Comprehensive Guide to Female Genital Herpes: Symptoms, Risks, and Effective Management
This comprehensive guide explores female genital herpes, including symptoms, risks, especially during pregnancy, and effective treatment options. Understanding early signs and seeking prompt medical advice can manage outbreaks and prevent transmission. Visual aids and awareness play key roles in early detection and health management.

Comprehensive Guide to Female Genital Herpes: Symptoms, Risks, and Effective Management
Genital herpes, a common sexually transmitted infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), impacts a significant portion of the population, with estimates suggesting that approximately 50 million Americans are affected. Among these, women constitute a large percentage, often facing challenges in symptom recognition and management. Despite its widespread prevalence, many women remain unaware of their infection status due to asymptomatic cases or misattribution of symptoms to other conditions. Increasing awareness through educational resources, including visual aids like genital herpes images online, plays a crucial role in early detection and prevention.
Understanding How Women Can Detect Genital Herpes
Detecting genital herpes can be challenging as a considerable number of women never experience noticeable symptoms. However, recognizing the signs during initial outbreaks is vital for prompt medical intervention. Typical symptoms that may occur during these episodes include a variety of physical sensations and visible signs. Early identification can prevent complications and reduce the risk of transmission to partners or infants during childbirth.
Symptoms commonly associated with initial outbreaks include:
Persistent itching or burning sensations in the vaginal, anal, or surrounding areas
Fever, chills, and flu-like symptoms indicating systemic response to infection
Discomfort or tingling sensations extending to the legs, buttocks, or groin regions
Unusual vaginal discharge that may be cloudy or discolored
Difficulty or pain during urination, often due to sore lesions
Lower abdominal discomfort or pains
Frequent headaches and fatigue, sometimes accompanying outbreaks
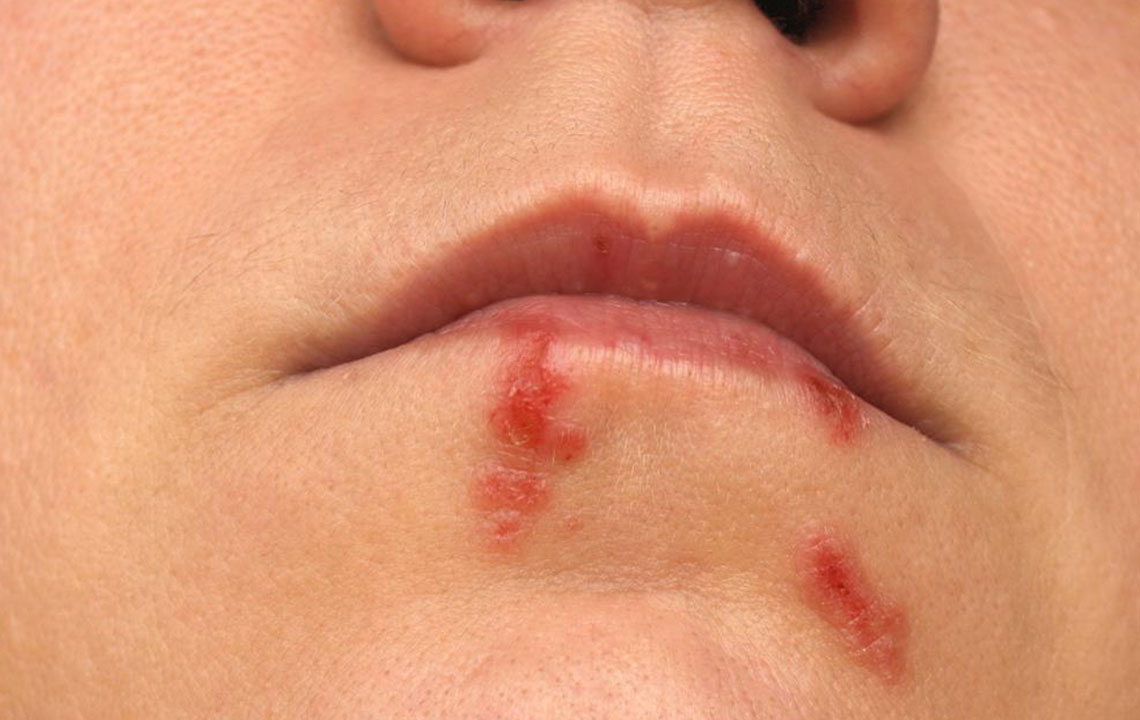
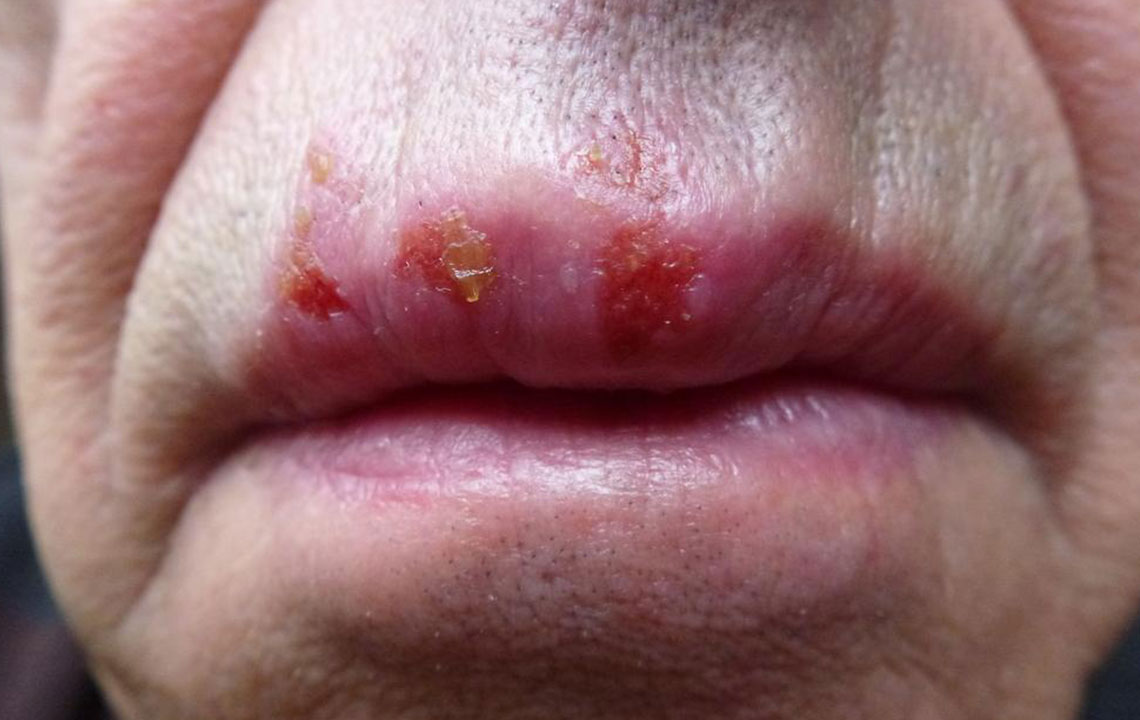
The first outbreak tends to be more severe, characterized by active sores and blisters that may appear in the genital, anal, mouth, and thigh areas. These outbreaks can cause significant discomfort and may be accompanied by systemic symptoms like fever. Subsequent episodes often tend to be milder, although they can still be contagious and cause distress.
Pregnancy and Genital Herpes: A Critical Concern
For pregnant women infected with genital herpes, there are additional health considerations. The primary concern is the risk of transmitting the virus to the newborn during delivery, which can result in neonatal herpes — a potentially life-threatening condition. Healthcare providers recommend close monitoring, antiviral treatments, and sometimes cesarean delivery to minimize transmission risks during childbirth. Regular prenatal checkups are essential for managing herpes safely during pregnancy, ensuring both maternal and neonatal health.
Available Treatment Options and Management Strategies
Medical diagnosis is critical in confirming genital herpes infection. Healthcare professionals typically utilize physical examinations, laboratory testing, and viral cultures to establish an accurate diagnosis. Once confirmed, various treatment options can reduce symptoms, suppress outbreaks, and lower transmission risks. The mainstay of treatment involves antiviral medications, but supplementary measures can enhance overall management.
Antiviral medications: Drugs like acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir are commonly prescribed to control outbreaks. These medications can be taken during outbreaks or as daily suppressive therapy to decrease the frequency and severity of episodes.
Maintaining personal hygiene: Proper hygiene of the genital area helps prevent secondary infections and reduces discomfort. Gentle cleansing with mild soaps and avoiding irritating products are recommended.
Supporting therapies: Some women find herbal remedies and nutritional supplements beneficial in supporting immune health and symptom management. However, these should always be discussed with healthcare providers to ensure safety and efficacy.
Preventing transmission is equally important. Consistent use of barrier protection methods such as condoms can significantly reduce the risk, although they do not eliminate it entirely. Open communication with sexual partners about herpes status and ongoing management is vital.
In summary, early recognition, timely medical intervention, and effective management strategies are critical components in controlling genital herpes. Visual references like genital herpes images can serve as helpful tools for women to identify symptoms early and seek medical care promptly. Increasing awareness and understanding of this common condition are essential steps towards reducing its impact on individuals’ health and well-being.