Effective Strategies for Managing Gout Flares: A Comprehensive Guide
This comprehensive guide offers effective methods for managing gout flare-ups, emphasizing both medical treatments and lifestyle modifications. It covers causes, symptoms, treatment strategies, and prevention tips to help sufferers control attacks, reduce pain, and protect joint health long-term.
Effective Strategies for Managing Gout Flares: A Comprehensive Guide
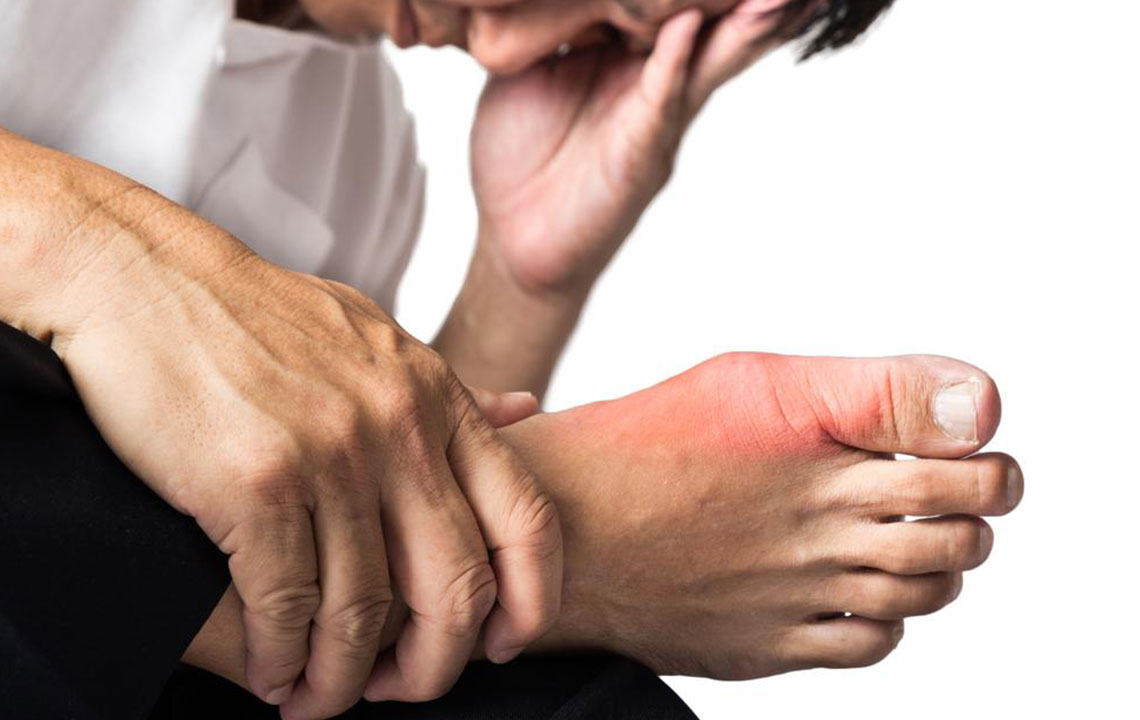
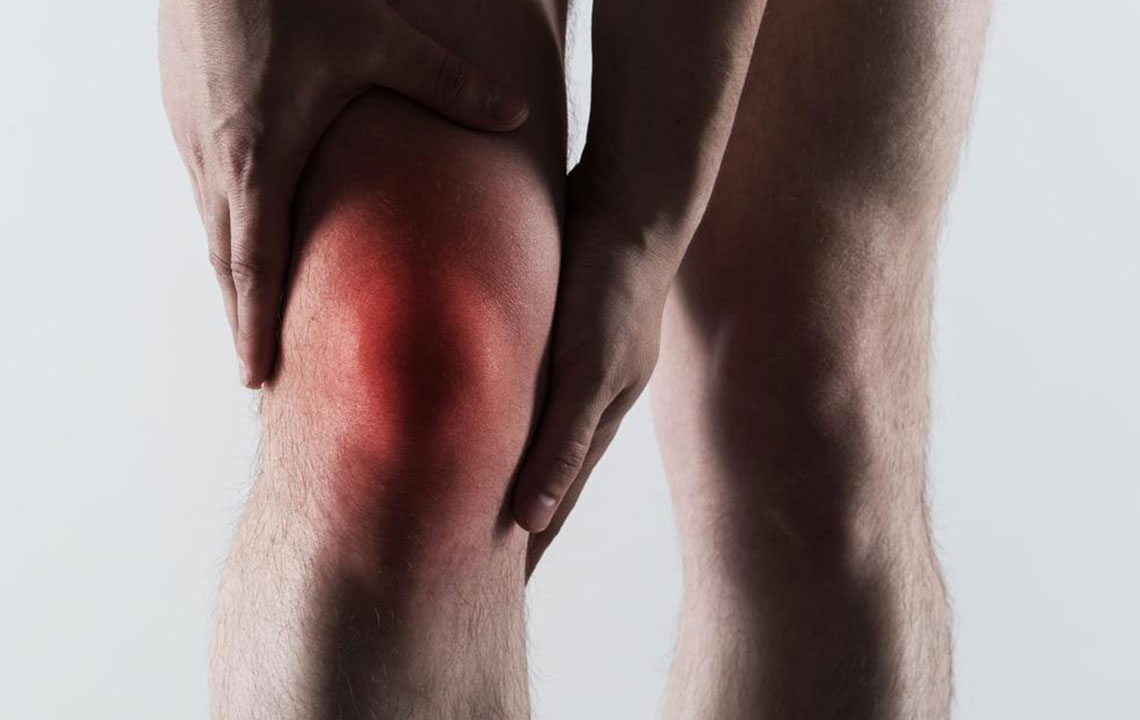
Gout is a complex form of inflammatory arthritis that manifests when excess uric acid in the bloodstream crystallizes within joints, leading to sudden and often severe episodes of pain. This condition primarily affects the joints, commonly striking the big toe, but it can also involve other areas such as the ankles, knees, wrists, hands, and feet. Understanding how to effectively manage gout flare-ups is essential for those affected, as repeated attacks can cause joint damage and impact overall quality of life. In this detailed guide, we explore the causes, symptoms, and most effective treatment strategies to help you control gout and reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
Understanding Gout: Causes and Risk Factors
Gout develops due to elevated levels of uric acid in the blood, known as hyperuricemia. When uric acid exceeds the kidney’s ability to eliminate it efficiently, it begins to crystallize into tiny, needle-shaped deposits within the joints. These deposits trigger an inflammatory response, resulting in the characteristic sudden and intense pain associated with gout attacks. Several factors contribute to increased uric acid levels:
Genetic predisposition plays a significant role, with some individuals inheriting a tendency for higher uric acid production or reduced renal clearance.
Dietary habits, especially high intake of purine-rich foods such as red meats, organ meats (liver, kidneys), shellfish, and certain fish varieties, can raise uric acid levels.
Alcohol consumption, particularly beer and spirits, impairs uric acid excretion, increasing the risk of attacks.
Soda and sugar-sweetened beverages containing fructose stimulate uric acid production.
Obesity and excess body weight significantly increase uric acid levels and the likelihood of gout.
Medical conditions like hypertension, diabetes, and kidney disease can also interfere with uric acid elimination, contributing to gout development.
Recognizing Gout Symptoms
The hallmark symptom of gout is a rapid onset of severe joint pain, often waking individuals during the night. Typical signs include:
Intense pain, often excruciating, localized in one joint—most commonly the big toe.
Swelling, warmth, and redness around the affected joint.
Reduced joint mobility during flare-ups.
Localized tenderness that worsens with touch or movement.
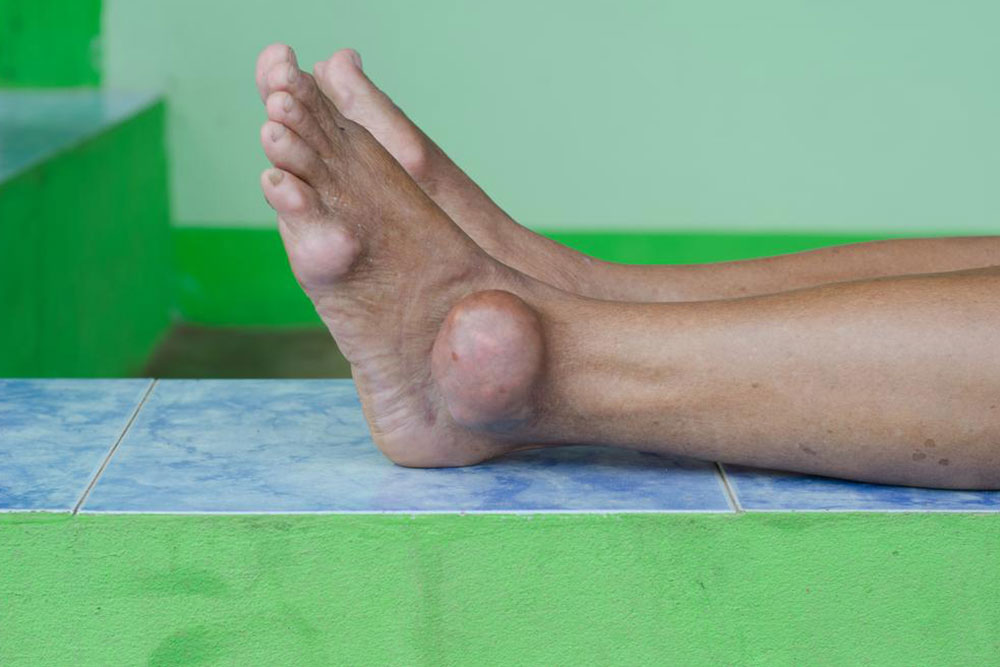
Gout episodes can last from a few days to several weeks if untreated. Between attacks, individuals often have no symptoms, but persistent elevated uric acid levels can lead to chronic gout, characterized by tophi—chalky deposits under the skin—and joint deformities.
Key Treatment Methods for Gout Flare-Ups
Effective management of gout involves addressing acute attacks promptly and adopting strategies to prevent future episodes. The primary goal is to reduce pain, minimize inflammation, and protect joint health. Combining medical treatments with lifestyle changes offers the most comprehensive approach.
Medical Interventions During Gout Attacks:
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Medications like ibuprofen and naproxen are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. It’s crucial to follow the recommended dosage and consult a healthcare provider before use.
Colchicine: An effective medication that decreases gout inflammation if taken early during an attack. It’s essential to adhere to prescribed dosages to avoid adverse effects.
Corticosteroids: Used when NSAIDs and colchicine are unsuitable or ineffective. These drugs can be administered orally or via injections to rapidly reduce inflammation.
Pain Management: Pain relievers such as acetaminophen may be used to manage discomfort, but they do not address underlying inflammation.
Lifestyle Modifications for Long-Term Control:
Rest and Elevation: During attacks, resting the affected joint and elevating it can decrease swelling and pain.
Applying Cold Therapy: Ice packs placed on the swollen joint can help diminish inflammation and provide quick relief. Wrap the ice in a cloth to prevent skin damage.
Hydration and Diet: Drinking plenty of water supports kidney function and uric acid excretion. Limiting high-purine foods reduces uric acid production, decreasing attack frequency.
Dietary Recommendations: Reduce intake of purine-rich foods such as organ meats, red meats, and certain seafood. Limit alcohol consumption, especially beer, and avoid sugar-sweetened beverages containing fructose.
Weight Management: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is vital. Slimming down reduces uric acid levels and alleviates joint stress.
Medication for Uric Acid Reduction: In cases of recurrent gout, doctors may prescribe urate-lowering therapies such as allopurinol or febuxostat. These medications help prevent future flare-ups by controlling uric acid levels over time.
Monitoring and Prevention Strategies:
Regular check-ups to monitor uric acid levels are crucial for detecting and managing potential issues before they cause pain.
Maintaining a consistent medication regimen if prescribed for hyperuricemia.
Avoiding triggers like stress, dehydration, and sudden temperature changes can help prevent attack recurrence.
Managing gout effectively requires a combination of prompt medical treatment during flare-ups and strategic lifestyle changes. Understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms early, and adopting preventive measures can significantly improve quality of life and reduce joint damage. If you experience recurrent episodes or complex symptoms, consulting with a healthcare professional is essential for personalized treatment planning. With proper management, gout can be controlled, allowing individuals to lead active, pain-free lives.