, stress management, and sufficient sleep is vital. Supplements rich in vitamins E and C support immune health and skin repair. Certain foods, such as chocolates and nuts, may trigger outbreaks in sensitive individuals; reducing intake during prodromal periods can be beneficial.
Natural remedies offer additional support during outbreaks. Applying lemon balm extract has antiviral properties that may reduce lesion duration. Cold packs and ice application can alleviate pain and swelling. Essential oils like peppermint oil have anecdotal benefits when used carefully and diluted. Aloe vera gel can provide soothing relief and support skin healing. A paste made from cornstarch and water can soothe irritated skin. These approaches should complement medical treatment rather than replace it.
In conclusion, managing cold sores effectively involves a combination of hygiene, timely medication, lifestyle adjustments, and natural remedies. Recognizing early symptoms, seeking prompt treatment, and adopting preventive measures can dramatically shorten outbreak duration and reduce discomfort. For persistent or severe cases, consulting healthcare providers is essential for personalized management strategies. With comprehensive care, individuals can better cope with cold sore outbreaks and minimize their impact on daily life.