Comprehensive Dietary Strategies to Alleviate Arthritis Symptoms
This comprehensive guide offers dietary strategies for arthritis management, emphasizing foods to avoid and beneficial anti-inflammatory options. Incorporating these nutritional tips can alleviate joint pain, reduce inflammation, and support overall joint health, improving quality of life for arthritis sufferers through mindful eating and lifestyle choices.
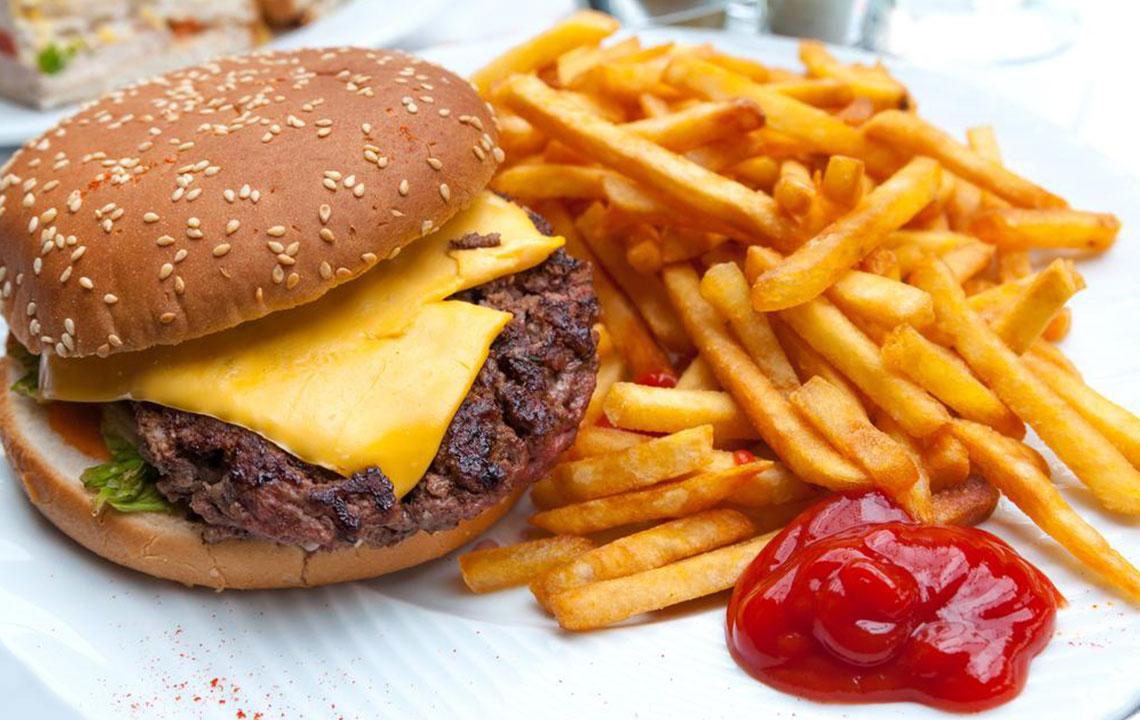

Effective Nutrition Tips for Managing Arthritis Pain and Inflammation
Arthritis is a common condition characterized by inflammation of the joints, leading to pain, stiffness, swelling, and sometimes significant mobility challenges. It affects millions of people worldwide, regardless of age or background. There are over 100 different types of arthritis, with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis being the most prevalent. In the United States alone, more than 50 million adults suffer from arthritis, making it a leading cause of disability. Children are also affected, with over 300,000 young individuals diagnosed with various forms of the disease. Managing arthritis effectively often requires a multifaceted approach, combining medication, physical therapy, and crucially, dietary modifications. The right nutritional choices can significantly influence the severity of symptoms, help reduce inflammation, and improve overall joint health.
Diet plays a vital role in managing arthritis. While there is no definitive cure through diet alone, certain foods are known to worsen inflammation, accelerate joint deterioration, and weaken immune function, thereby exacerbating symptoms. Conversely, incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into your daily routine can provide relief and slow disease progression. Understanding which foods to avoid and which to embrace is essential for those seeking natural ways to alleviate joint discomfort. Consistency and mindful eating are key to seeing long-term benefits.
Fried and Processed Foods – Regular consumption of fried, fast, and highly processed foods like chips, burgers, and frozen meals has been linked with increased systemic inflammation. Numerous scientific studies suggest that reducing intake of these items can help decrease inflammatory responses, support immune health, and improve overall well-being.
Red Meat – Red meat contains high levels of saturated fats and omega-6 fatty acids, which are known to promote inflammation in the body. Many arthritis sufferers notice a decrease in joint pain and swelling after limiting red meat consumption and opting for leaner protein sources.
Sugary and Refined Carbohydrates – Foods rich in refined sugars, such as candies, pastries, sodas, and processed snack foods, contribute to increasing inflammation markers in the body. Cutting back on these can help stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce joint swelling and discomfort.
Gluten-Containing Grains – Wheat, barley, and rye can trigger inflammatory responses in people with gluten sensitivities or autoimmune disorders like rheumatoid arthritis and celiac disease. Avoiding gluten may significantly decrease joint swelling, pain, and stiffness in sensitive individuals.
Dairy Products – Some individuals are sensitive or allergic to dairy proteins, which can worsen symptoms. Transitioning to plant-based alternatives such as nuts, lentils, tofu, and plant-based milks can meet dietary protein needs without aggravating inflammation or joint pain.
Alcohol and Tobacco – Both substances are harmful to joint health and immune function. Studies show that smoking increases the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis and can worsen existing symptoms. Limiting alcohol consumption and quitting smoking are crucial steps toward better joint health and overall wellness.
In contrast, certain foods possess natural anti-inflammatory properties that can aid in reducing arthritis symptoms. Incorporating these into a balanced diet could lead to considerable improvements in joint comfort and mobility. Consistently enjoying a variety of these nutrient-dense foods can help in managing inflammation and improving quality of life.
Fatty Fish – Fish like salmon, mackerel, sardines, and trout are rich sources of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA. Consuming 3-4 ounces of these fish several times a week can reduce joint inflammation, lessen stiffness, and improve mobility.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil – Used as a primary cooking oil, olive oil contains healthy monounsaturated fats and a compound called oleocanthal, which acts similarly to anti-inflammatory medications. Regular use can help lower bad cholesterol levels, fight oxidative stress, and combat inflammation.
Soy Products – Edamame, tofu, tempeh, and soy milk are rich in plant-based proteins, isoflavones, and fiber. These nutrients contribute to reducing joint pain and inflammation, making soy a beneficial addition to an arthritis-friendly diet.
Cherries and Berries – Berries such as strawberries, blueberries, and blackberries contain anthocyanins, plant compounds with potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. These fruits can help decrease the frequency and severity of gout attacks, a form of arthritis.
Broccoli – This cruciferous vegetable is loaded with vitamins, minerals, and sulforaphane, a natural compound that supports bone health and reduces cartilage breakdown. Regularly eating broccoli can slow arthritis progression.
Green Tea – Rich in antioxidants known as catechins, green tea can suppress inflammatory pathways and protect joint cartilage from damage. Drinking a few cups daily may contribute to joint health.
Citrus Fruits – Oranges, lemons, grapefruits, and limes are high in vitamin C, which is essential for collagen synthesis and immune support. Adequate vitamin C intake is associated with decreased inflammation levels.
Beans – Kidney beans, black beans, lentils, and chickpeas are packed with protein, fiber, and antioxidants. They help lower inflammation markers like C-reactive protein (CRP) and support muscle strength and endurance.
Before making significant dietary changes, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to tailor recommendations to your specific needs. Some individuals may experience joint pain exacerbation from nightshade vegetables like tomatoes and peppers; therefore, monitoring personal reactions is essential. Complementing diet modifications with stress management techniques, such as meditation, yoga, and breathing exercises, can also support overall joint health and enhance quality of life.